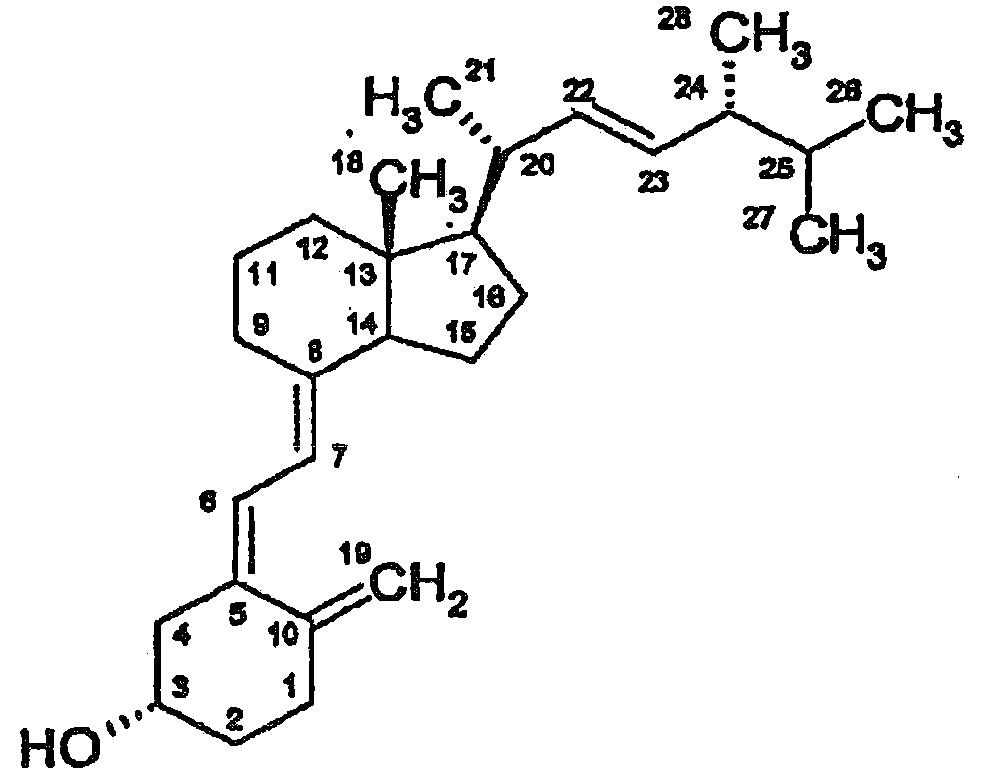
Method and reagent for determining vitamin d metabolites
A technology of vitamins and hydroxyvitamins, applied in biological testing, material inspection products, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1: Preparation of vitamin D releasing agent
[0075] Sodium toluenesulfonate was dissolved in water and adjusted to a final concentration of 1M sodium toluenesulfonate, 100 mM sodium citrate, and 50 mM iron(III) chloride with a stock solution of 1 M sodium citrate and 1 M iron(III) chloride.
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2: Binding of 25-OHD antibody on solid phase
[0077] Antibodies to 25-OH-vitamin D3 or 25-OH-vitamin D2 were diluted to a concentration of 1 μg / ml in Tris salt buffer at pH 8.0. The cavity of a microtiter plate (Maxisorb, Nunc) was coated with 100 μl of antibody dilution, dried at 37°C and left at 4°C until assayed.
Embodiment 3
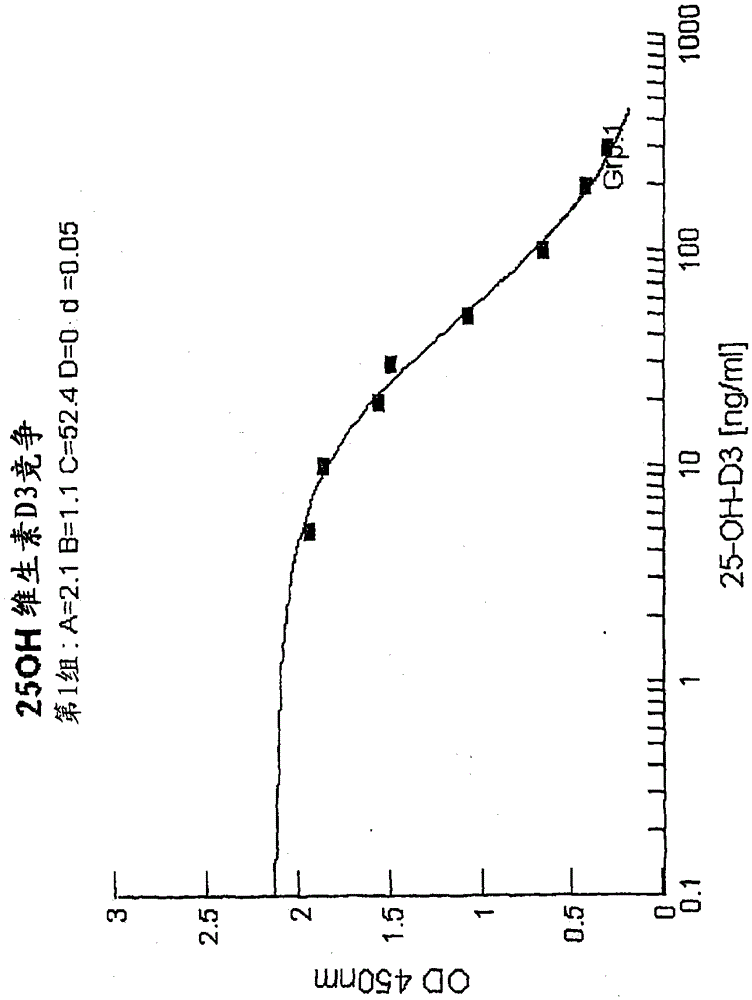
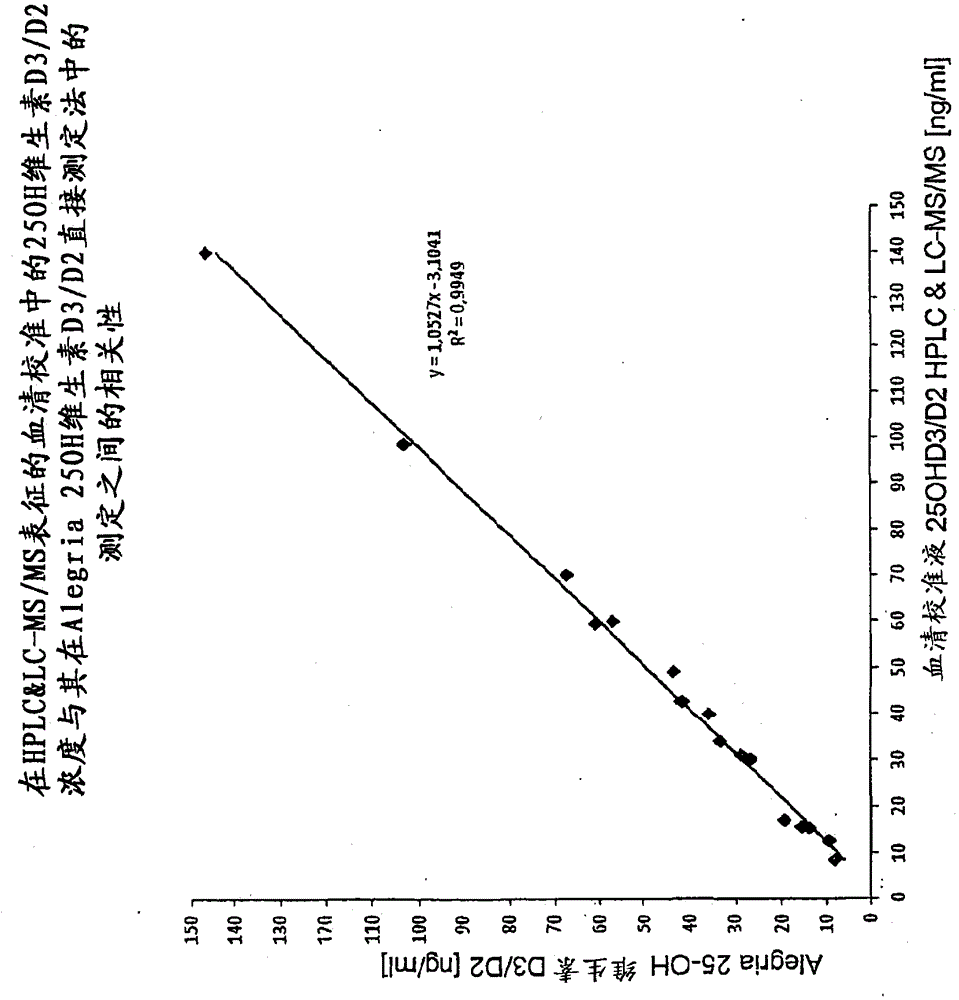
[0078] Example 3: Competitive binding assay
[0079] Serum matrix without vitamin D (Seracon, Seracare Inc.) had been mixed with the established 25-OHD3 concentrations. 80 μl of each concentration series were filled into microtiter plate cavities pre-coated with 25-OHD-biotin tracer and incubated for 5 minutes at RT (20-27° C.) to allow tracer resolubility. Next, 80 [mu]l of the vitamin D releasing agent of Example 1 was added to the sample and mixed. 100 μl of the sample diluted with vitamin D releaser was transferred into the 25OHD-antibody coated cavity and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes. Next, the sample mixture was removed and the cavities were washed 3 times with 200 μl each of wash buffer. The biotin-25OHD tracer bound to the antibody was detected by means of a peroxidase-labeled streptavidin and tetramethylbenzidine (TMB)-chromogenic reaction. Optical density was measured at 450 nm after the substrate reaction was stopped by adding 100 μl of 50 mM phos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com