Method for predicting residual fatigue life of composite material adhesive bonding repair structure
A technology for composite materials and fatigue life, which is applied in the direction of applying repetitive force/pulsation force to test material strength, analyze materials, and measuring devices, etc. It can solve the problems of large amount of calculation and cumbersome steps, and achieve the effect of simplifying steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
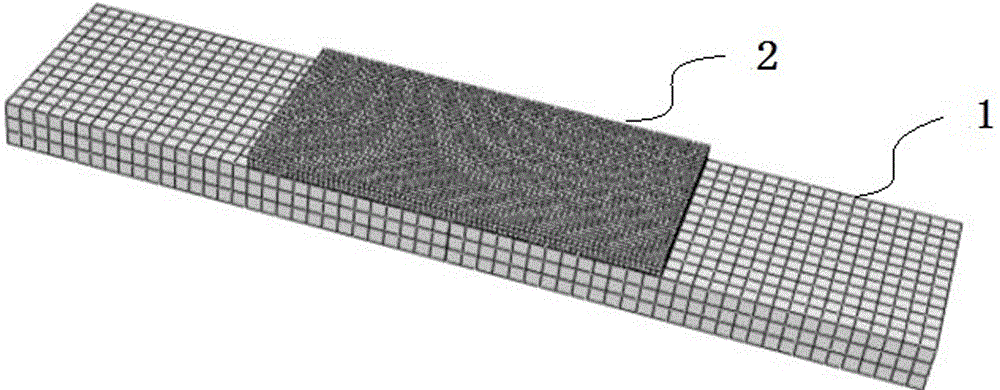
[0029] Using T300 / E51 carbon fiber composite patch to repair the damaged LY12CZ aluminum alloy plate with central crack by single-sided adhesive bonding, and predict the fatigue life of the repaired structure.
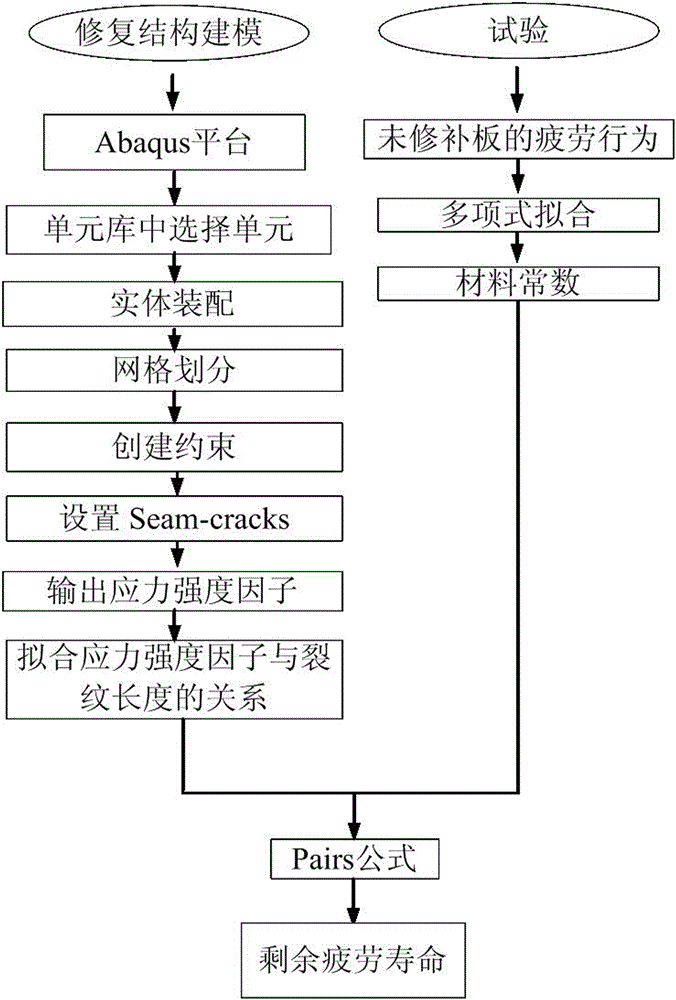
[0030] First, test the relationship between the crack growth rate of the damaged cracked plate and the amplitude of the stress intensity factor under alternating loads, and fit the data points in the logarithmic coordinate system Obtain the Paris formula material constants C and m under the test conditions, and the calculation result is C=6.3496×10 -12 , m=3.72972.
[0031] Secondly, the finite element modeling of the single-sided adhesive bonded composite structure with cracks was carried out. According to the characteristics of each material in the repair structure, three-dimensional solid element C3D8R, continuous shell element SC8R and three-dimensional viscous element COH3D8 are selected from the Abaqus software library for solid modeling. The location of each ...
Embodiment 2
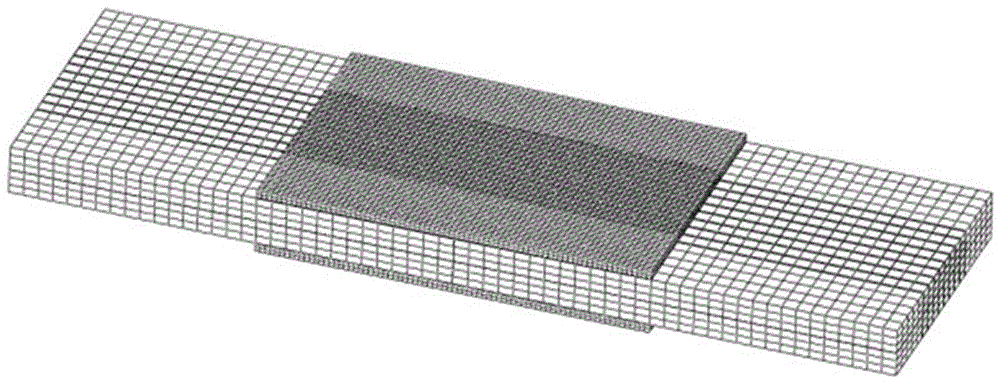
[0039] The T300 / E51 carbon fiber composite patch was used to repair the LY12CZ aluminum alloy metal plate with a central crack by double-sided adhesive bonding, and the remaining fatigue life of the repaired structure was predicted.
[0040] First, the relationship between the crack growth rate and the stress intensity factor of the damaged cracked plate under the action of alternating load is obtained through experiments, and the data points are fitted in the logarithmic coordinate system Fit the material constants C and m under the test conditions in the Paris formula, where C=6.3496×10 -12 , m=3.72972.
[0041] Secondly, the finite element modeling of the double-sided adhesive bonded composite structure with cracks was carried out. According to the characteristics of each material in the repair structure, the three-dimensional solid element C3D8R, the continuous shell element SC8R and the three-dimensional viscous element COH3D8 suitable for metal plates, adhesive layers ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com