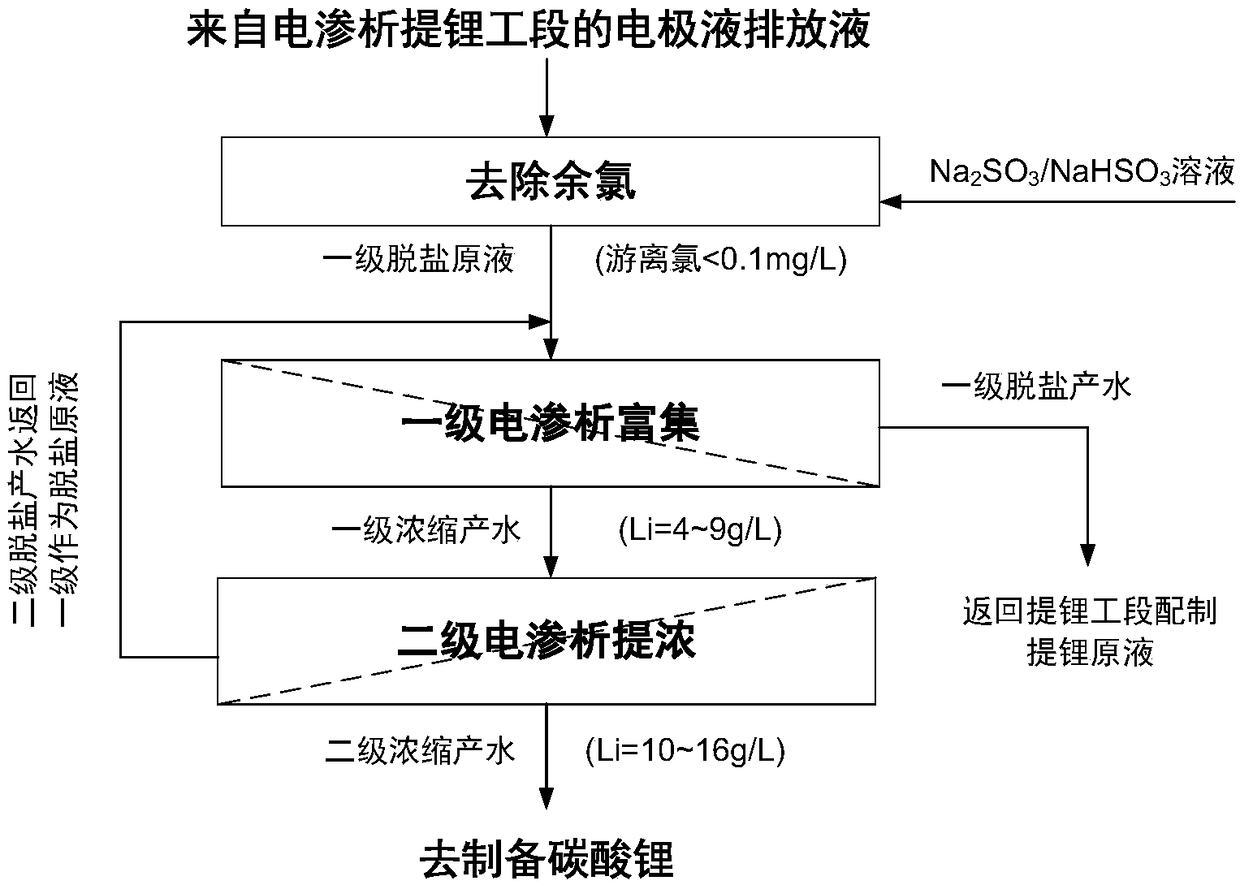
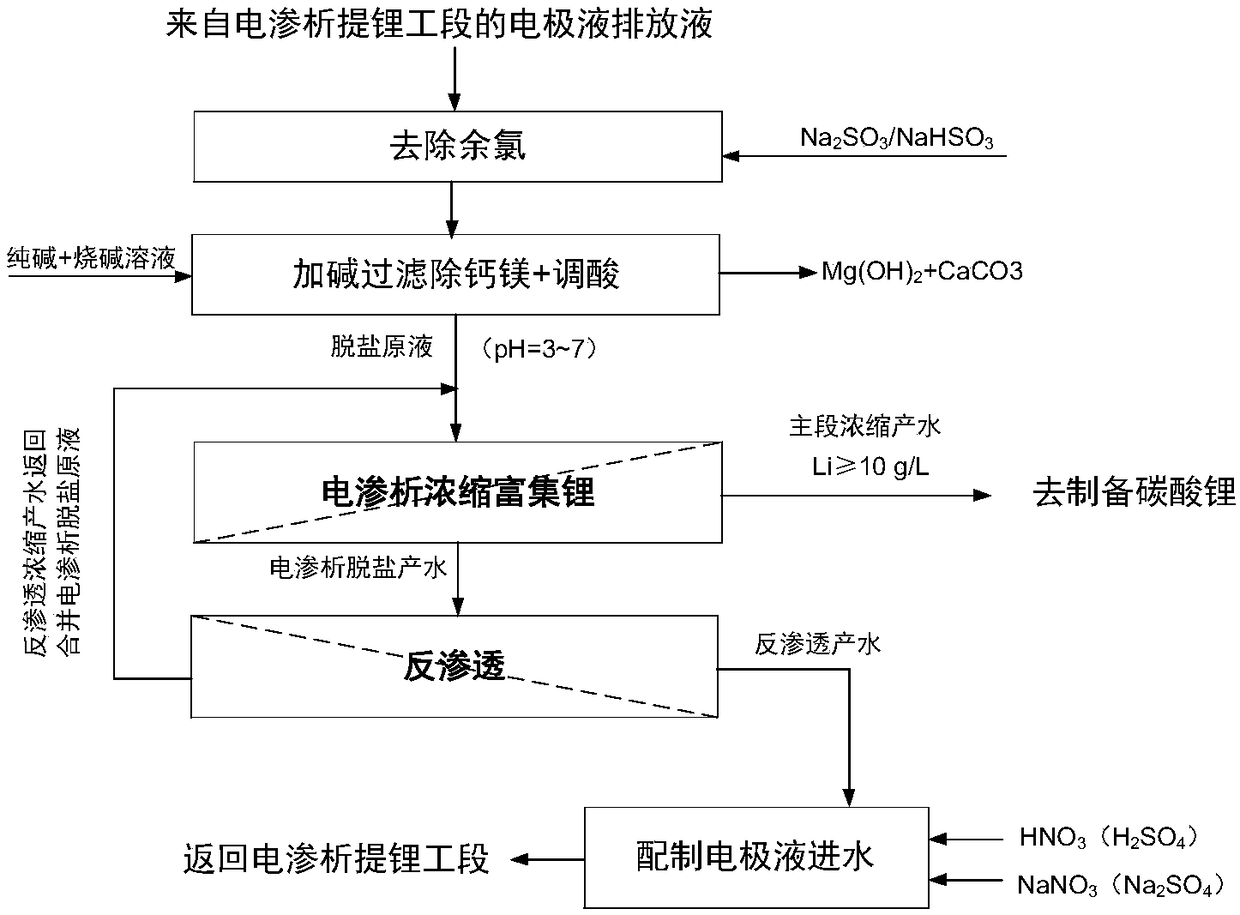
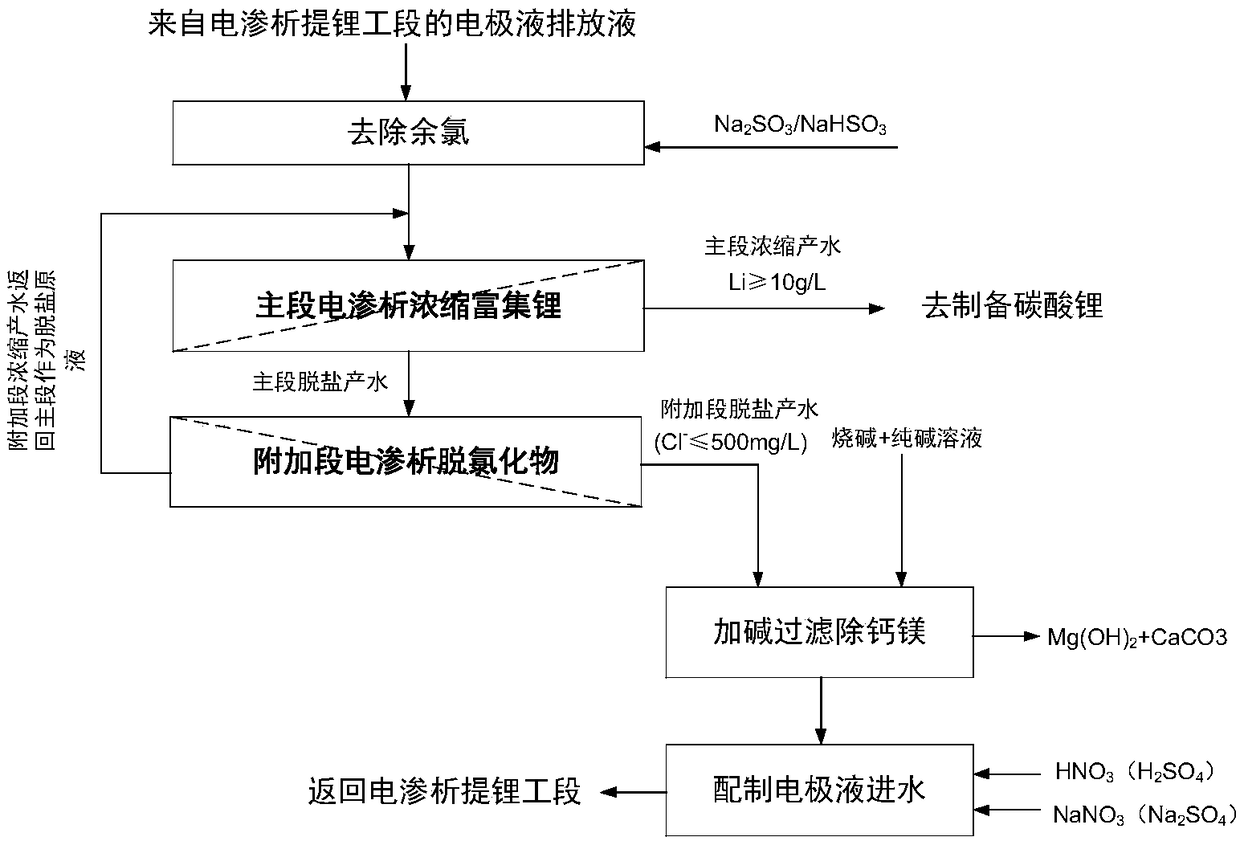
A method for recovering electrode discharge liquid in the electrodialysis lithium extraction process of high-magnesium solution
A recovery method, electrodialysis technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, general water supply conservation, etc., can solve problems such as brine resources and surrounding environmental pollution, environmental pollution around salt lakes, ion exchange resin damage, etc., to protect the surrounding area The effect of environment, high promotion value and continuous process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] This example is used to illustrate the treatment effect of the electrode discharge liquid (nitrate system) in the process of extracting lithium from the stock solution with a medium-high magnesium-lithium ratio.
[0040] A kind of electrode discharge liquid produced by electrodialysis lithium extraction process with medium and high magnesium-lithium ratio (Mg / Li=15~100) salt lake old brine as raw material, containing 867mg / L lithium, 1150mg / L sodium, 52.9mg / L potassium, 910mg / L magnesium, 17.8mg / L calcium, 2621mg / L chloride ion, 11970mg / L nitrate, 