A method for efficiently and safely discharging waste lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion battery, waste technology, applied in battery recycling, waste collector recycling, recycling technology and other directions, can solve the problems of electrolyzed water easily producing hydrogen and oxygen, affecting production efficiency, and having potential safety hazards, and achieving broad industrial application Prospects, improved discharge safety, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A high-efficiency and safe discharge method for waste lithium-ion batteries, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Add a certain amount of regenerated graphite powder and fine sand into the box containing the stirring device, and the volume ratio of graphite powder to fine sand is 10:1;
[0033] (2) The waste lithium-ion battery to be treated is added in the device, and the volume ratio of graphite powder and lithium-ion battery is 4:1;
[0034] (3) Start the stirring device, stir for a certain period of time, stop, and discharge the battery under static conditions, and the discharge time is 12h;
[0035] (4) After 12 hours, sieve the powder in the box and the waste lithium-ion battery, disassemble the separated lithium-ion battery, and recycle graphite powder and fine sand to continue to discharge the waste lithium-ion battery.
[0036] Adopt present embodiment to the voltage change of waste lithium ion battery discharge as follows figure 1 As shown, it shows ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A high-efficiency and safe discharge method for waste lithium-ion batteries, comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) Add a certain amount of regenerated graphite powder and fine sand into the box containing the stirring device, and the volume ratio of graphite powder to fine sand is 8:1;
[0040] (2) The waste lithium-ion battery to be treated is added in the device, and the volume ratio of graphite powder and lithium-ion battery is 2:1;
[0041] (3) Start the stirring device, stir for a certain period of time, stop, and discharge the battery under static conditions, and the discharge time is 12h;
[0042] (4) After 12 hours, sieve the powder in the box and the waste lithium-ion battery, disassemble the separated lithium-ion battery, and recycle graphite powder and fine sand to continue to discharge the waste lithium-ion battery.
[0043] The voltage change of the waste lithium-ion battery discharged by using this embodiment shows that the voltage of a lithium cob...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A high-efficiency and safe discharge method for waste lithium-ion batteries, comprising the following steps:
[0046](1) Add a certain amount of regenerated graphite powder and fine sand into the box containing the stirring device, and the volume ratio of graphite powder to fine sand is 5:1;
[0047] (2) The waste lithium-ion battery to be treated is added in the device, and the volume ratio of graphite powder and lithium-ion battery is 1:1;
[0048] (3) Start the stirring device, stir for a certain period of time, stop, and discharge the battery under static conditions, and the discharge time is 24h;
[0049] (4) After 24 hours, sieve the powder in the box and the waste lithium-ion battery, disassemble the separated lithium-ion battery, and recycle the graphite powder and fine sand to continue to discharge the waste lithium-ion battery.
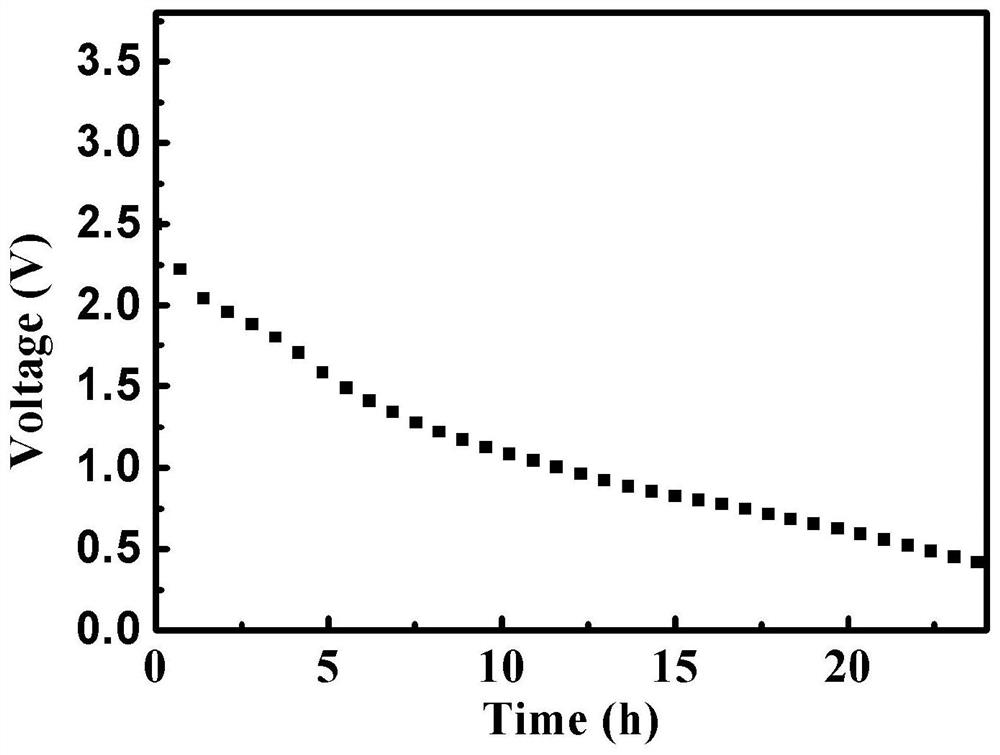
[0050] The voltage change of the waste lithium-ion battery discharged by this embodiment shows that the voltage of a lithium cobalt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com