Wind Power Generator
A technology for wind turbines and generators, which is applied in the directions of wind turbines, wind turbine combinations, and wind power generation, and can solve problems such as being unsuitable for wind power generation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
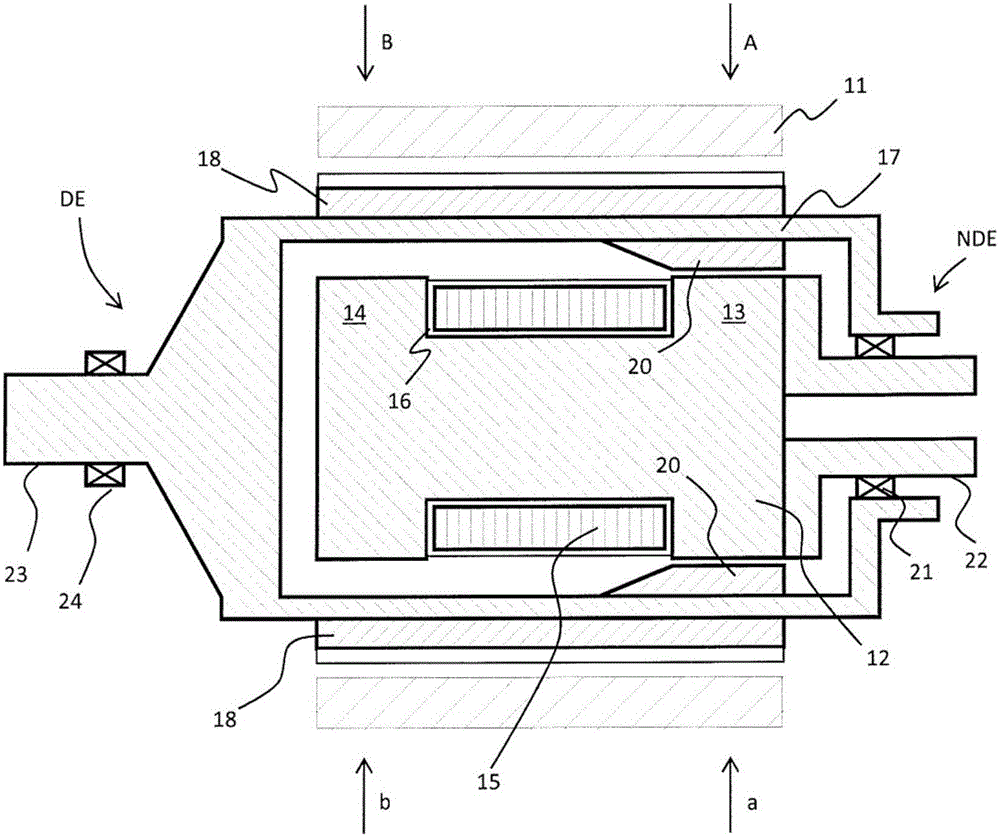
[0018] figure 1 A cross-sectional view of a wind power generator according to an embodiment of the present invention is shown. The generator is cut in half in the longitudinal direction which is the direction of the axis of the generator. figure 1 The stator 11 of the generator is shown, which is the outermost part of the generator. The stator is equipped with stator windings. The stator windings of the generator of the present disclosure may be of any known type of winding. Usually, the stator winding is a multi-phase winding, preferably a three-phase winding. Since the rotor structure of the wind generator of the invention forms magnetic poles comparable to permanently magnetized magnetic poles, the stator windings can have the design normally used in conjunction with synchronous generators. More specifically, the stator winding is formed in the stator core such that the axial length of the stator winding corresponds to the length of the stator core. The stator windings...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com