Primer and method for detecting XRCC1 gene polymorphism
A technology for gene polymorphism and amplification primers, which is applied in the field of primers for detecting XRCC1 gene polymorphisms, can solve the problems of lack of specificity and high sensitivity, and achieve the effects of good specificity, high sensitivity and improved detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 Primers
[0020] The inventor designed a large number of primers for the gene polymorphism site of XRCC1, and selected primers with good specificity through optimization and comparison of primer reaction conditions. The primers provided by the present invention include PCR amplification primers and SNaPshot PCR primers, and the PCR amplification primers and SNaPshot PCR primers are corresponding. All primer sequences provided by the present invention are compared through UCSC database, and there is no known SNP site.
[0021]
Embodiment 2
[0022] The specificity of embodiment two primers
[0023] The primers provided by the present invention were blasted in UCSC, and the amplified fragment of the XRCC1_R399Q primer was located at chr19: 44055651-44055888, with a length of 238bp. The result is as figure 1 As shown, the amplified fragments of the primers all covered the corresponding detection sites, and there were no other homologous genes.
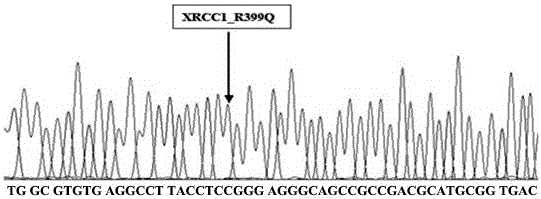
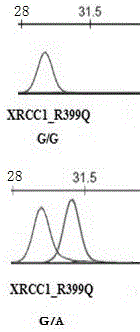
[0024] The PCR amplification primers in Table 1 were used to amplify and Sanger sequence the test samples respectively. The sequencing results showed that the fragments amplified by the primers matched the reference sequence of the XRCC1 gene. The results were as follows: figure 2 shown. Using the SNaPshot PCR primers in Table 1, the SNaPshot method is used for detection, and the results are as follows image 3 shown. from image 3 It can be seen that the relative position of each product peak and the bases incorporated in the sequencing reaction are in line with expec...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 Specificity of the method for detecting XRCC1 gene polymorphism
[0033] The specificity of this assay is defined as the negative coincidence rate. This test defines the detection of the XRCC1_R399Q G / G genotype as a negative result. The SNaPshot method provided by the present invention was used to detect 9 samples, and at the same time, the ARMS method was used for verification. The detection results of the SNaPshot method are consistent with those of the ARMS method, as shown in Table 4. The specificity of this detection method is 100%.
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com