Method for compounding and directly pyrolyzing sludge
A sludge, direct technology, applied in the field of high-efficiency thermochemical disposal of organic solid waste and environmental protection, to achieve the effect of wide application, simplified process flow and reduced energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
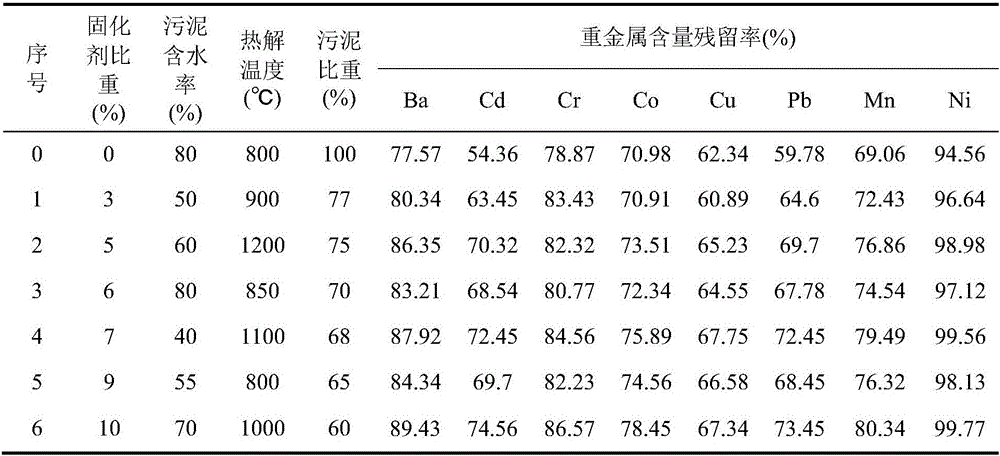
[0017] The dewatered sludge in the present embodiment is taken from Nanjing Chengbei Sewage Treatment Plant (same as the following examples), and the water content mass ratio of the treated sludge is 50%, the water content mass ratio of pine branches is 20%, and the average particle size is 2mm. The curing agent is attapulgite, the particle size is 20 mesh, and the mass ratio of silicon to aluminum is 60%. Mix the sludge, biomass and attapulgite evenly according to the ratio of 77%: 20%: 3%, put it into the pyrolysis furnace, raise the temperature to 500°C, keep it for 30 minutes, and then further rise to the pyrolysis temperature of 900°C, keep it 10min.
[0018] The heavy metal ions contained in the sludge are Ba, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Mn, Cd, Pb, and the content and form of heavy metals in the residue after pyrolysis are detected by ICP and XRD respectively. According to the concentration of heavy metals in the solid phase Residue rate and degree of morphological conversion were...
Embodiment 2
[0021] In this example, the water content of the treated sludge is 60%, the water content of pine branches is 17%, the average particle size is 4mm, the curing agent is attapulgite, the particle size is 15 mesh, and the silicon-aluminum mass ratio is 80%. Mix the sludge, biomass and attapulgite according to the ratio of 75%: 20%: 5%, put it into the pyrolysis furnace, raise the temperature to 550°C, keep it for 30 minutes, and then further raise it to the pyrolysis temperature of 1200°C, keep it 15min. According to the ICP result of table 1, compared with embodiment 1, the residual rate of each heavy metal ion in the solid phase all increases to some extent, and this shows that along with the bigger of curing agent ratio, the raising of pyrolysis temperature, the concentration of heavy metal The degree of curing is also relatively improved. The XRD results of solid phase residues showed that the degree of form transformation of heavy metals also increased, which may be the re...
Embodiment 3
[0023] In this embodiment, the moisture content of the treated sludge is 80%, the moisture content of pine branches is 15%, the average particle size is 6mm, the curing agent is kaolin, the particle size is 13 mesh, and the mass ratio of silicon to aluminum is 60%. Mix the sludge, biomass and kaolin evenly according to the ratio of 70%: 24%: 6%, put them into the pyrolysis furnace, raise the temperature to 600°C, keep it for 25min, and then further raise the pyrolysis temperature to 850°C, and keep it for 20min. According to the ICP result of table 1, it can be seen that compared with Example 2, the residual rate of each heavy metal ion in the solid phase has been reduced, but compared with Example 1, it has been increased, which shows that although the curing agent ratio However, the reduction of pyrolysis temperature will also reduce the residual rate of heavy metals in the solid phase. At the same time, the XRD results of the solid phase residue also showed that the form tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com