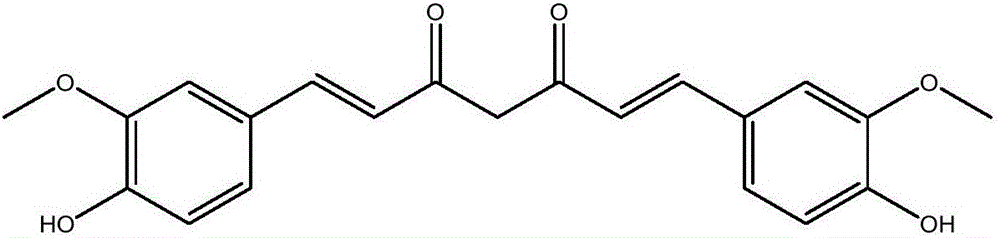
Application of curcumin to preparation of drug for killing fish epizoic infusorians
A technology of curcumin and ciliates, which is applied to the application field of curcumin in the preparation of drugs for killing fish ectoparasitic ciliates, which can solve problems such as economic losses, great harm to human health, and high residues of chemical drugs, and achieve broad application prospects , Abundant raw materials, low price effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1: The killing effect of curcumin on the infective larvae of Melonella polyps
[0019] (1) Preparation of medicine: Weigh 2 mg of curcumin powder, use 20 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to promote dissolution, add 761.25 μL of pure water, and make up a 2560 mg / L primary stock solution. Take 150μL of primary stock solution and 1350μL of pure water to make 1.5mL of 256mg / L secondary stock solution. The two-fold gradient dilution method was used to prepare 1.5 mL each of 128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125, and 0 mg / L (control group) liquids. Taking the DMSO content (0.13%) in the highest concentration chemical solution used in the experiment as the standard, a control solution containing 0.13% DMSO was prepared.
[0020] (2) Take a 96-well plate, add 100 μL of an aqueous solution containing about 500 larvae to each well, and then add 100 μL of the drug solution of different concentrations to each well, so that the final curcumin concentration in each well is...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: The killing effect of curcumin on the adult worm
[0024] (1) Drug preparation: the same as in Example 1.
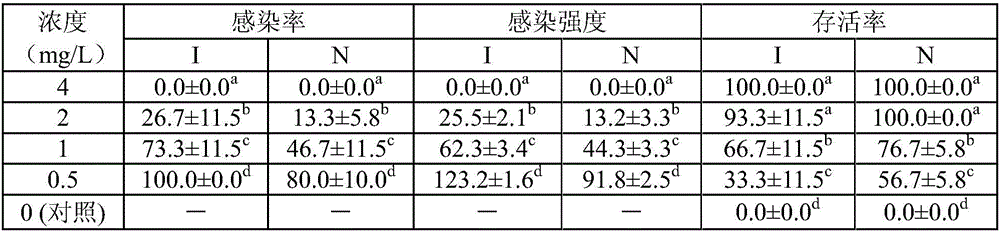
[0025] (2) Add 200 μL of the insect liquid containing about 60 mature adults to each well of the 24-well plate and accurately count the number of adults in each hole, and then add 200 μL of curcumin liquid at different concentrations to make the final drug concentration sequentially 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1, and 0 mg / L (control group), each drug concentration is set in 3 parallel. The experimental temperature was kept at 23±0.5℃, and the lethal time of each foraminifera within 5h and the number of surviving adults in each hole were recorded under a 4x objective lens, and the 5h mortality and half effective concentration (EC 50 ). After the above counting is completed, count the number of cysts formed in each well for 6 hours, and place the 24-well plate in a constant temperature incubator at 23±0.5°C, split and incubate for 16 hours, record the number of hatc...
Embodiment 3
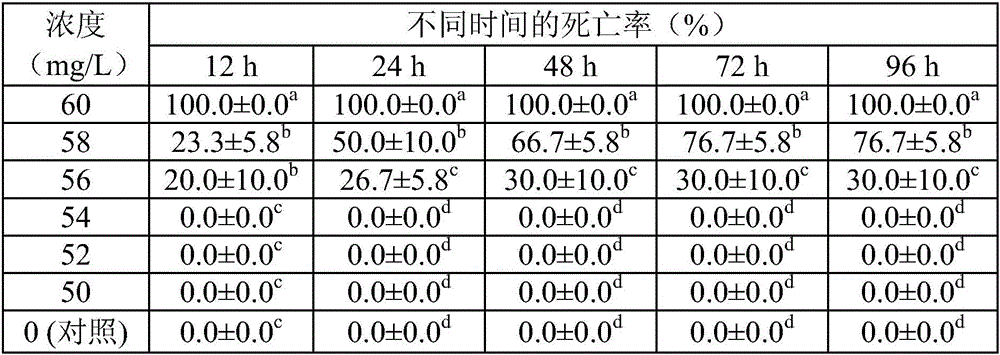
[0029] Example 3: The killing effect of curcumin on the cysts of Melon
[0030] (1) Drug preparation: the same as in Example 1.
[0031] (2) Add 200μL of worm fluid containing about 30 mature cucurbita worm adults to each well of the 24-well plate, and let it stand for 6 hours. After the cysts are formed, count the number of cysts in each hole, and then add 200μL of different concentrations. The concentration of the final drug is 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1, and 0 mg / L (control group), and three drug concentrations are set in parallel. After adding the medicine, place the 24-well plate in a constant temperature incubator at 23°C for 16 hours, observe the incubation under a 4x microscope, count the number of hatched larvae in each hole, and calculate the average number of hatched larvae per cyst, calculation formula as follows:
[0032] The average number of larvae hatched per cyst=the number of larvae in each hole / the number of cysts in each hole.
[0033] The results showed that: the hi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com