Construction method of two-dimensional optical address codes suitable for visible light OCDMA (Optical Code Division Multiple Access) communication
A construction method and optical address technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems such as the difficulty of having both large code sets and low cross-correlation values, and the limited selection of wave numbers, so as to improve the performance of codewords, improve the communication quality, and improve the degree of freedom. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples.
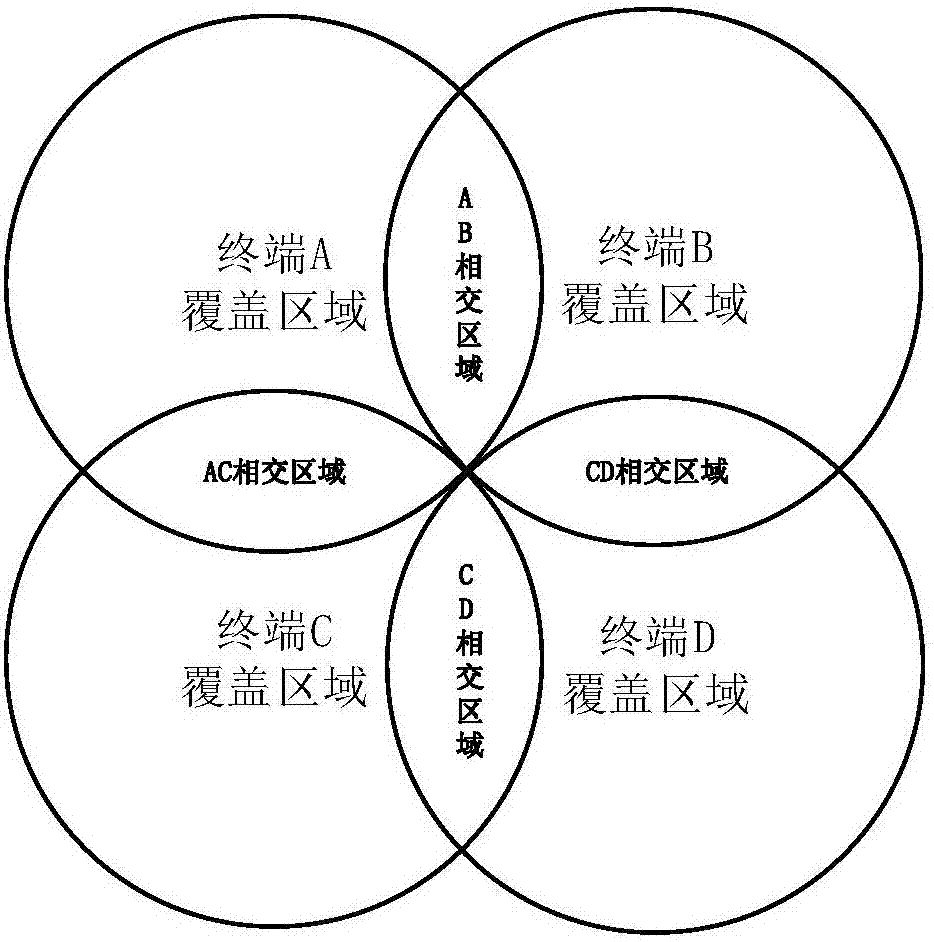
[0026] refer to figure 1 , the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: Select (N, ω, λ from the one-dimensional optical address code a =1,λ c =1) Optical Orthogonal Code OOC, where N is the code length, ω is the code weight, and λ a is the maximum autocorrelation sidelobe, λ c is the maximum cross-correlation value;
[0028] The (40,4,1,1) optical orthogonal code OOC is selected from the one-dimensional optical address code as the time-domain spread spectrum code, and its code set is 3. Take one of the code words (1100100000000100000000000000000000000000) as an example (abbreviated as 11001000000001).
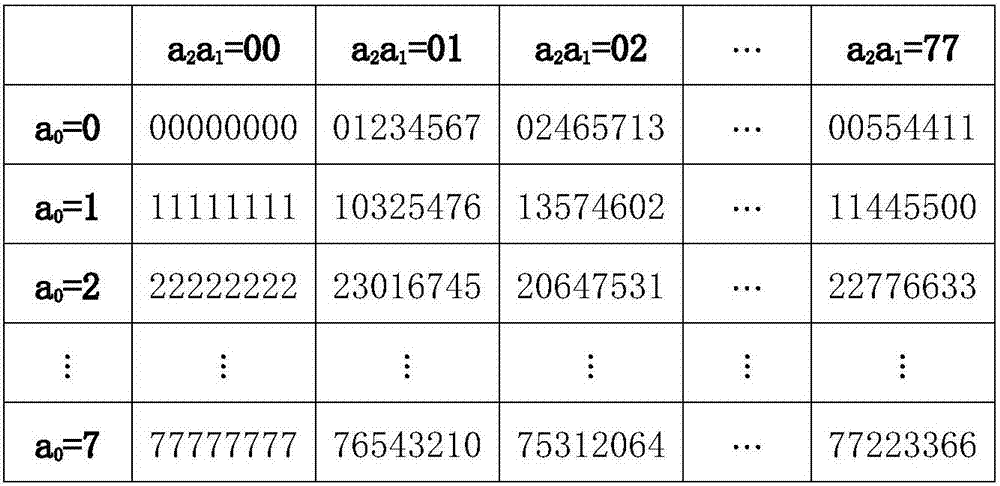
[0029] Step 2: In the prime field Z P =Select an irreducible n-order polynomial q(x) on {0,1,2,...,P-1}, where P is a prime number and n is any positive integer;
[0030] Pick one in the prime field Z 2 = irreduc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com