Underwater acoustic sensor network routing algorithm and system using harmonic field
An underwater acoustic sensing and routing technology, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, network topology, etc., can solve problems such as failure to find routing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
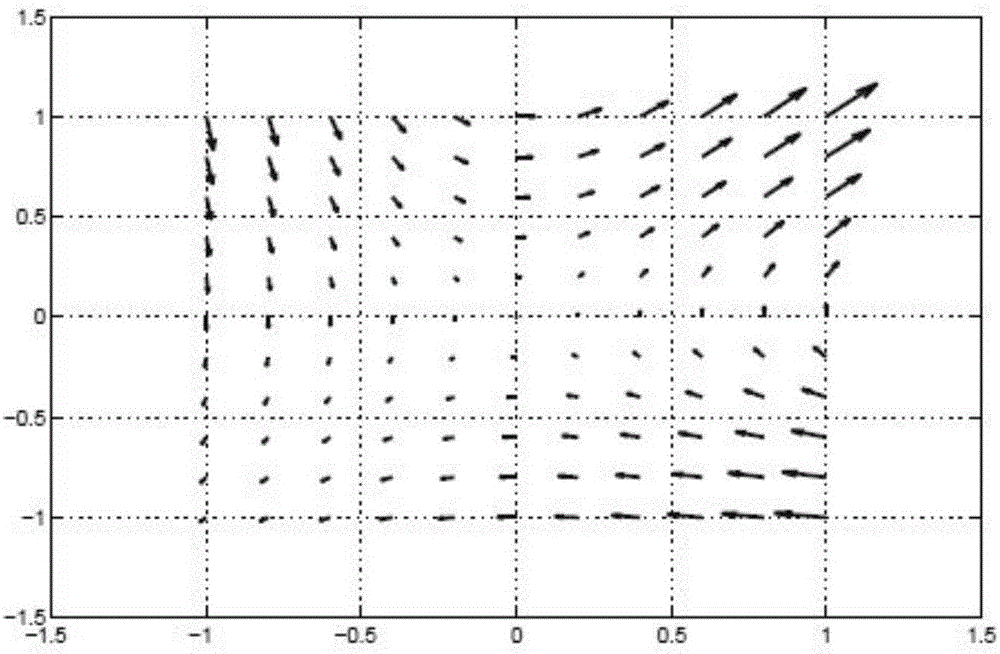
[0027] This implementation process uses the potential field theory, that is, the harmonic potential field method to obtain the routing of the underwater wireless sensor network; the harmonic potential field is a method based on the harmonic function, which overcomes the three-dimensional space path planning through the harmonic function and boundary conditions Minimal point problems in , without constant path maintenance.
[0028] According to potential field theory, the harmonic function is the solution to the following Laplace equation:
[0029]
[0030] where φ is a scalar representing the potential value, x i is the i-th dimension Cartesian coordinates, and n is the dimension of the space. By solving the above Laplace equation, what is obtained is a continuous potential function φ, which represents a path or route.
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation steps of the underwater acoustic sensor network routing algorithm provided in this embodim...
Embodiment approach
[0044] As a preferred embodiment of constructing a route from the sending node to the gateway node, that is, to define the route according to the underwater three-dimensional grid, the method includes:
[0045] If there is a sensor node in the underwater three-dimensional grid that the continuous curve of the route passes through, then the sensor node is selected as the relay node of the route;
[0046] If there are multiple sensor nodes in the underwater three-dimensional grid, the sensor node closest to the curve is selected as the relay node of the route;
[0047] If the sending node, relay node, and gateway node cannot form a complete route from the sending node to the gateway node, adjust the potential of the local minimum point, and then use the selected relay node until the sending node, relay node, gateway node The node can form a complete route from the sending node to the gateway node.
[0048] In practice, it is assumed that the topology of the network is known in ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this Embodiment 2 also provides an underwater acoustic sensor network routing system, including:
[0054] A sending node and a gateway node; where the sending node and the gateway node are suitable for establishing an underwater acoustic sensor network route.
[0055] The routing of the underwater acoustic sensor network constructed in the second embodiment is as described in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com