Method for node matching and resource competition in full-duplex wireless network
A wireless network and resource competition technology, which is applied in the field of node pairing and resource competition, can solve the problems of inability to implement channel measurement and interference assessment, inability to directly exchange information, and high signaling overhead, and achieve reliable and efficient co-channel two-way transmission.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention. It should be understood that these examples are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. In addition, it should be understood that after reading the teachings of the present invention, those skilled in the art can make various changes or modifications to the present invention, and these equivalent forms also fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
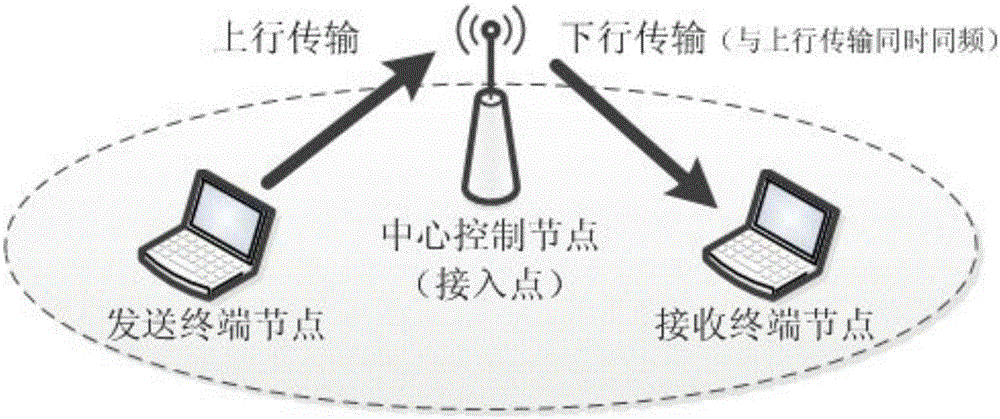
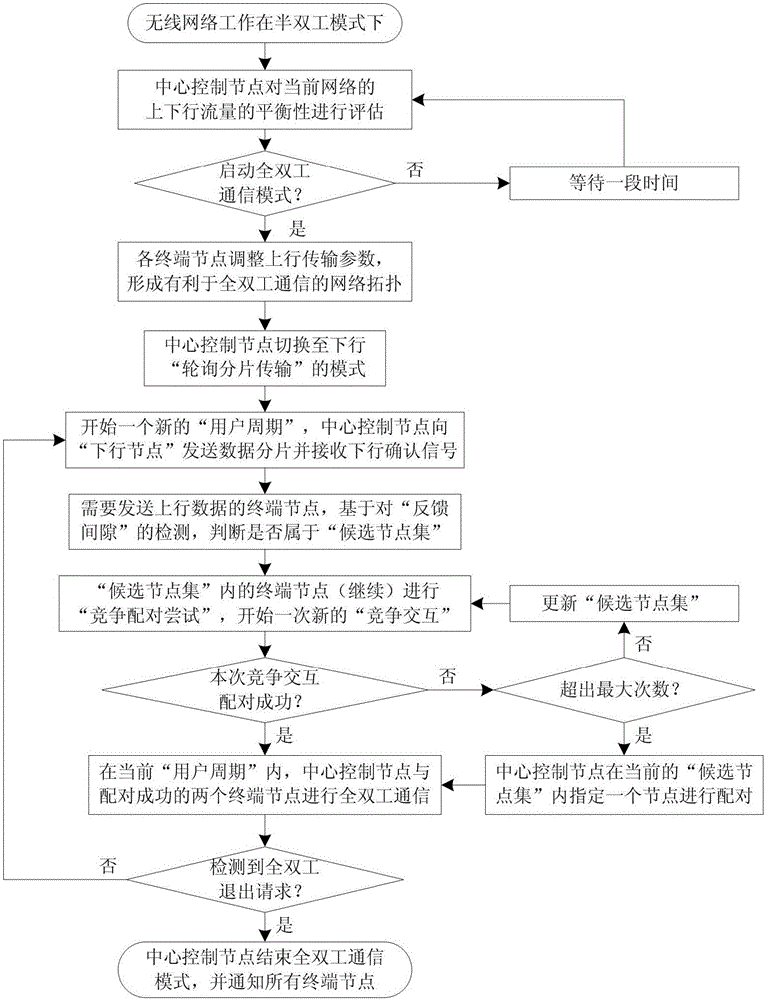
[0033] Embodiments of the present invention relate to a method for node pairing and resource competition in a full-duplex wireless network. The working scenario is an asymmetric full-duplex wireless network, such as figure 2 As shown, the so-called non-peer full-duplex wireless network specifically refers to a multi-user communication system composed of a full-duplex central control node (or access point) and multiple half-dup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com