Automatic focusing method for microscope cell glass slide scanning based on machine learning
An automatic focusing and machine learning technology, applied in microscopes, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of slow calculation speed, slow focusing speed, and large amount of calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0026] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 5 To illustrate this embodiment, a machine learning-based automatic focusing method for scanning microscope cell slides in this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0027] Step 1. Start;
[0028] Step 2. Select spiral scan, serpentine scan or random serpentine scan and the number of areas to be scanned according to the situation of the slide;
[0029] The scanning method is determined by the user according to the number of cells in the slide; if the number of cells in the slide is sparse, choose helical scanning; if the number of cells in the slide is large and the preparation is uniform, choose serpentine scanning; it needs to be completed within three minutes For scanning, choose random serpentine scanning;
[0030] Step 3. Before scanning the whole slide, by controlling the loading platform to move along the XY axis according to the scanning method selected in step 2, randomly sele...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0038] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the specific process of random serpentine scanning in the step two is:
[0039] The random probability P in the random serpentine scan is determined by the number of areas scanned each time, and the formula is:
[0040] p = q A
[0041] Wherein, q is the number of areas to be scanned determined in step 2, and A is the number of scannable areas of the slide;
[0042]In the process of snake-like movement, a probability prediction is performed before each position scan. The probability prediction process is: generate a random number between 0 and 1. If it is less than P, it is selected for prediction, otherwise it is a prediction Not selected, if it is predicted to be selected, scan this area, otherwise skip scanning, and control the loading platform to move along the XY axis to the next image area to be collecte...
specific Embodiment approach 3
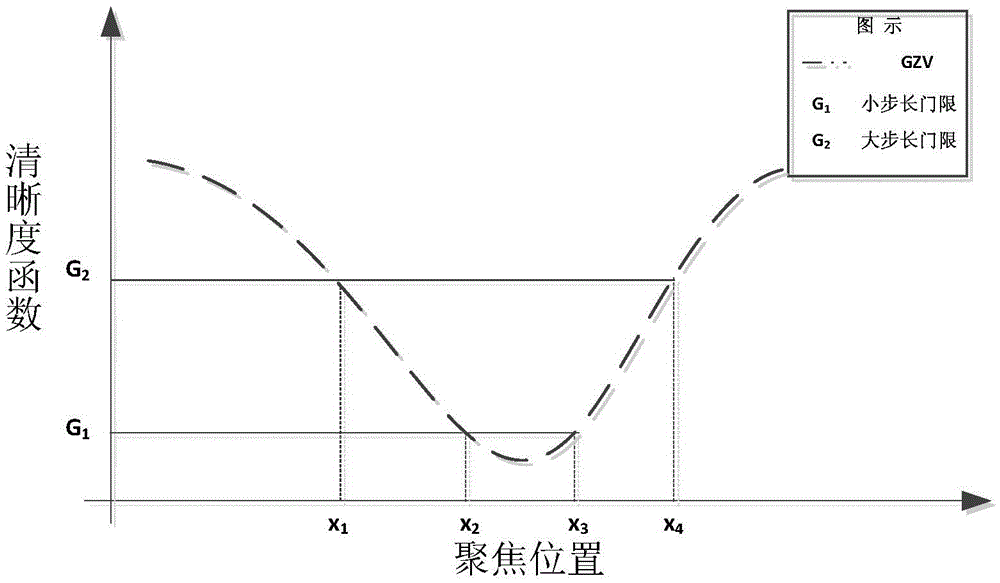
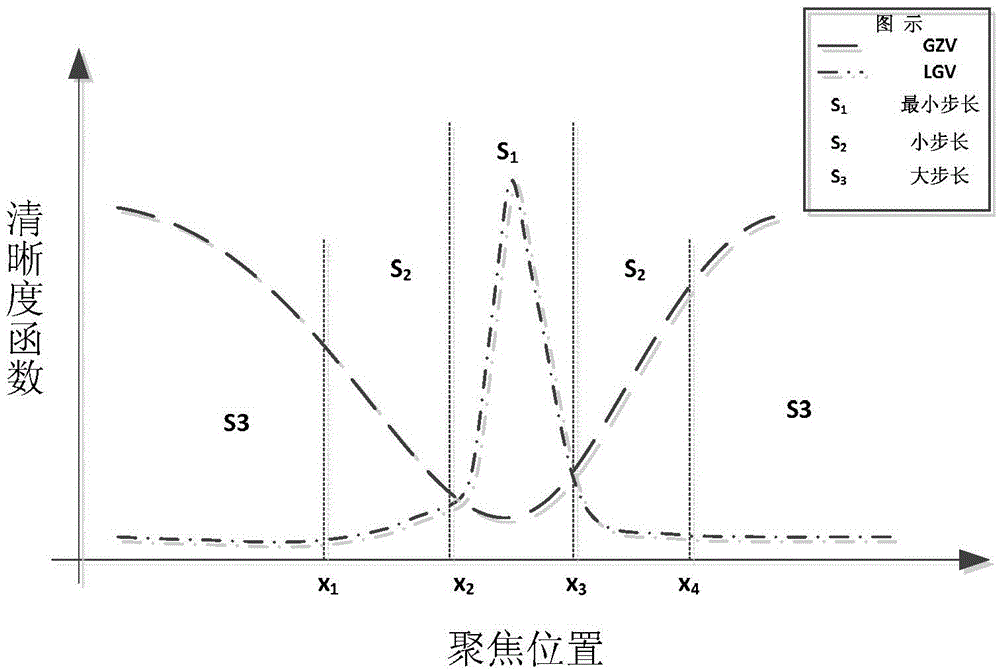
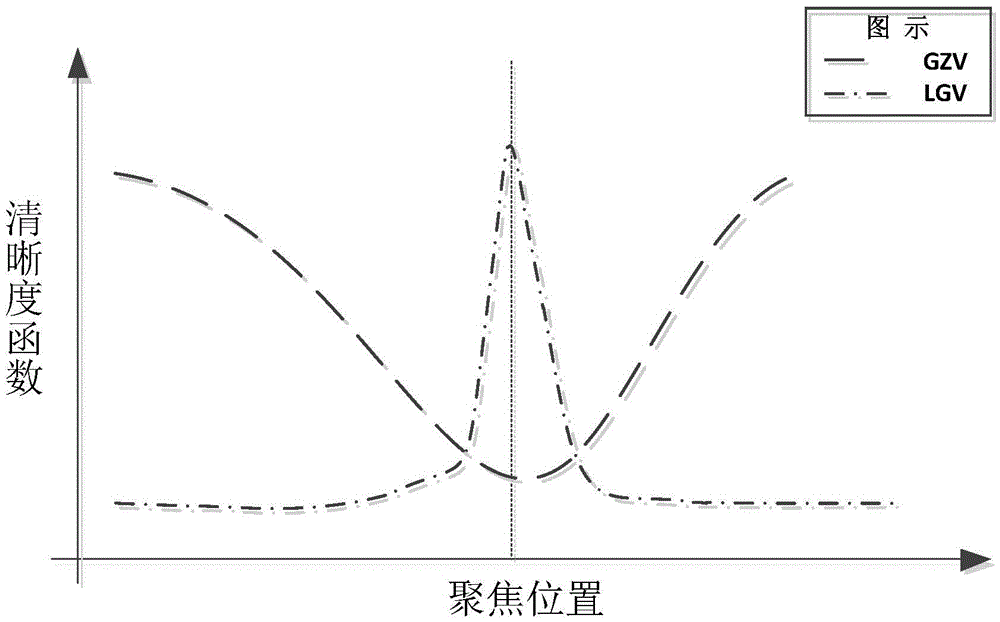
[0044] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that in the step 3, before performing the full slide scanning of the glass slide, the scanning mode selected in step 2 is controlled to move along the XY axis by controlling the loading platform , randomly select 5 areas on the slide to sample, each area gets the clearest photo by focusing, and then calculate the threshold value of the low gray value statistical method (LGV) based on the 5 clearest photos, and focus with variable step climbing method The threshold in the strategy and the three step sizes that control the movement of the loading platform along the Z axis, the three step sizes are: the minimum step size s 1 , small step size s 2 , large step size s 3 ; The specific process is:
[0045] Step 31. By controlling the loading platform to move up and down along the Z axis to the vicinity of the effective image of the slide, set it as the starting position, search u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com