Extremely-thin flexible heat-radiation film and method for manufacturing the same
A heat dissipation film and flexible technology, applied in the field of flexible heat dissipation film and its production, can solve the problems of increased thermal resistance, difficulty in punching graphite pressed materials, unfavorable use, etc., achieve high thermal conductivity and heat dissipation performance, excellent heat dissipation performance, and easy processing and use Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
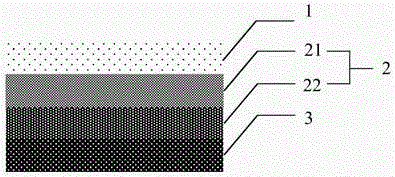
[0087] Such as figure 1 As shown, the ultra-thin flexible heat dissipation film of the present invention includes a carrier film 1, a heat dissipation layer group 2, and a protective film layer 3 from top to bottom, wherein the heat dissipation layer group includes a heat dissipation adhesive film layer 21 and a heat dissipation metal film layer 22.
[0088] 1. Ratio preparation
[0089] 1) Preparation of magnetized high thermal conductivity powder
[0090] The carbonyl method commonly used in this field is used to cover the surface of the graphite powder with magnetic nickel to form a nickel-coated graphite powder material. That is, under the conditions of normal pressure and 40-100 ° C, carbon monoxide reacts with active metal nickel to form nickel carbonyl, and then the formed nickel carbonyl is circulated through the thermal decomposer repeatedly, so that the carbonyl is continuously deposited on the surface of the original graphite powder particles Decompose and deposit...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Such as figure 1 As shown, the ultra-thin flexible heat dissipation film of the present invention sequentially includes a carrier film 1, a heat dissipation layer group 2, and a protective film layer 3 from top to bottom, wherein the heat dissipation layer group includes a heat dissipation adhesive film layer 21, a heat dissipation metal film layer 22, and The difference of Embodiment 1 is that the heat dissipation metal film layer 22 is formed on the surface of the carrier film, and the heat dissipation adhesive film layer 21 is formed on the surface of the heat dissipation adhesive film layer.
[0134] 1. Ratio preparation
[0135] 1) Preparation of magnetized high thermal conductivity powder
[0136] According to the ratio of nickel to graphite in parts by weight of 10:60, the carbonyl method commonly used in this field is used to cover the surface of graphite powder with magnetic nickel to produce high-purity nickel-coated graphite powder.
[0137] Wherein, the we...
Embodiment 3
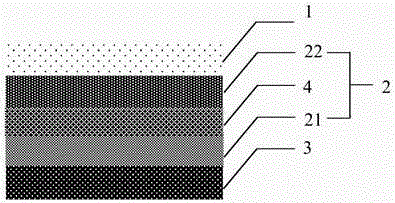
[0174] Such as image 3 As shown, the flexible heat dissipation film of the present invention includes a carrier film 1, a heat dissipation metal film layer 22, an ultra-thin double-sided adhesive tape 4, a heat dissipation adhesive film layer 21, and a protective film layer 3 from top to bottom. The difference between it and Embodiment 1 That is, the heat dissipation metal film layer 22 and the heat dissipation adhesive film layer 21 are respectively formed on the carrying film layer and the protective film layer, and are bonded together by the ultra-thin double-sided adhesive tape 3 to form a heat dissipation layer group.
[0175] 1. Ratio preparation
[0176] 1) Preparation of magnetized high thermal conductivity powder
[0177] According to the weight ratio of iron and graphite as 10:60, the carbonyl method commonly used in this field is used to cover the surface of graphite powder with magnetic iron to produce high-purity iron-coated graphite powder.
[0178] Wherein, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com