Rotavirus-encoded small RNA molecule regulating self proliferation
A technology of rotavirus, RV-VSRNA1755, applied in the field of biomedicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1. Small RNA sequencing analysis during rotavirus infection
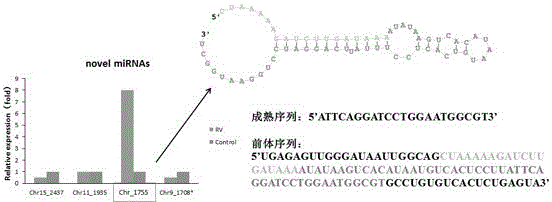
[0023] The isolated wild-type rotavirus ZTR-68 (preservation unit: General Microbiology Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms; deposit number: CGMCC No.5265) was infected with sensitive cells MA104 cells and then analyzed by small RNA deep sequencing. The expression profile of microRNAs during virus infection was studied, and it was found that the expression levels of 40 microRNAs changed after rotavirus infection. After comparison with multiple databases (miRBase database, Rfam database, GeneBank database, etc.) and RT-PCR verification, it was found that four of the 40 differentially expressed microRNAs were new small RNA molecules with unknown functions. Among them, the miRNA molecule with the largest expression difference level is RV-VSRNA1755, and the structure and sequence of the precursor neck loop have been predicted ( figure 1 ), but its role and function in the p...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2. Detection of expression level of RV-VSRNA1755 molecule after infection of different host cells by different strains (wild strains and laboratory strains) and its time-sensitive expression
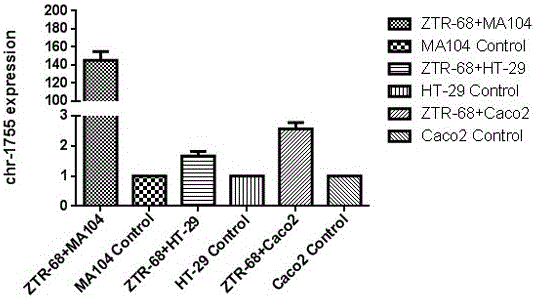
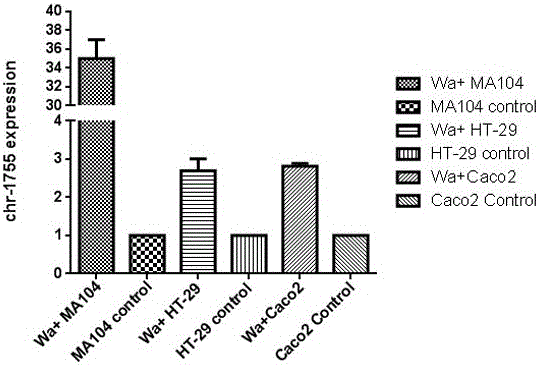
[0026]After infecting MA104 cells, HT-29 cells and Caco2 cells with the isolated wild strain ZTR-68 strain and the laboratory strain Wa strain, respectively, the expression of RV-VSRNA1755 was detected, and the small molecule was up-regulated at different levels ( image 3 , Figure 4 ). Compared with other host cells, the wild strain and laboratory strain had the highest expression level after infecting MA104 cells ( image 3 , Figure 4 ). We also detected the up-regulated expression of RV-VSRNA1755 to varying degrees after infection of MA104 cells with five G-type rotavirus strains preserved in the laboratory, indicating that the production of RV-VSRNA1755 molecules is not only for G1 type, but also for other genotypes. This regulatory molecule is also present in vi...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3, Research on the role of RV-VSRNA1755 molecule in rotavirus proliferation
[0028] Inhibitors and mimics targeting RV-VSRNA1755 molecules were synthesized, respectively transfected into host cells (MA104 cells), and infected with rotavirus 24 hours after transfection. After qRT-PCR experiment verification, compared with the control MA104 cells, the expression level of RV-VSRNA1755 was significantly up-regulated and down-regulated ( Figure 7 ). Intracellular viral RNA was extracted 16 hours after RV infection, and the transcription of rotavirus genome NSP3 and VP7 was detected by real-time PCR. The results of NSP3 showed that the copy number of NSP3 in the down-regulated 1755 group increased faster than that in the up-regulated 1755 group at the same time point, and the up-regulated 1755 group inhibited the virus proliferation ( Figure 8 A). The results of VP7 showed that compared with the control infection group, when the RV-VSRNA1755 molecule was up-regu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com