Laser capable of monitoring cutting state in real time
A real-time monitoring and laser technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of difficulty in real-time control, explosive perforation of metal materials, low processing efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the utilization rate of light sources, fast response time, and fast cutting speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
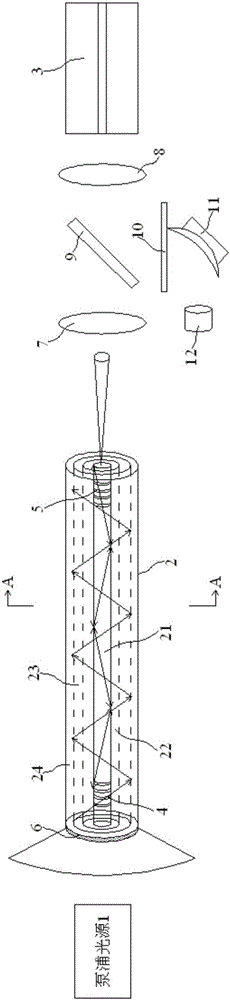
[0017] Embodiment 1: A laser for real-time monitoring of the cutting state, including a pumping light source 1, a cladding fiber 2 and a transmission fiber 3, the pumping light source side pumps or end pumps the cladding fiber 2, the The clad fiber 2 further includes a laser gain medium core 21 located at the center, and the laser gain medium core 21 is sequentially coated with a glass isolation layer 22, a fluorescent material layer 23 and an outer cladding 24 from the inside to the outside, and the laser gain medium core 21 The refractive index of the glass isolation layer 22 is greater than the refractive index of the glass isolation layer 22. The refractive index of the glass isolation layer 22 is greater than the refractive index of the fluorescent material layer 23. The refractive index of the fluorescent material layer 23 is greater than the refractive index of the outer cladding 24. The input of the cladding optical fiber 2 The end and the output end are respectively pr...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: A laser for real-time monitoring of the cutting state, including a pumping light source 1, a cladding fiber 2 and a transmission fiber 3, the pumping light source side pumps or end pumps the cladding fiber 2, the The clad fiber 2 further includes a laser gain medium core 21 located at the center, and the laser gain medium core 21 is sequentially coated with a glass isolation layer 22, a fluorescent material layer 23 and an outer cladding 24 from the inside to the outside, and the laser gain medium core 21 The refractive index of the glass isolation layer 22 is greater than the refractive index of the glass isolation layer 22. The refractive index of the glass isolation layer 22 is greater than the refractive index of the fluorescent material layer 23. The refractive index of the fluorescent material layer 23 is greater than the refractive index of the outer cladding 24. The input of the cladding optical fiber 2 The end and the output end are respectively pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com