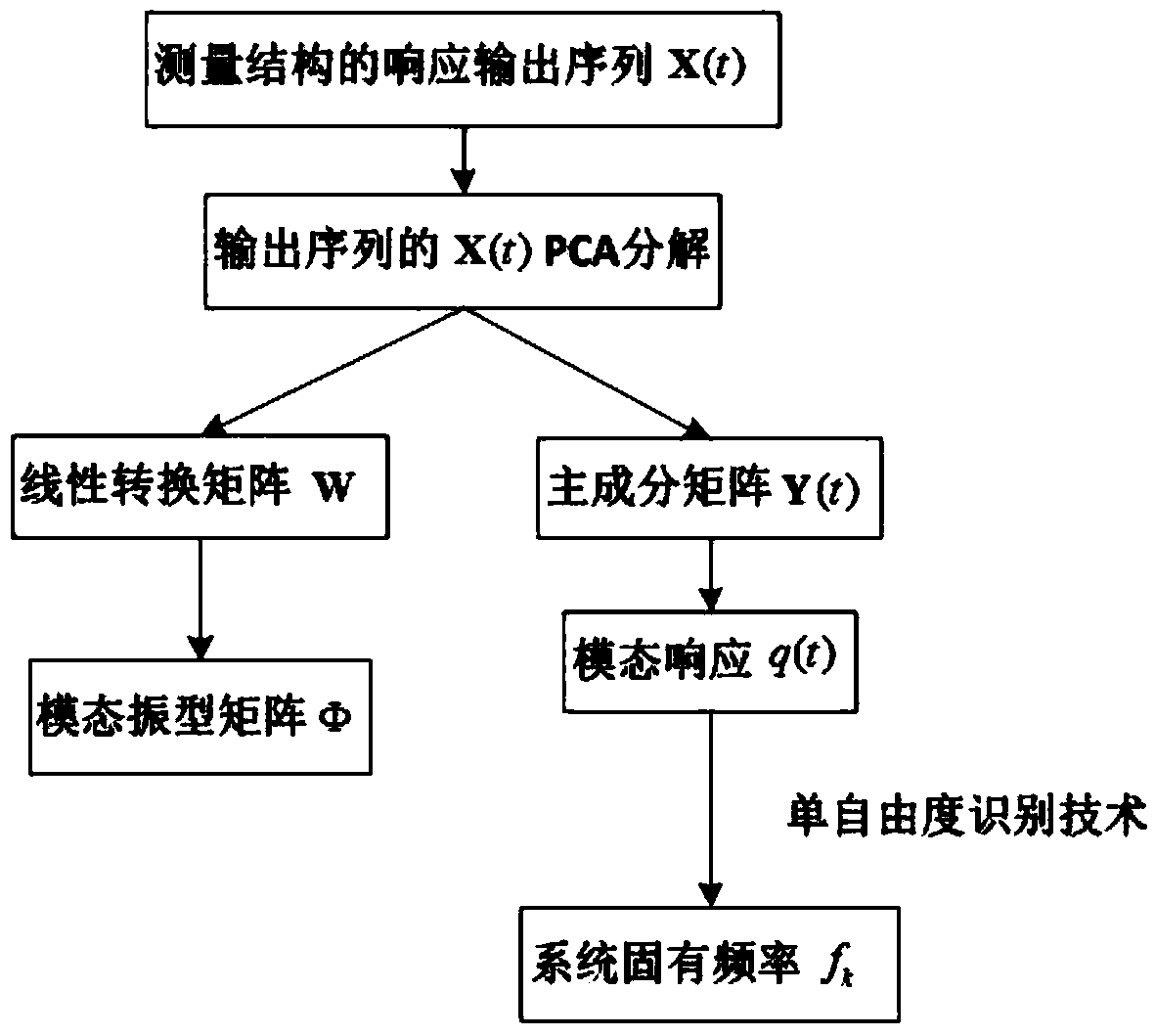
On-line identification method of time-varying working mode based on eigenvector recursion with forgetting factor
A technology of eigenvector and forgetting factor, which is applied in the field of modal parameter identification of linear time-varying structure by principal component analysis, and can solve the problem of inability to identify modal parameters online.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0141] Such as image 3 As shown, it is a three-degree-of-freedom spring oscillator system that simulates environmental excitation. The system is a slow time-varying system with weak damping. The mass m of block 1 1 is time-varying, m 2 、m 3 The mass remains constant to simulate a time-varying mass system; the external excitation uses Gaussian white noise with a mean value of 0 and a variance of 1 (in many practical problems, external environments that are difficult to measure are often simulated with white noise to solve problems) .
[0142] In this embodiment, the method for identifying working modal parameters of a linear time-varying structure based on eigenvalue eigenvector recursion with forgetting factor recursive principal component analysis uses a three-degree-of-freedom spring oscillator to simulate a time-varying structure, wherein, m 2 =1kg, m 3 = 1 kg; k 1 =1000N / m,k 2 =1000N / m,k 3 =1000N / m; c 1 =0.01N.s / m,c 2 =0.01N.s / m,c 3 =0.01 N.s / m. The initial d...
Embodiment 2
[0188] Such as Figure 32 As shown, it is the finite element model diagram of discretizing the cantilever beam into 40 elements;
[0189] In this embodiment, the method of principal component analysis linear time-varying structure working modal parameter identification method using eigenvalue eigenvector recursion with forgetting factor uses density-time-varying cantilever beams to simulate time-varying structures, wherein the beam parameter setting As follows: the size is 1×0.02×0.02m 3 (length × width × height), the cross-sectional area is A=W×H=4×10 -4 m 2 , the moment of inertia is I=WH 3 / 12, Young's modulus E=2.1×10 11 N / m 2 , Poisson's ratio u=0.3, the density is
[0190] Figure 33 For the proposed method to identify the frequency, sliding window recursive principal component analysis algorithm to identify the first-order natural frequency and the comparison chart of the theoretical first-order natural frequency;
[0191] Figure 34 A comparison chart for th...
Embodiment 3
[0236] Figure 55 is the block diagram of the working mode parameter device design system;
[0237] Figure 56 is the design block diagram of the upper computer;
[0238] Such as Figure 55 Shown, the time-varying structure operating mode parameter identification device based on the recursive principal component analysis algorithm of band forgetting factor of the present invention, comprises by OMAP processor (possess dual-core structure, ARM core+DSP core, has low power consumption , strong data processing capability) composed of control and data processing modules, give full play to the ability of DSP signal processing and ARM control; vibration data acquisition module (including signal input, signal conditioning, A / D data acquisition and conversion, etc. ); storage module (store a large amount of vibration data); liquid crystal display module (use LCD liquid crystal screen as output to display diagnostic results and waveform information); power supply module (responsible...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com