Preparation method of antimicrobial bacterial cellulose material
A technology of bacterial cellulose and organosilicon quaternary ammonium salt, which is applied in the direction of medical preparations of non-active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of limited load capacity, easy shedding, bioaccumulation, and toxic and side effects, and achieve Mild and simple reaction conditions, good mechanical strength and high reaction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The amino-functionalized bacterial cellulose material was prepared according to the following steps:
[0040](1) Add 60g of N,N-dimethyl-N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]octadecylammonium chloride to 40g of methanol solution to prepare 60% mass ratio of N,N-dimethoxy Methyl-N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]octadecylammonium chloride solution;
[0041] (2) Add 10 mL of deionized water to a 25 mL beaker, then add 10 pieces of purified bacterial cellulose wet membranes with a diameter of 1.5 cm, place the beaker in a water bath magnetic stirrer, and the reaction conditions are 25 ° C and 20 rpm;
[0042] (3) Add 0.23mL of prepared N,N-dimethyl-N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]octadecylammonium chloride solution to the above system, the final concentration is 3.1×10 -3 mmol / L;
[0043] (4) Add glacial acetic acid dropwise to adjust the pH to 4.0, and continue stirring for 48 hours at 25°C and 20 rpm;
[0044] (5) Collecting the reacted bacterial cellulose membrane, washing with deio...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The amino-functionalized bacterial cellulose material was prepared according to the following steps:
[0055] (1) Add 10 mL of deionized water to a 25 mL beaker, then add 10 pieces of purified bacterial cellulose wet membranes with a diameter of 1.5 cm, place the beaker in a water bath magnetic stirrer, and the reaction conditions are 5 ° C and 20 rpm;
