Transistor laser and its manufacturing method
A transistor laser, base layer technology, applied in semiconductor lasers, lasers, laser parts and other directions, can solve problems such as unfavorable device optical devices or monolithic integration of electrical devices, and achieves omitting design and manufacturing steps, convenient integration, and easy integration. effect achieved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
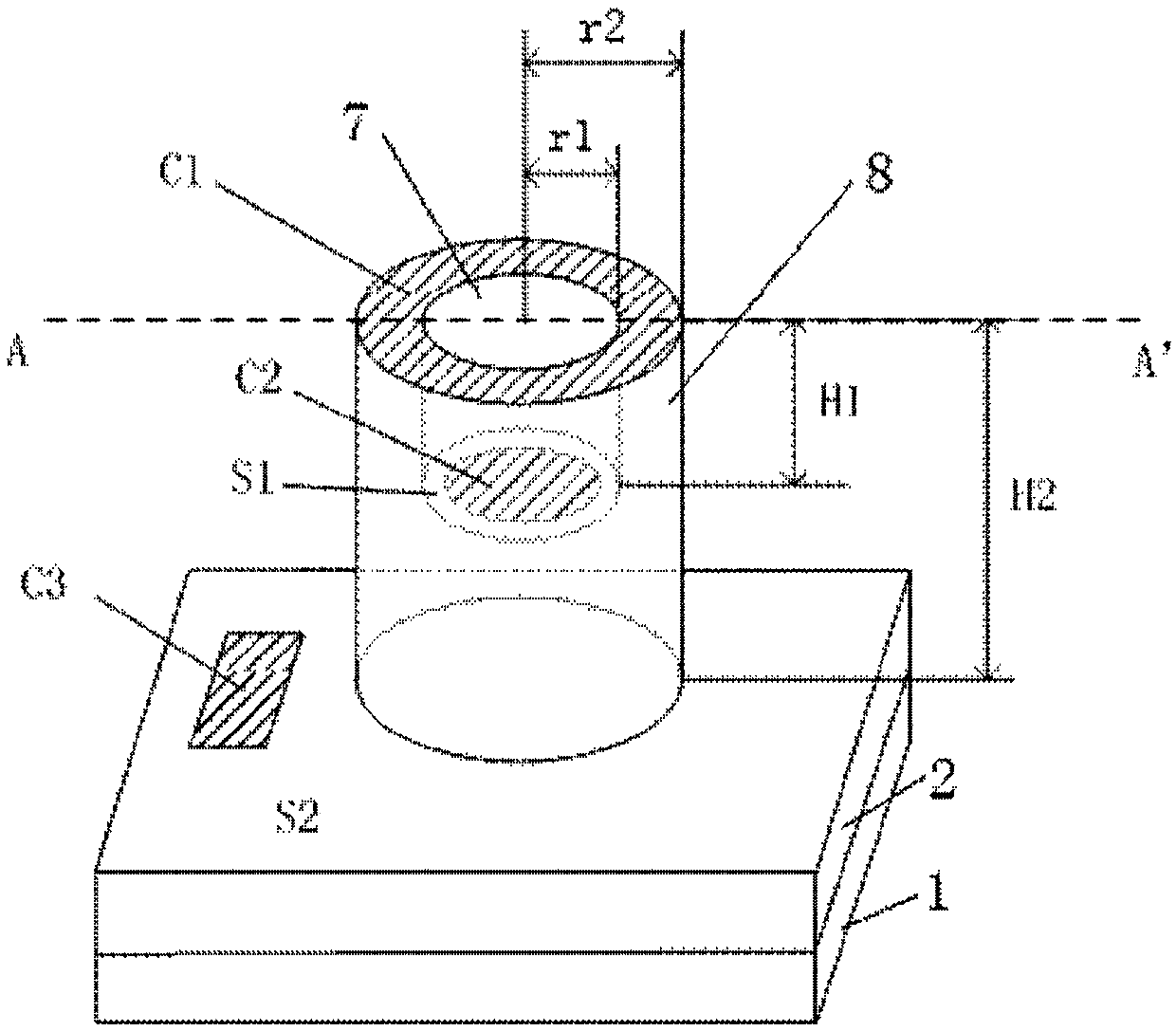
[0051] In a first exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a transistor laser and a fabrication method thereof are provided. figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of the transistor laser according to the first embodiment of the present invention. like figure 1 As shown, the transistor laser of this embodiment includes: a substrate 1, a lower collector layer 2, a columnar structure 8, and a columnar hole 7 disposed in the columnar structure 8, wherein the columnar structure 8 and the columnar hole 7 are both circular in cross section , and coaxially arranged, the first surface S1 is arranged at the bottom of the columnar hole 7, the second surface S2 is arranged on the surface of the lower collector layer, the emitter electrode C1 is arranged on the upper surface of the columnar structure 8, and the base electrode C2 is arranged on the upper surface of the columnar structure 8 On the first surface S1, the collector electrode C3 is disposed on the second surface S...
