A Method for Removing Metal Artifacts from CT Images
A technology of metal artifacts and CT images, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the influence of metal artifacts, large amount of calculation, slow speed, etc., and achieve the accuracy of the disease The effect of judging and removing metal artifacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
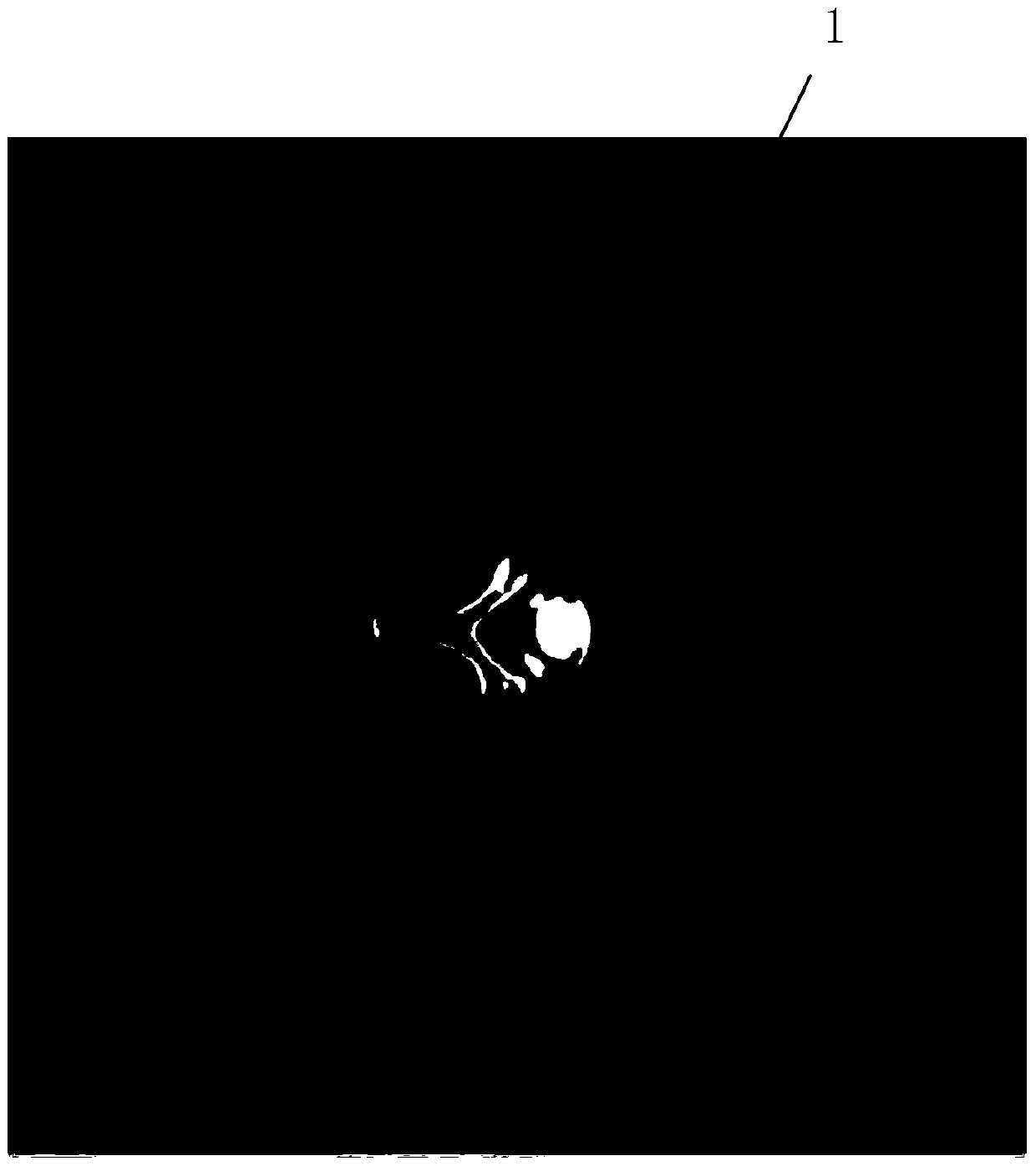
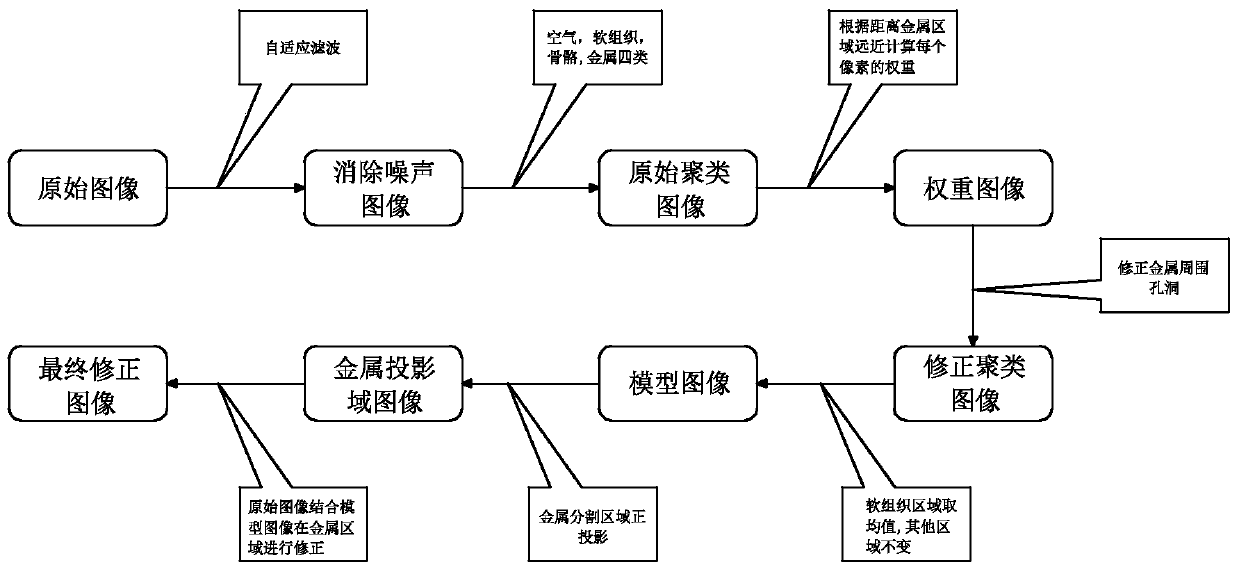
[0051] see figure 1 , a method for removing metal artifacts from CT images, the step of removing metal artifacts comprises:
[0052] A. Image preprocessing: use the adaptive filtering method to remove noise and some streak artifacts in the CT image to obtain the original reconstructed image; the present invention uses median filtering to eliminate part of the noise, and more complex filtering methods can be used in principle to better eliminate noise.