[0056] (2) Add 4.62mL of prepared N,N-dimethyl-N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]octadecylammonium chloride solution to the above system with a concentration of 6.2×10 -2 mmol / L;
[0057] (3) Add glacial acetic acid dropwise to adjust the pH to 4.0, and continue stirring for 48 hours at 5°C and 20 rpm;
[0058] (4) Collecting the reacted bacterial cellulose membrane, washing with deionized water repeatedly to obtain the grafted bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0059] Characterization tests and performance experiments were carried out on the bacterial cellulose prepared by the above modification, including:
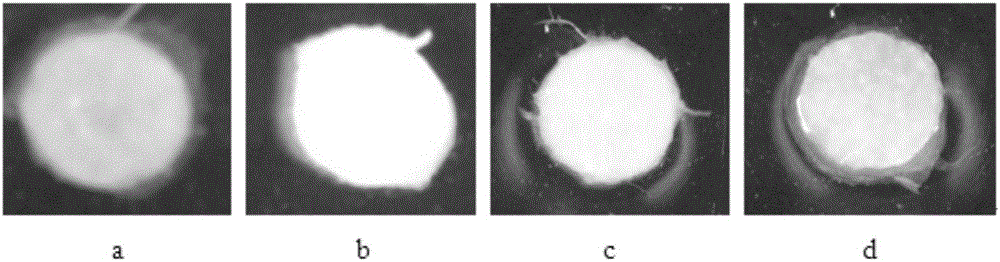
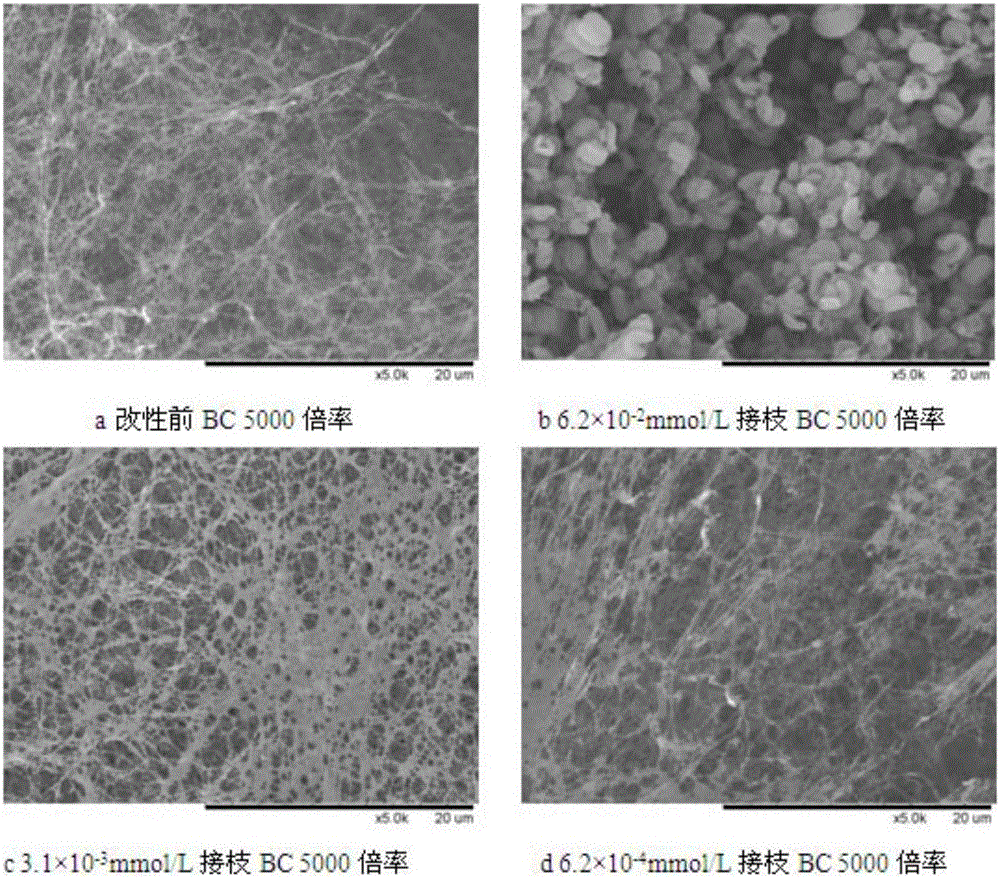
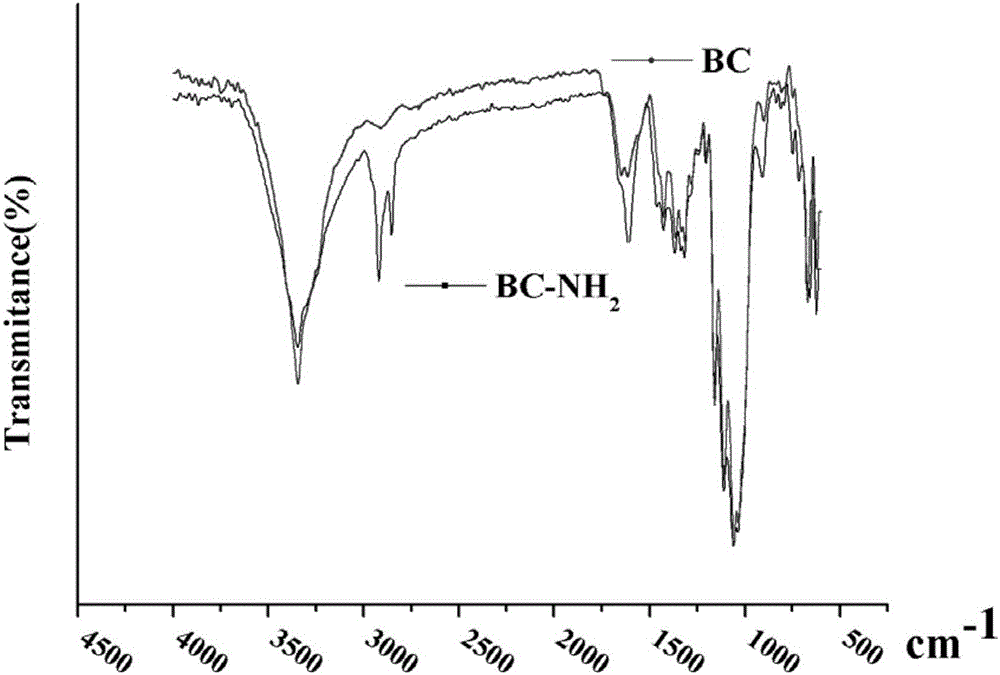
[0060] ①Compar...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The amino-functionalized bacterial cellulose material was prepared according to the following steps:
[0072] (1) Add 10 mL of deionized water to a 25 mL beaker, then add 10 pieces of purified bacterial cellulose wet membranes with a diameter of 1.5 cm, place the beaker in a water bath magnetic stirrer, and the reaction conditions are 60 ° C and 20 rpm;
[0073] (2) Add 0.23mL of prepared N,N-dimethyl-N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]octadecylammonium chloride solution to the above system with a concentration of 3.1×10 -3 mmol / L;
[0074] (3) Add glacial acetic acid dropwise to adjust the pH to 4.0, and continue stirring at 60°C and 20 rpm for 48 hours;
[0075] (4) Collecting the reacted bacterial cellulose membrane, washing with deionized water repeatedly to obtain the grafted bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0076] Characterization tests and performance experiments were carried out on the bacterial cellulose prepared by the above modification, including:
[0077] ①Comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com