no. 2 example
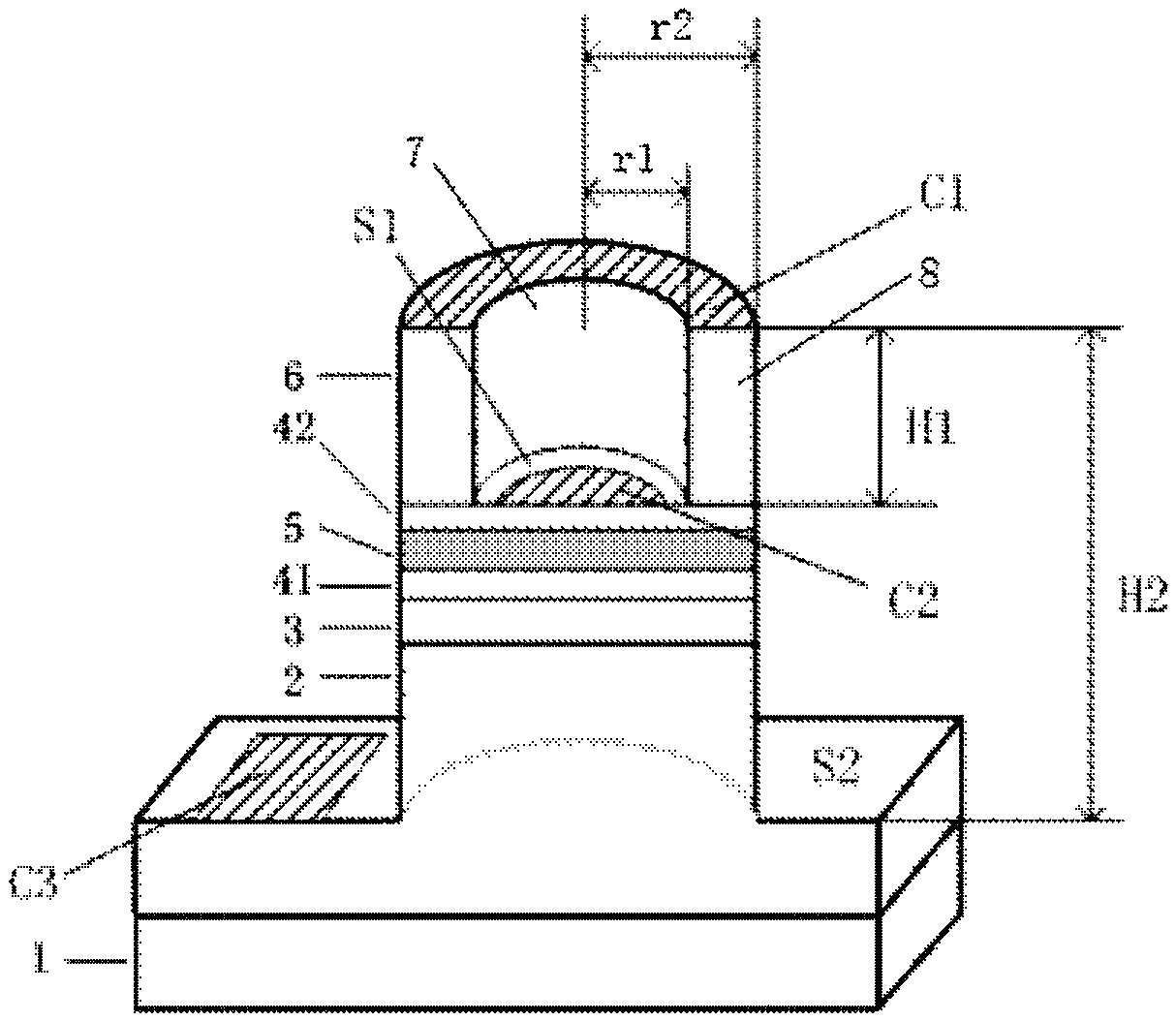
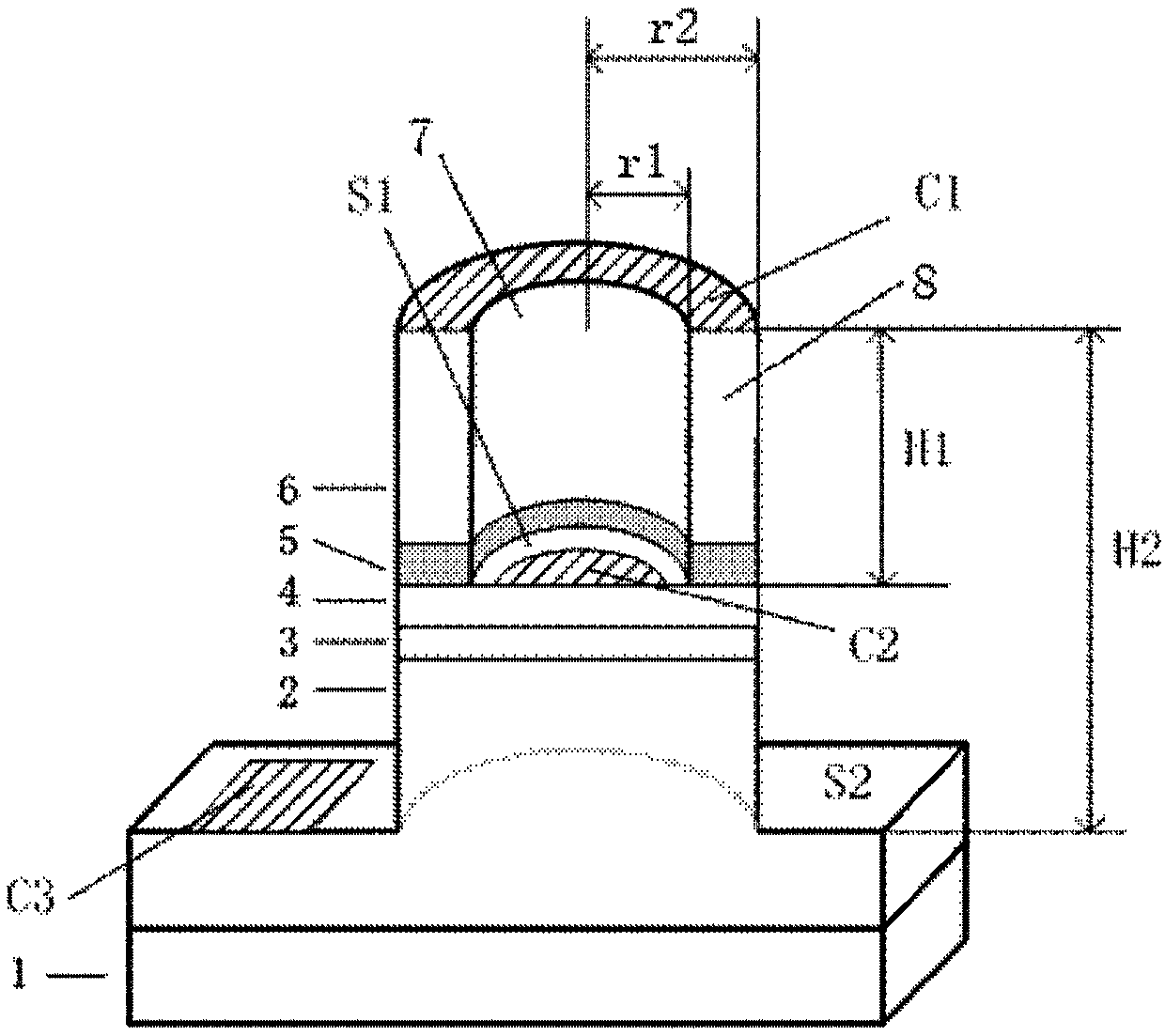
[0072] In a second exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a transistor laser and a fabrication method thereof are provided. and figure 1 Similarly, the transistor laser of this embodiment includes: a substrate 1, a lower collector layer 2, a columnar structure 8, and a columnar hole 7 disposed in the columnar structure 8, wherein the cross sections of the columnar structure 8 and the columnar hole 7 are both circular, And coaxially arranged, the first surface S1 is arranged at the bottom of the columnar hole 7, the second surface S2 is arranged on the surface of the lower collector layer, the emitter electrode C1 is arranged on the upper surface of the columnar structure 8, and the base electrode C2 is arranged at the bottom of the columnar hole 7. On one surface S1, the collector C3 is disposed on the second surface S2.
[0073] see image 3 , the transistor laser comprises from bottom to top: a substrate 1, a lower collector layer 2, a collector layer 3, a base lay...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com