Method and device for determining the polarity of rotor poles, variable frequency machines and electric rotating machines
A technology for rotating electrical machines and rotors, applied in the field of rotating electrical machines and synchronous motors, which can solve problems such as failure to provide results, low energy density magnet demagnetization, and insufficient reliability, and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of undesired rotation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
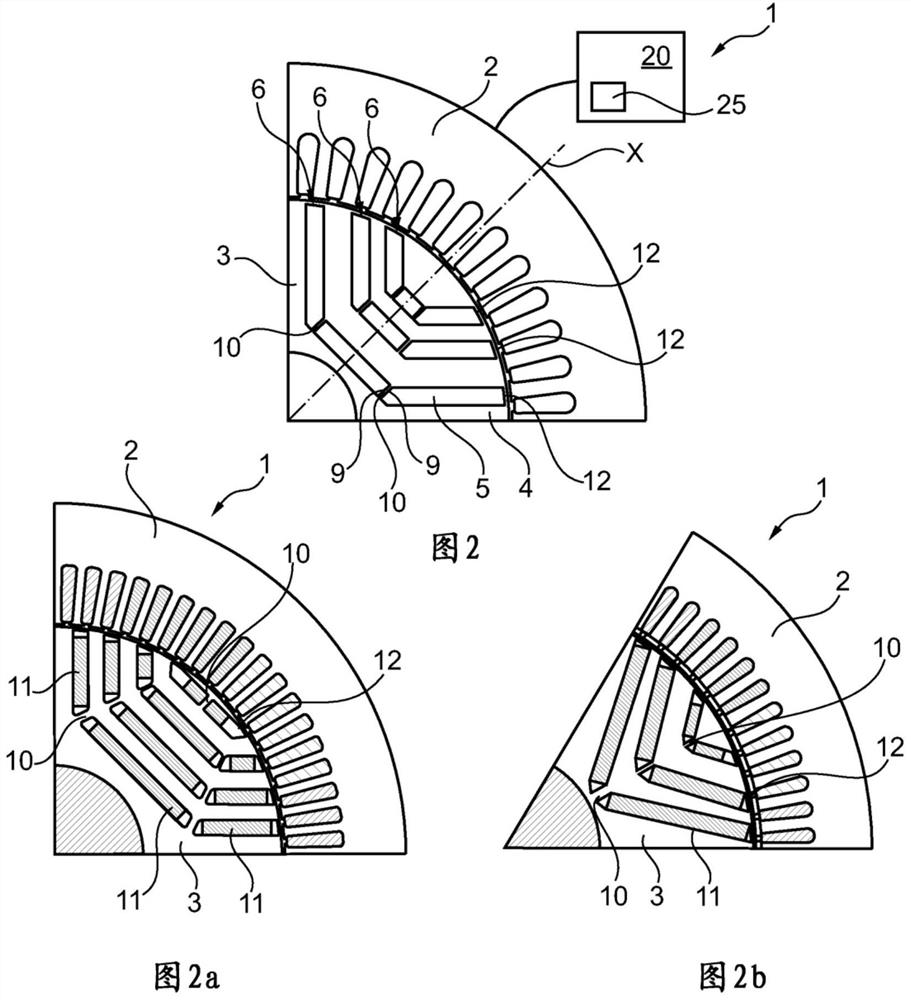
[0097] figure 1 There is shown a rotating electric machine 1 comprising a stator 2 and a flux concentrating rotor 3 having a magnetic rotor block 4 in which seats 5 are formed to define poles of the rotor, each pole having a radial axis X.
[0098] In this example, the rotor comprises nine seats 5 per pole arranged in 3 concentric rows 6 around each pole, the concavities of the rows facing the air gap. Row 6 comprises three seats 5 arranged successively in a row. The three rows 6 of the same pole are of decreasing length in the direction of the air gap, the longest on the axis of rotation and the shortest on the air gap side.
[0099] Seat 5 is in an elongated form. The seats 5 each comprise 2 short sides 9 , between which the respective short sides 9 of two consecutive seats 5 in the same row 6 define a material bridge 10 . The material bridges 10 generally extend along a longitudinal axis Z of the bridges, which is oriented so as to approach the radial axis X of the corr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com