1.4mg / L sulfate and 30mg / L free chlorine, pH 1.8. Get 50L of this discharge liquid, add 4% sodium sulfite solution 71mL (Na 2 SO 3 :Cl 2 =1.96), fully mixed and reacted for 3 minutes, and the free chlorine of the feed liquid after the reaction was measured to be 0.08mg / L. Use an electrodialyzer consisting of 9 pairs of CIMS positive membranes and ACS negative membranes produced by ASTOM Corporation of Japan alternately arra...
Embodiment 2
[0045] This example is used to illustrate the treatment effect of the electrode discharge liquid (nitrate system) in the process of extracting lithium from the raw liquid with a low-to-medium magnesium-lithium ratio.
[0046] A kind of electrode discharge liquid produced by electrodialysis lithium extraction process with medium and low magnesium-lithium ratio (Mg / Li=1~15) material liquid as raw material, containing 2724mg / L lithium, 1146mg / L sodium, 166mg / L potassium, 899mg / L magnesium, 55.9mg / L calcium, 13230mg / L chloride ion, 10050mg / L nitrate, 4.2mg / L sulfate and 102mg / L free chlorine, the pH is 1.9. Take 50L of this discharge liquid, add 10% sodium bisulfite solution 68mL (NaHSO 3 :Cl 2 =1.48), fully mixed and reacted for 4 minutes, and the free chlorine of the feed liquid after the reaction was measured to be 0.05 mg / L. The same electrodialysis device as in Example 1 was used. Take 0.77L of deionized water as the concentrated solution inlet water, and the dechlorinati...
Embodiment 3
[0051] This example is used to illustrate the treatment effect of the electrode discharge solution (nitrate system) in the process of extracting lithium from the ultra-high magnesium-lithium ratio stock solution.
[0052] A kind of electrode discharge liquid produced by electrodialysis lithium extraction process with ultra-high magnesium-lithium ratio (Mg / Li>100) material liquid in the raw material, containing 202mg / L lithium, 405mg / L sodium, 9.9mg / L potassium, 910mg / L L magnesium, 4.1mg / L calcium, 1475mg / L chloride ion, 6229mg / L nitrate, 0.3mg / L sulfate, 14mg / L free chlorine, pH 1.7. Get 50L of this discharge liquid, add 1% sodium sulfite solution 250mL (Na 2 SO 3 :Cl 2 =3.60), fully mixed and reacted for 3 minutes, and the free chlorine of the feed liquid after the reaction was measured to be 0.03mg / L. The same electrodialysis device as in Example 1 was used, only the membranes were replaced with monovalent ion-selective positive membrane CSO and negative membrane ASV pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com