Multi-temporal hyper-spectral image classification method based on spatial-spectral feature preserving global geometric structure
A hyperspectral image and geometric structure technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve problems such as spectral drift, wrong spectral neighbors, and large consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
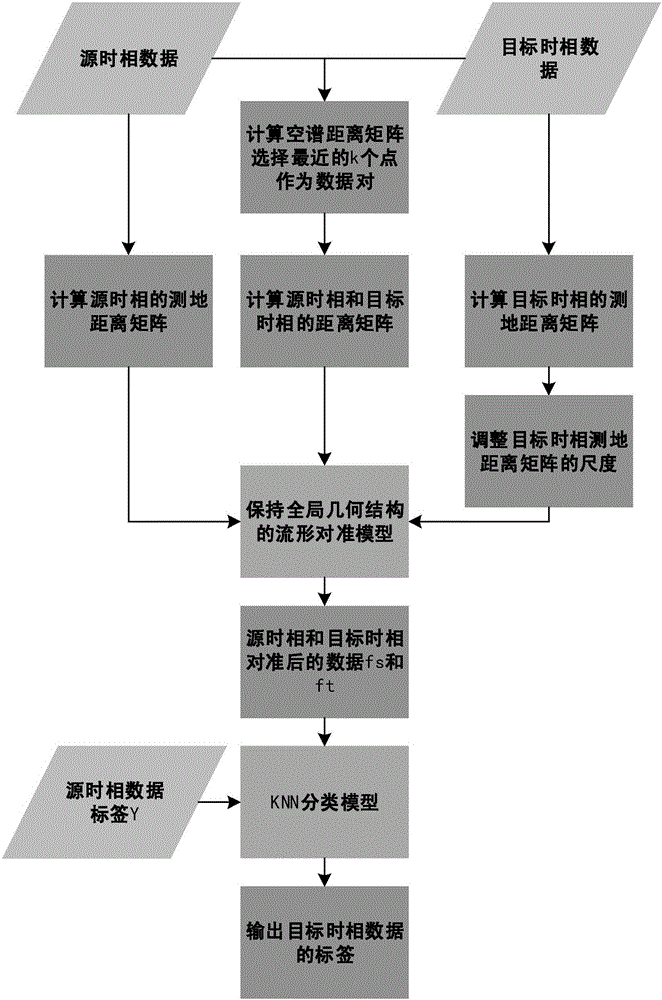
[0025] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the multi-temporal hyperspectral image classification method based on spatial spectral features to maintain global geometric structure in this embodiment, the specific process is:
[0026] Step 1. Input the spectral matrix X of the samples in the source image and the target image s 、X t and x s 、X t The space coordinate Z 1 ,Z 2 , and X s The corresponding category label vector Y for each row;
[0027] Step 2. Calculate X s 、X t For each type of sample in the source image, select k samples with the smallest spatial spectral distance in the target image as the data pairs that need to be matched;
[0028] Step 3. Calculate X s ,X t The geodesic distance matrix D s,s ,D t,t , and use the data pair to calculate the distance matrix D between the source image and the target image s,t , adjust X s ,X t scale, with D s,s 、D t,t 、D s,t Build a distance matrix D;
[0029] Step 4, put ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the calculation of X in the second step s 、X t The spatial spectral distance d, each type of sample in the source image selects k samples with the smallest spatial spectral distance in the target image as the data pairs that need to be matched; the specific process is:
[0032]
[0033]
[0034] d=d spectral d spatial
[0035] where d spectral and d spatial Represents the Gaussian similarity measure of the source image and the target image on the spectrum and space, respectively, x s i Indicates the i-th sample of the source image, z s i Indicates the spatial coordinates of the i-th sample of the source image, x t j Indicates the jth sample of the target image, z t j Indicates the spatial coordinates of the jth sample of the target image, σ spectral ,σspatial Represent the Gaussian weight parameters on the spectrum and space respectively; the value ranges o...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that: the number of categories C is 7, and k is 1-20.
[0039] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com