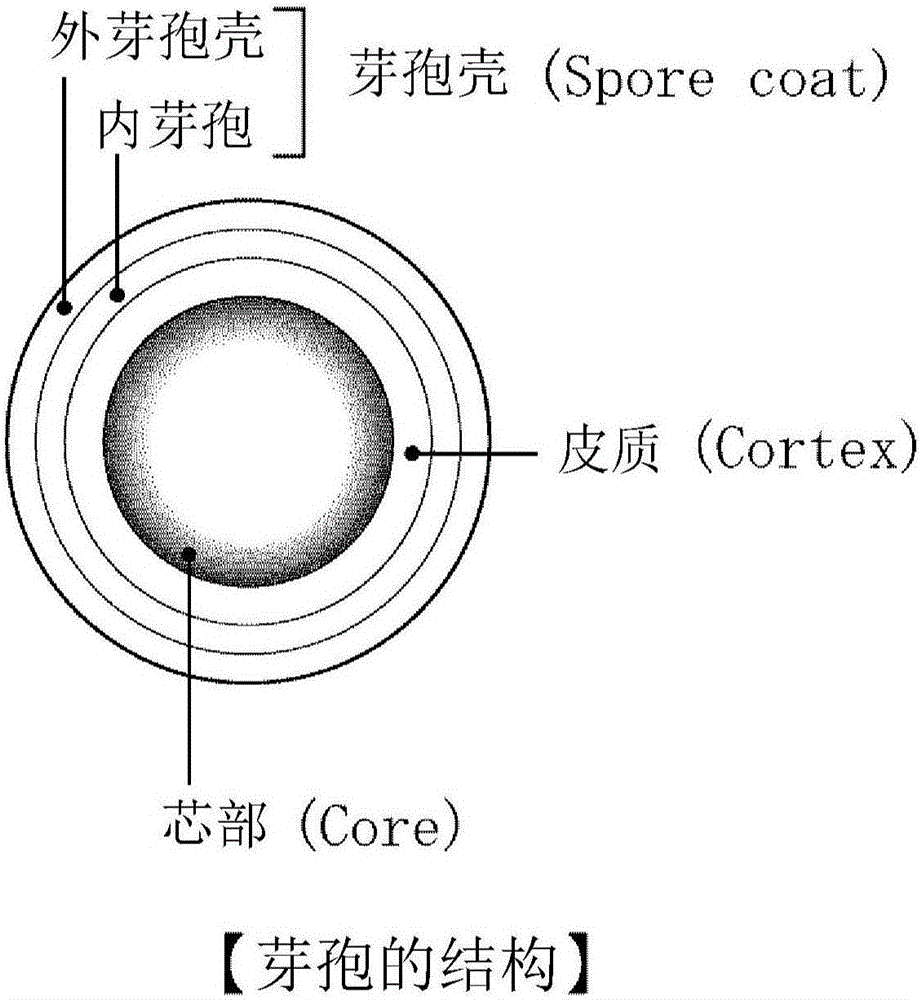
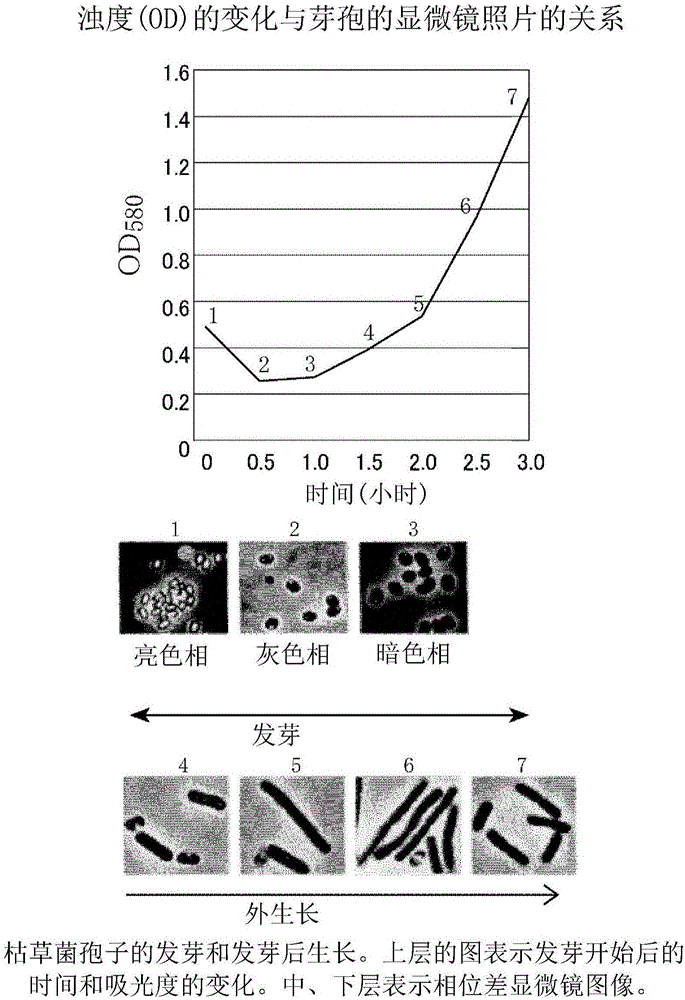
Method of sterilizing or inactivating heat-resistant spore-forming bacteria
A treatment method and heat-resistant technology, applied in heating, heating preservation of seeds, heating preservation of meat/fish, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain sufficient sterilization effect and difficulty in practical application, and achieve simple equipment, low income, and low price low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0074] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described based on the drawings.
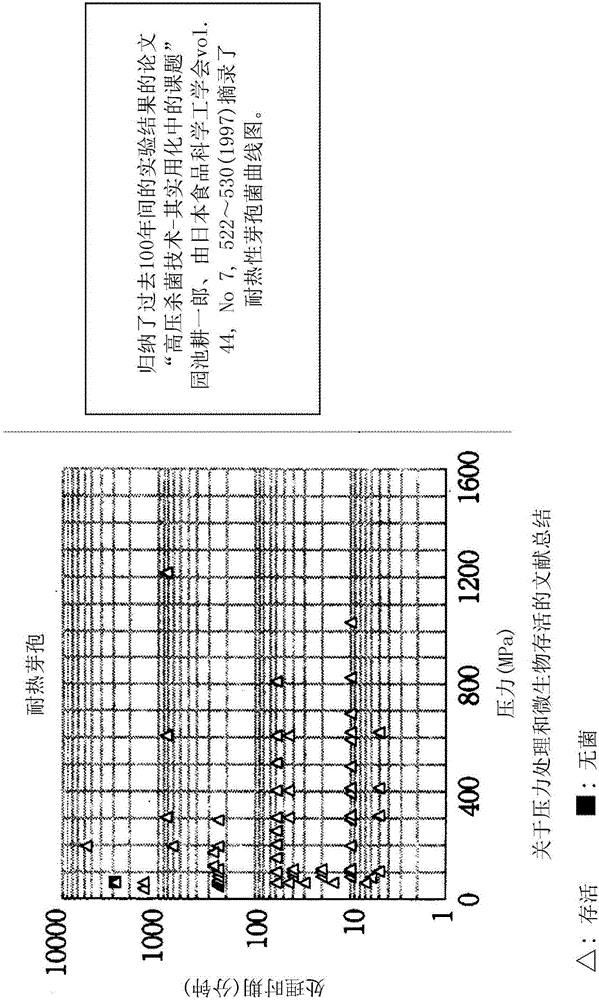
[0075] figure 1As mentioned above, a part of the paper published by Koichiro Sonoike on the bactericidal effect of high-pressure treatment on heat-resistant spores in the past 100 years is shown. The result that high pressure cannot be sterilized.
[0076] Regarding the sterilization of microorganisms by high-pressure treatment, the effects differ greatly between non-thermostable bacteria and thermostable bacteria.
[0077] That is, for non-heat-resistant bacteria, the effect of high-pressure treatment is remarkable, and it was also confirmed that heating during pressurization is more effective.
[0078] Thus, for example, in the case of most vegetative cells, Gram-negative bacteria, molds / yeasts, killed bacterial species are more observed.
[0079] However, as described above, heat-resistant spores have been shown to be difficult to sterilize at a pressure of 400 MPa or more, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com