Method for space-time adaptive processing of airborne radar based on EFA and MWF
A space-time adaptive, airborne radar technology, applied in the field of radar, can solve the problems of reduced calculation, large calculation, general performance in the main lobe clutter area, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing calculation and efficient use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
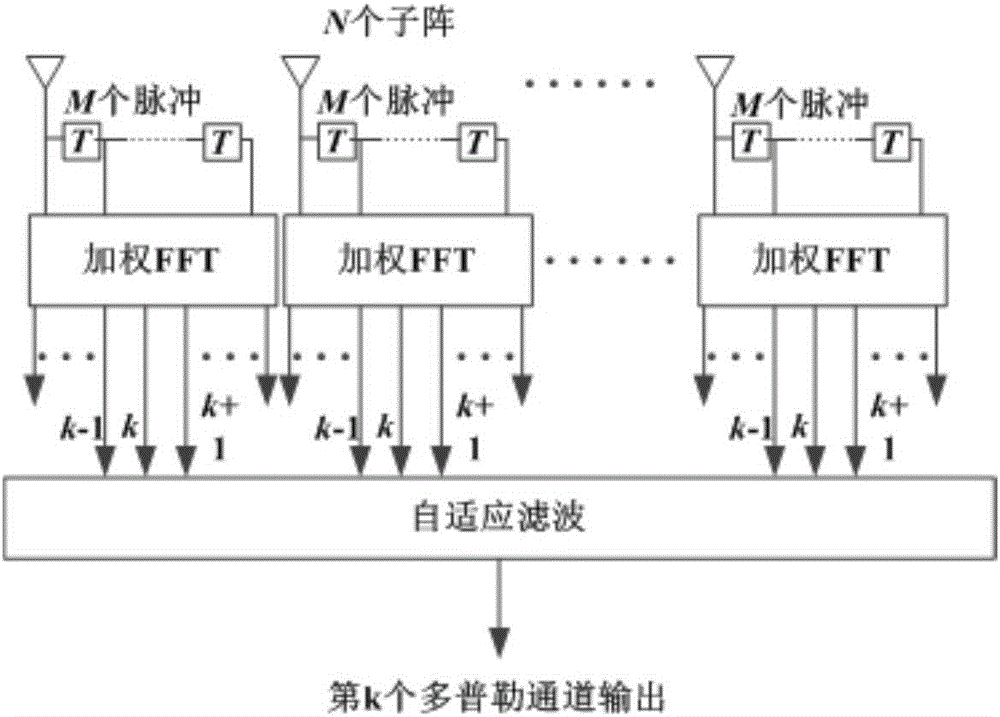
[0022] refer to figure 1 , is a realization block diagram of an airborne radar space-time adaptive processing method based on EFA and MWF of the present invention, and this kind of airborne radar space-time adaptive processing method based on EFA and MWF comprises the following steps:
[0023] Step 1: Perform airspace dimensionality reduction processing on the echoes received by the airborne radar within a coherent processing interval (CPI), obtain N subarrays contained in the airborne radar within a coherent processing interval (CPI) after airspace dimensionality reduction, and Denote the echo received by the nth sub-array of the airborne radar after space dimension reduction within a coherent processing interval (CPI) as x n , and then use the extended factorization method (EFA) to analyze the echo x received by the nth sub-array of the airborne radar after space dimensionality reduction within a coherent processing interval (CPI) n Perform weighted fast Fourier transform (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com