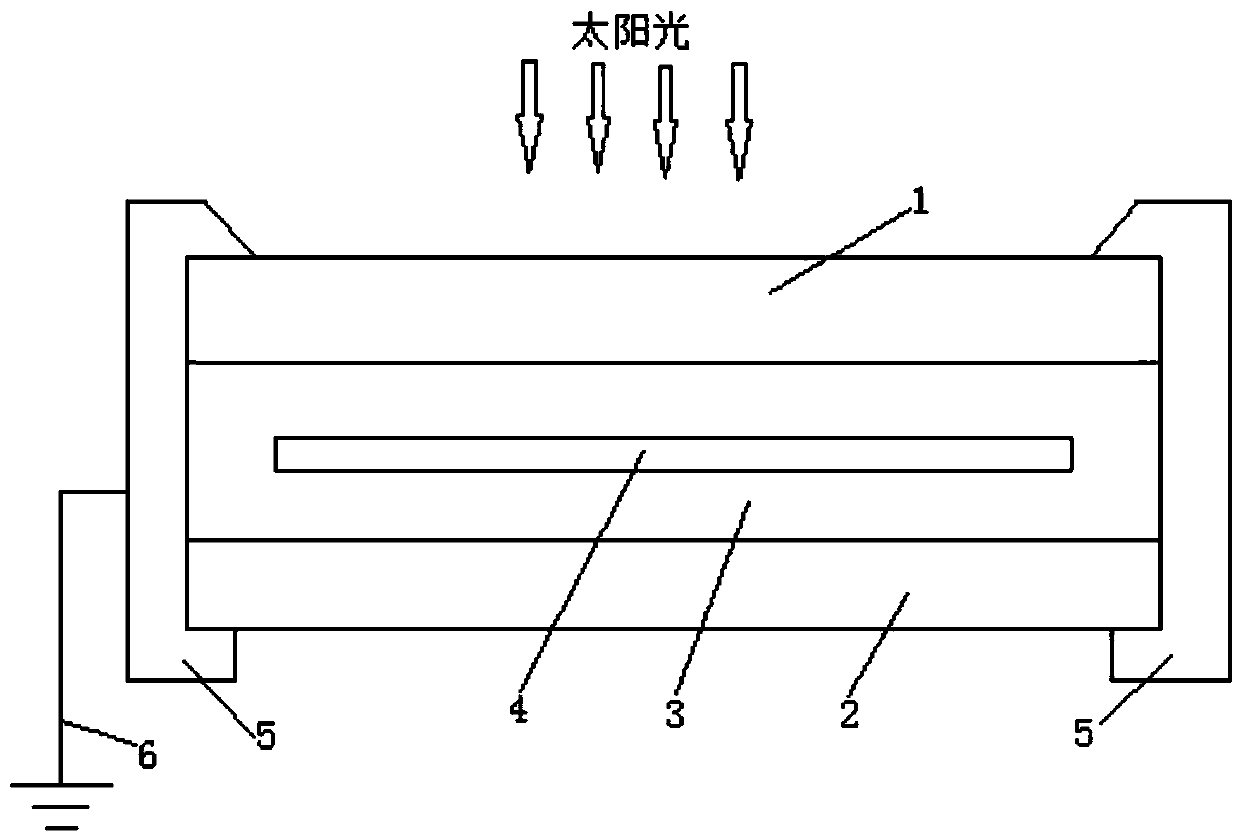
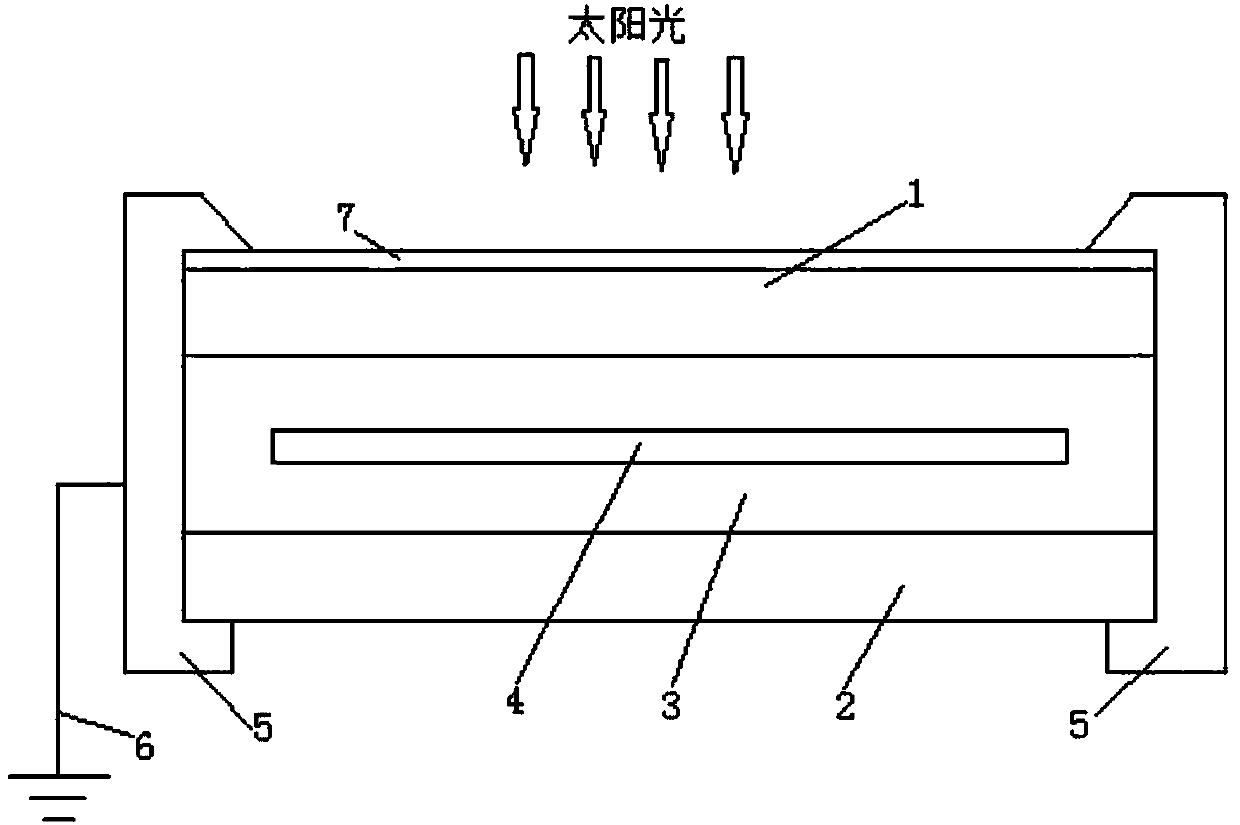
Photovoltaic module and photovoltaic power generation system
A photovoltaic module and light-receiving surface technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of insufficient bonding force between a single-layer anti-reflection film and a substrate, low anti-reflection performance of the anti-reflection film, and single control means, etc., to reduce internal stress. , Good anti-reflection effect, and the effect of increasing power generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
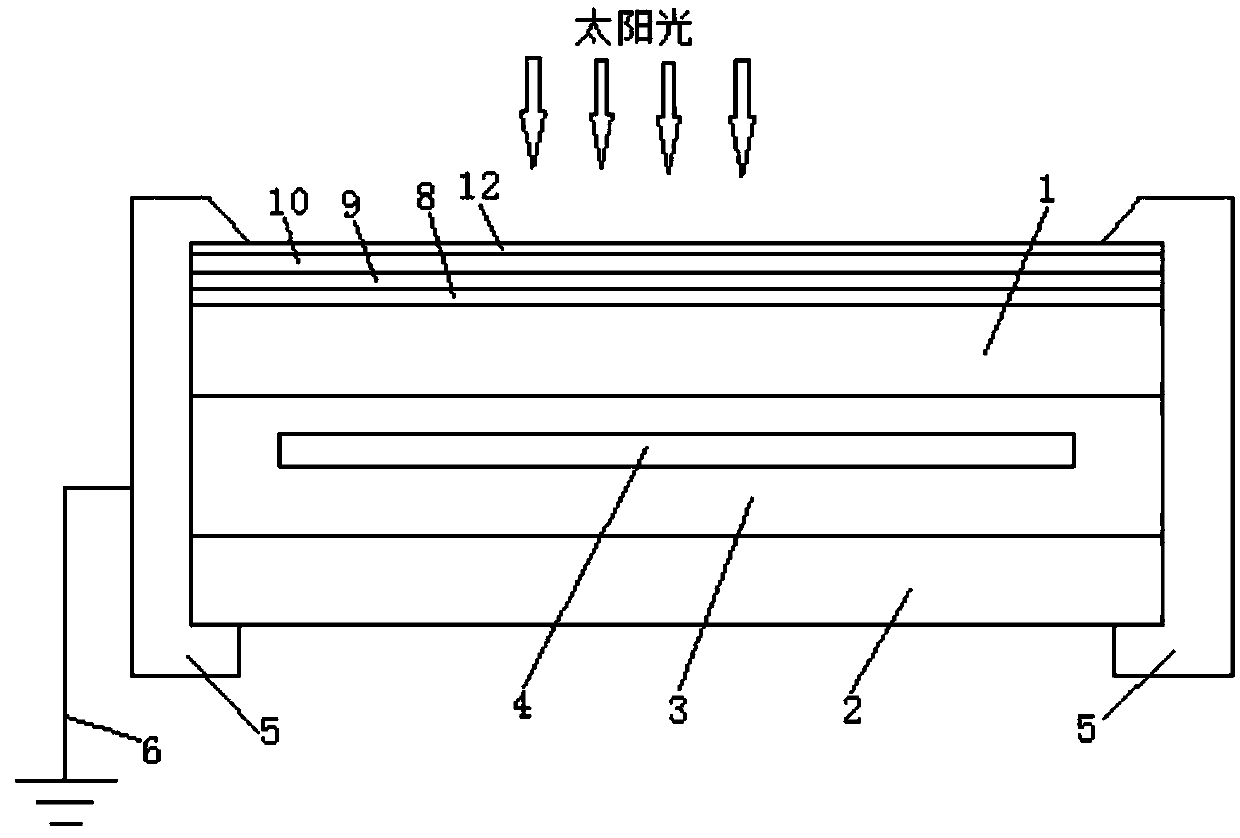
[0050] On the surface of a glass substrate with a thickness of 3mm, magnetron sputtering deposits a 20nm silicon oxide film layer as the first barrier layer 8; then, a 10nm Nb-doped titanium dioxide film is deposited on the silicon oxide film layer by magnetron sputtering layer as the conductive film layer 9; then on the Nb-doped titanium dioxide film layer, magnetron sputtering is used to deposit a 110nm silicon oxide film layer as the silicon-containing hydrophilic film layer 10; then on the silicon-containing hydrophilic film layer 10, CVD The titanium dioxide-based film layer 12 of 5nm is deposited by