Temperature compensating circuit of power amplifier
A technology of temperature compensation circuit and power amplifier, applied to power amplifiers, improved amplifiers to reduce temperature/power supply voltage changes, amplifiers, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve precise control of output power of power tubes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
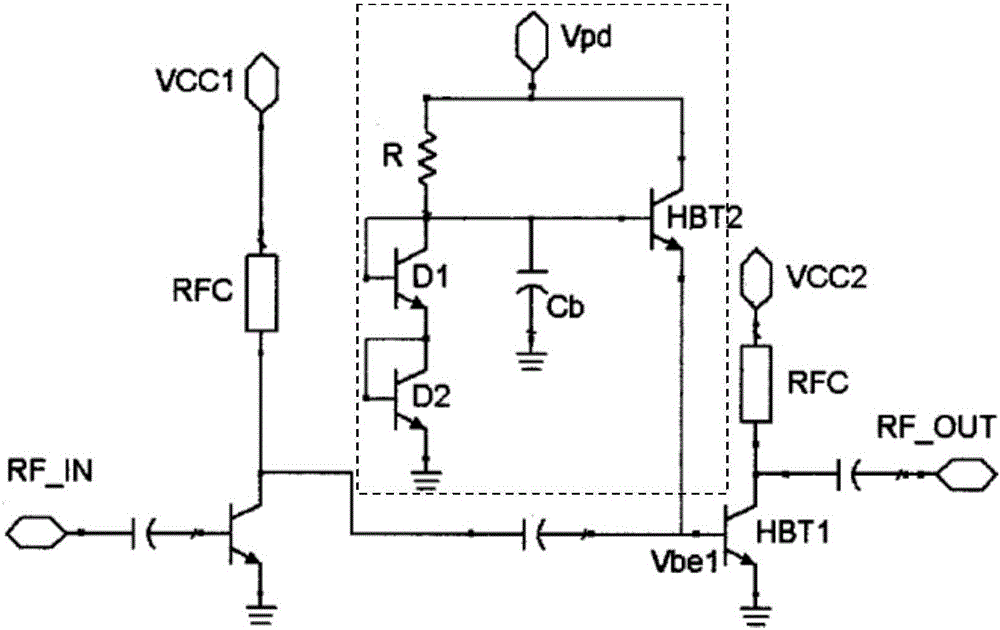
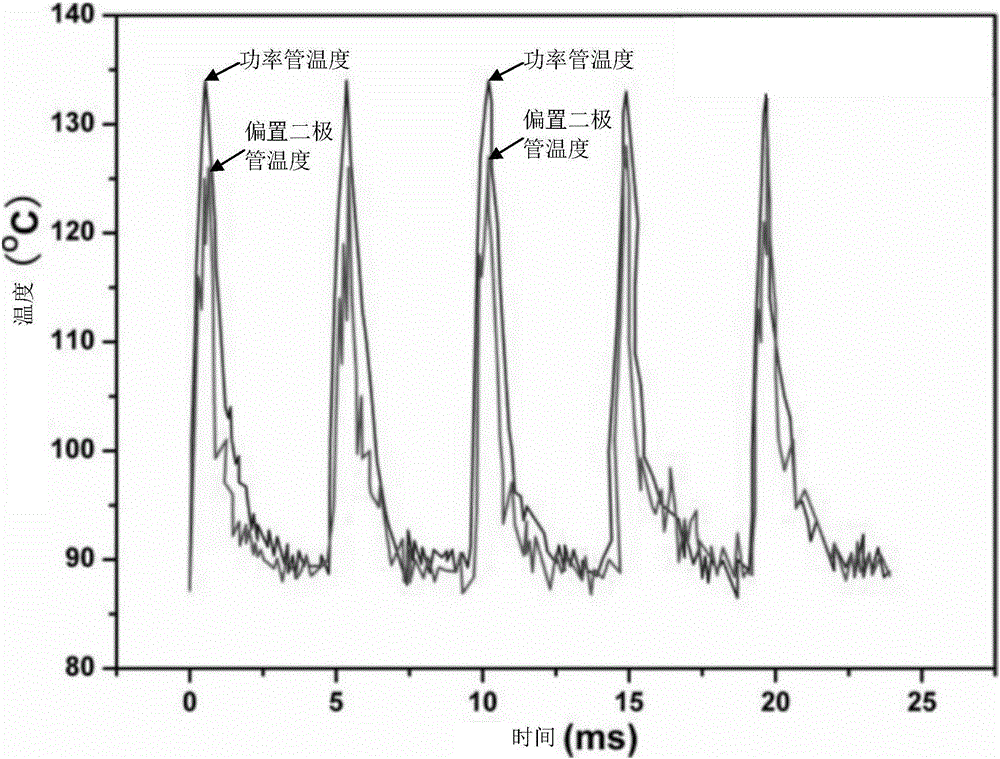
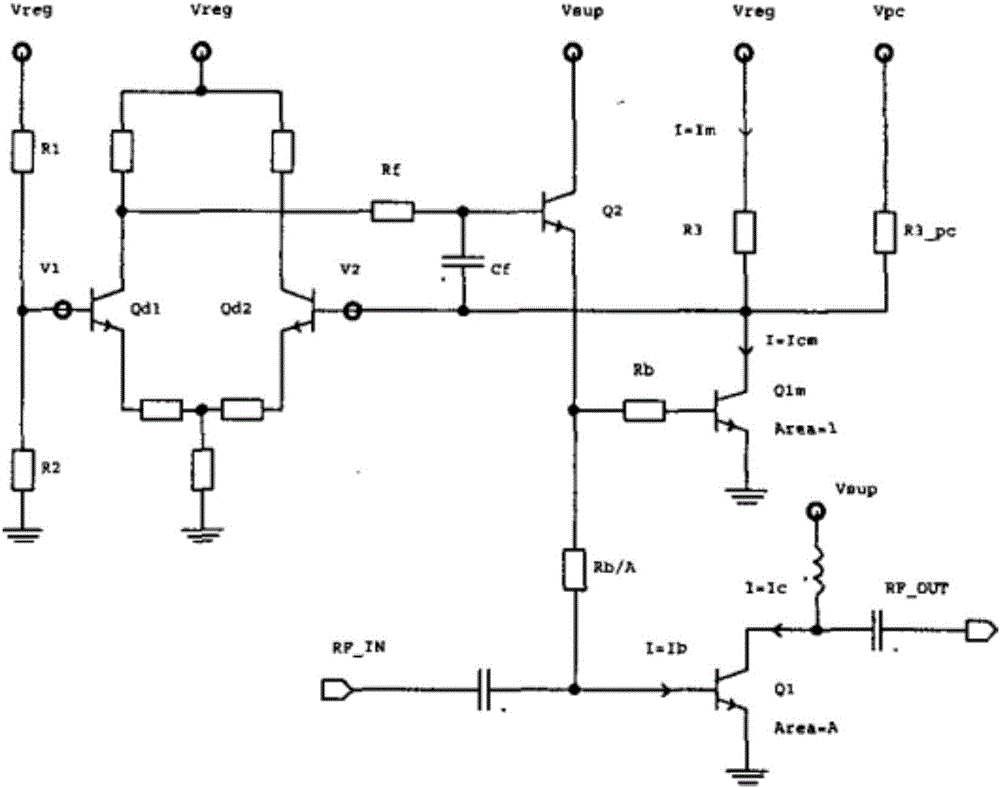
[0029] see Figure 4, which is Embodiment 1 of the power amplifier and its bias circuit of the present application. The whole circuit is composed of current bias circuit, temperature compensation circuit and amplifier circuit. The current bias circuit is used to provide a constant bias current Is, which can be understood as a current source, and can also be realized by a voltage source or a self-bias circuit. The temperature compensation circuit provides the temperature-compensated bias current ipwr for the base of the power transistor Q1 after performing temperature compensation on the bias current Is. The temperature compensation includes three aspects: first, when the power tube is working normally and below the threshold temperature, the collector current change of the power tube is positively correlated with the temperature change; second, when the power tube is working normally and below the threshold temperature In the above, the collector current change of the power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com