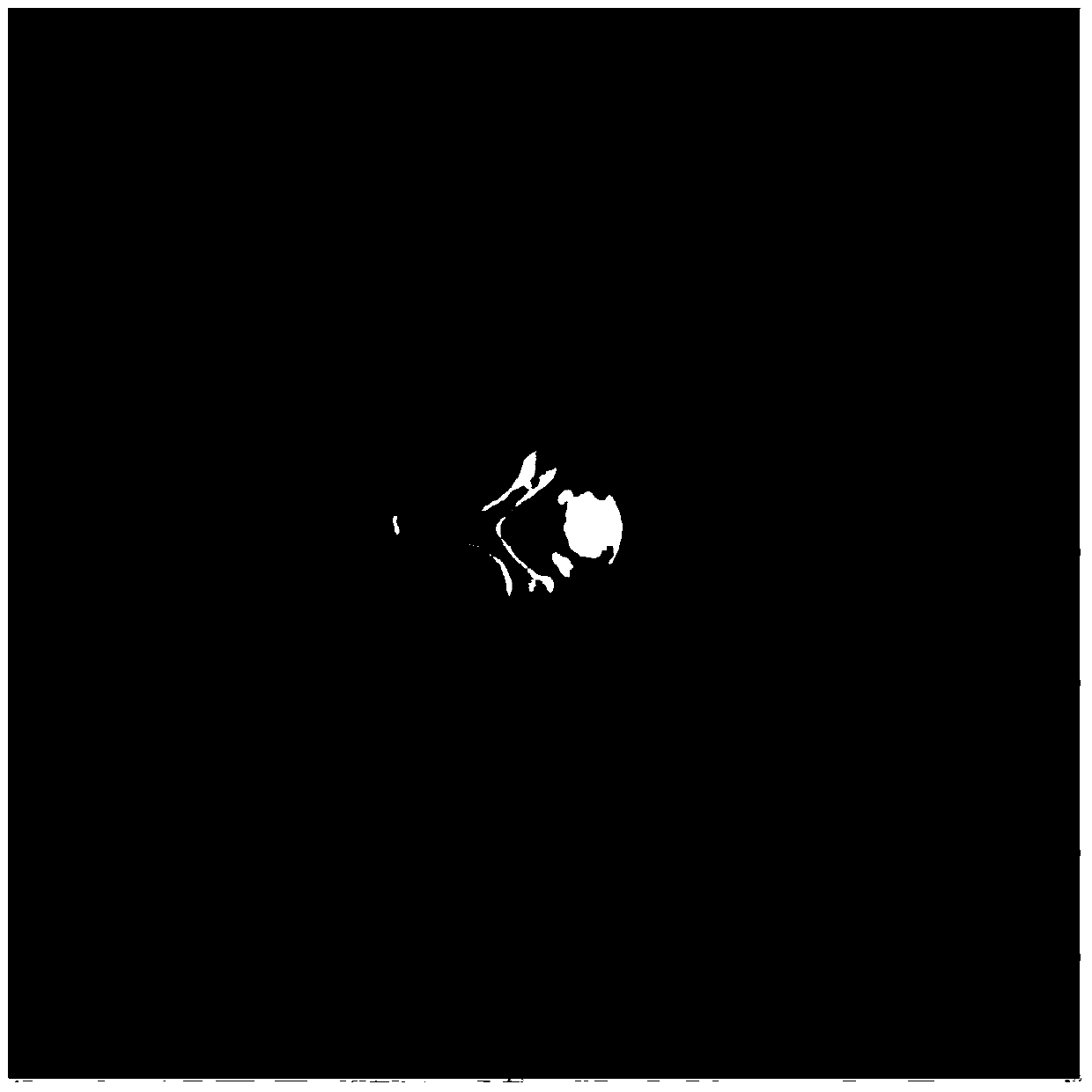
[0053] figure 2 It is the original CT image, and the original CT image is the CT reconstructed image that has not been processed to eliminate metal artifacts. It can basically be equivalent to the image in the traditional sense, but the format may be somewhat different (dicom, etc.). image 3 It is the image after adaptive filtering (because the noise of the original image is very small, the difference between the preprocessed image and the original image is not obvious).
[0054] B. Image segmentation: using a clustering s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com