the method; then the glass deposited with the above film layer is subjected to tempering heat treatment, and the glass after the tempering heat treatment is used as the cover glass 1 of the photovoltaic module, and the film layer on the surface of the tempered glass faces the side of the photovoltaic module The light-receiving surface and the metal frame 5 of the photovoltaic ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] On the surface of a glass substrate with a thickness of 4mm, magnetron sputtering deposits a 25nm silicon oxynitride film layer as the first barrier layer 8; then adopts magnetron sputtering to deposit 15nm Ta-doped The titanium dioxide film layer is used as the conductive film layer 9; then on the Ta-doped titanium dioxide film layer, the silicon oxide film layer of 110nm is deposited by magnetron sputtering as the silicon-containing hydrophilic film layer 10; then on the silicon-containing hydrophilic film layer 10 A 3nm titanium dioxide-based film layer 12 is deposited by CVD; then the glass deposited with the above film layer is tempered and heat-treated, and the tempered glass is used as the cover glass 1 of the photovoltaic module, and the film layer on the surface of the tempered glass faces the photovoltaic The light-receiving surface of the module, and the metal frame 5 of the photovoltaic module is in contact with the Ta-doped titanium dioxide film layer 9, the...
Embodiment 3
[0054] On the surface of a glass substrate with a thickness of 4mm, magnetron sputtering deposits a 10nm zirconia film layer as the first barrier layer 8; then, a 5nm W-doped titanium dioxide film is deposited on the zirconia film layer by magnetron sputtering layer as the conductive film layer 9; then on the W-doped titanium dioxide film layer, magnetron sputtering is used to deposit a 105nm silicon oxide film layer as the silicon-containing hydrophilic film layer 10; then on the silicon-containing hydrophilic film layer 10, CVD The titanium dioxide-based film layer 12 of 7nm is deposited by the method; then the glass deposited with the above film layer is tempered and heat-treated, and the glass after the tempered heat treatment is used as the cover glass 1 of the photovoltaic module, and the film layer on the surface of the tempered glass faces the side of the photovoltaic module. The light-receiving surface, and at the same time, the metal frame 5 of the photovoltaic module...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com