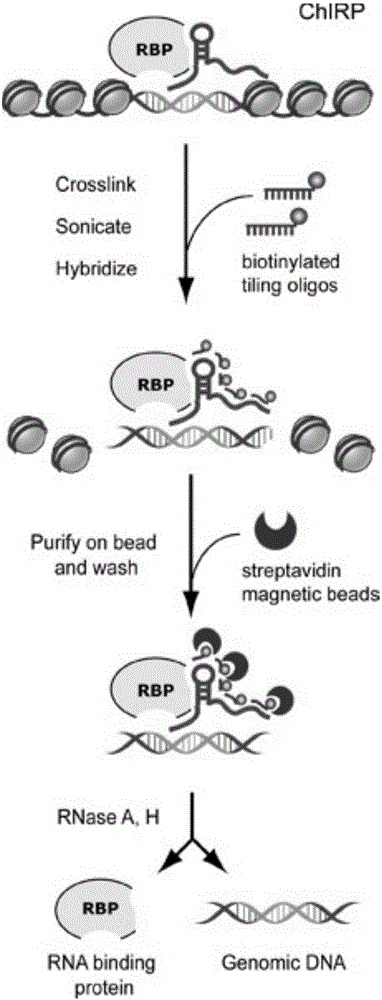
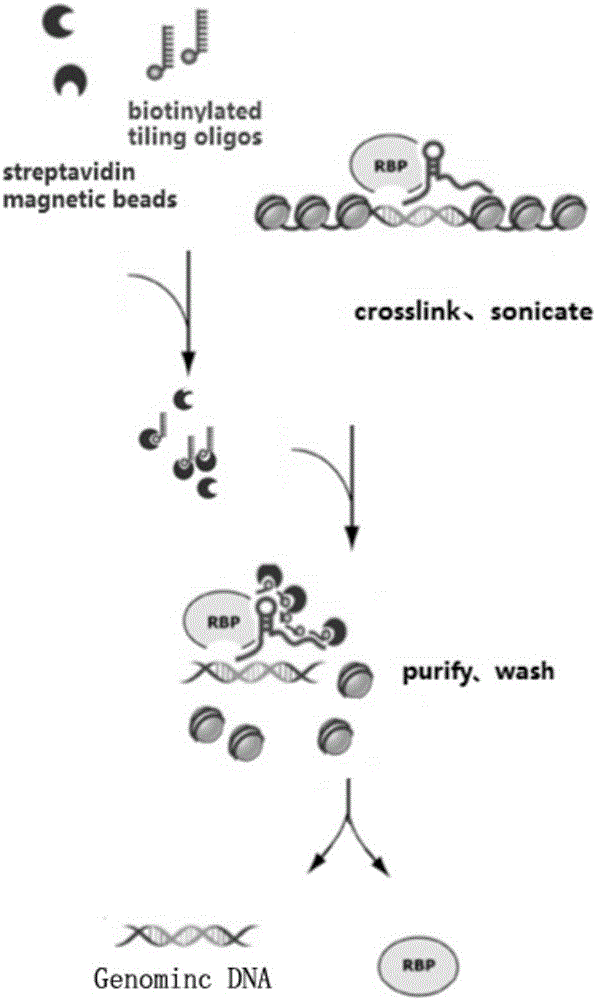
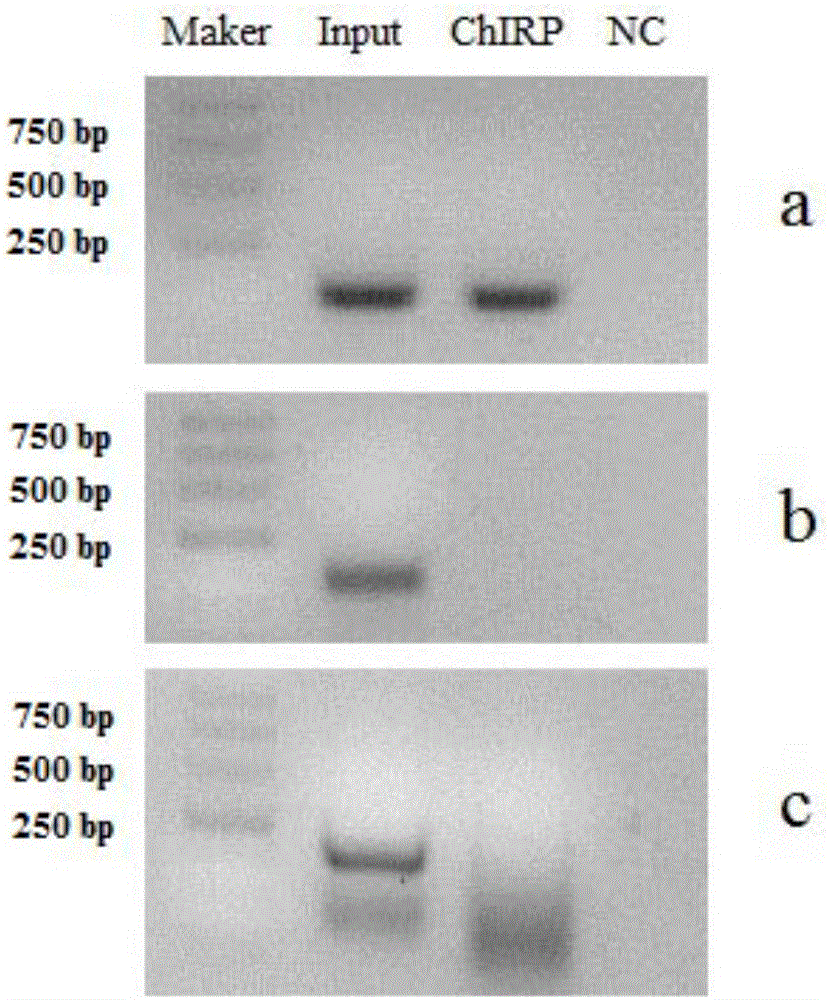
RNA (ribonucleic acid)purification chromatin separation technique
A separation technology and chromatin technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve the problems of low hybridization efficiency between probe sets and RNA, poor sensitivity, and low specificity of ChIRP technology. Achieve the effects of saving experimental costs, enhancing detection specificity, and improving hybridization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] In this example, a ChIRP experiment was carried out for TINCR. TINCR is a long non-coding RNA, the species is human, the target gene is TGFBI, and the experimental material is human epidermal tissue.
[0054] A chromatin separation technique for RNA purification, comprising the following steps:
[0055] S1. Preparation of chromatin lysate
[0056] S11, cross-linked cells
[0057] All steps for crosslinking cells were performed at room temperature. 1v / v% formaldehyde PBS is prepared from 37% formaldehyde and PBS according to the volume ratio of 27:973, and it must be prepared and used immediately.
[0058] ①Suspend the cells with 1v / v% formaldehyde in PBS, pipette and mix well, shake and rotate at room temperature for 10 minutes, centrifuge at 1500-2000rpm for 5min and crosslink again;
[0059] ②End the cross-linking reaction, add 0.1mL of 1.25M glycine (about 0.01g) solution, shake and rotate at room temperature for 5 minutes; centrifuge at 2000RCF for 5 minutes, re...
Embodiment 2
[0102] In this example, a ChIRP experiment was carried out for FENDRR. FENDRR is a long non-coding RNA, the species is human, the target gene is NIPA1, and the experimental material is hLF cells.
[0103] A chromatin separation technique for RNA purification, comprising the following steps:
[0104] S1. Preparation of chromatin lysate
[0105] The steps described in Example 1 are the same.
[0106] S2, magnetic bead pretreatment
[0107] The steps described in Example 1 are the same.
[0108] S3. Preparation of probe-magnetic bead complex
[0109] S31. Probe pretreatment
[0110] In this embodiment, a plurality of probes are designed for lncRNA to form a probe group. The probe groups of the experimental group are Even group and Odd group, each of 5 probes in Even group and Odd group, and the blank control group (NC group) contains 5 probes. strip probes (see Table 1). Before pretreatment, the probe groups of the experimental group and the blank control group were config...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com