Transgenic breeding method producing astaxanthin in crop seed endosperm
A technology of astaxanthin and seed embryos, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of lack of synthetic astaxanthin and decreased nutritional value, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The present invention finds through research that PSY, CrtI, BHY and BKT are four essential key enzymes in order to synthesize astaxanthin in crop endosperm. Based on the above research basis, the present embodiment establishes a transgenic breeding method for producing astaxanthin in rice endosperm, which specifically includes the following steps:
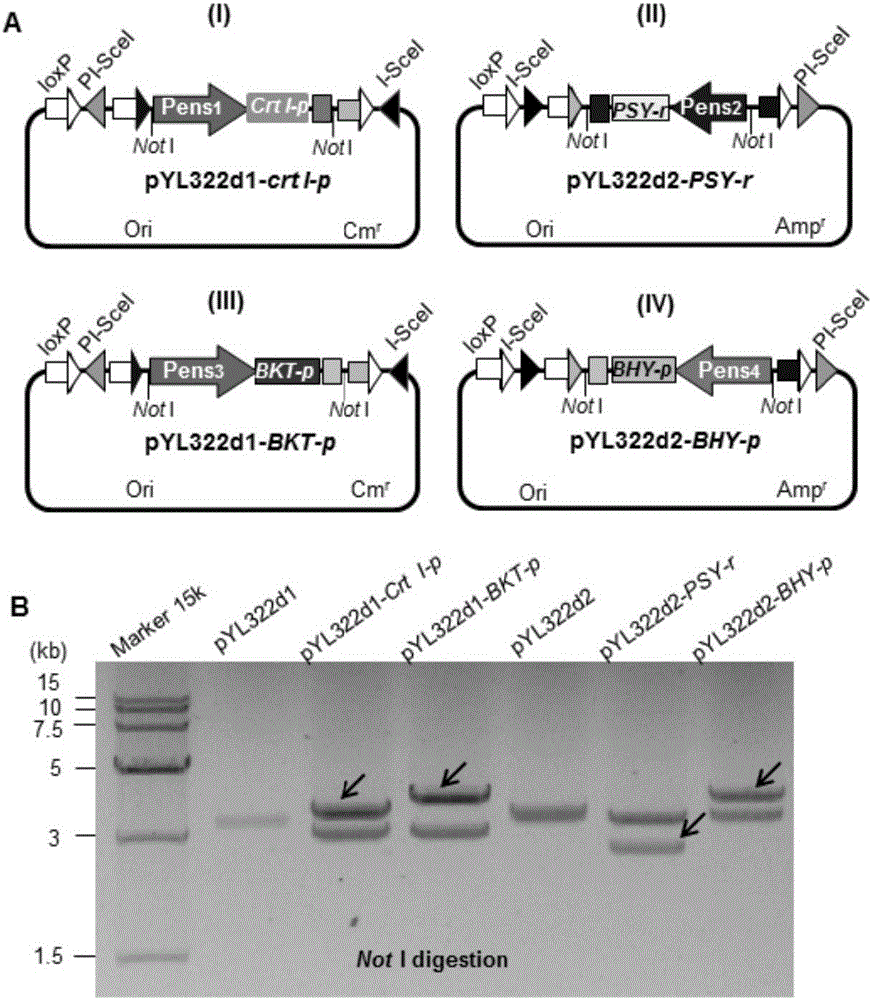
[0037] S1. Construction of four essential gene expression cassettes:
[0038] S11. Synthesis of the coding regions of four essential genes (PSY-r, CrtI-p, BHY-p and BKT-p): Using the PSY gene (GenBank No.U32636.1) of maize as a template, according to monocotyledonous plants and rice Codon preference, using the Codon Optimization Tool program to optimize the codon, synthetically obtain the PSY-r of the DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1, clone it into a plasmid vector, and determine its sequence by sequencing; Erwinia Erwinia uredovoracrtI gene (GenBank No. D90087) as a template, according to the codon preference of monocoty...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Appearance and HPLC detection of astaxanthin in transgenic rice endosperm:
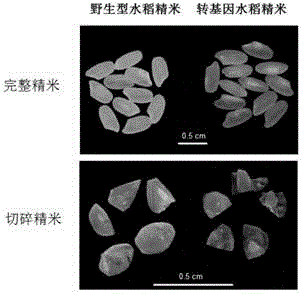
[0081] Observation of astaxanthin in the endosperm of transgenic rice: After the transgenic rice seeds introduced with the above four genes were processed into polished rice (removing the seed coat) and the rice grains were chopped and observed, it can be seen that the inside and outside of the whole polished rice are orange-red ( Figure 6 ), indicating that astaxanthin was synthesized in the endosperm.
[0082] Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) identification of astaxanthin from transgenic rice seeds: Take 0.1 g of rice seeds and grind them into powder on ice, add 2 mL of methanol and continue to grind uniformly for 5 min; 100rpm) extraction for 10min; centrifuge at 4°C 8000rpm for 5min to collect the supernatant; repeat the extraction of the precipitate until the precipitate is white; centrifuge the supernatant at 4°C 8000rpm for 5min and then combine the supernata...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com