A screening method for analgesic activity polypeptide
An active polypeptide and analgesic technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of restricting the application of ω-MVIIA, complicated modification, unable to solve the C-terminal amidation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1. Discovery of ω-MVIIA knottins by means of bioinformatics
[0025] Conotoxin ω-MVIIA belongs to the knottin family. Knottin, which has the same disulfide bond skeleton as ω-MVIIA, is a polypeptide with potential analgesic activity. In this regard, the present invention conducts bioinformatics analysis on the existing 2193 members in the knottin database (the KNOTTIN database, http: / / knottin.cbs.cnrs.fr), and finds that 1574 members have the same The disulfide bond backbone (see figure 1), in the present invention, this kind of polypeptide is called ω-MVIIA-like knottin (ω-MVIIA-like knottin). Most of these ω-MVIIA knottins were derived from spiders (775) and cone snails (530), and quite a few were from insects (59), plants (27) and viruses (53). ω-MVIIA knottins from spiders and cone snails are usually neurotoxic, and there are few functional studies on ω-MVIIA knottins from other sources. The functions of insect ω-MVIIA knottins have been defined to involve pheno...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1. Synthesis and identification of the housefly phenol oxidase inhibitor MdPOI gene
[0039] According to the protein sequence of the housefly phenol oxidase inhibitor MdPOI (SEQ ID NO.4, GenBank: P81765), its gene sequence was deduced, and the codons of the MdPOI gene were optimized according to the codon usage frequency of Escherichia coli. The sequence of the MdPOI gene is SEQ ID NO.3.
[0040] The MdPOI gene was synthesized by chemical method (Shanghai Jierui Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), after BamHI / HindIII double enzyme digestion, it was connected into the prokaryotic expression vector pET-32a that had been digested by the same enzyme, and the recombinant plasmid pET-32a-MdPOI was verified by DNA sequencing (See figure 2 B).
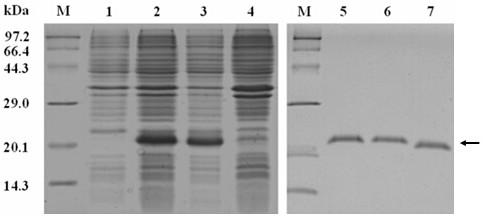
[0041] 2. Expression and purification of recombinant MdPOI
[0042] The correct recombinant plasmid pET-32a-MdPOI was introduced into the competent cells of Escherichia coli Origami (DE3) strain by heat shock method, and the genetically engi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com