Layered mode decision method used for scalable video coding
A coding mode and video coding technology, applied in digital video signal modification, electrical components, image communication, etc., can solve the problem of rational use of key frame information, poor performance of fast SVC coding system, lack of coding mode correlation model, and lack of coding layers Correlation Models etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
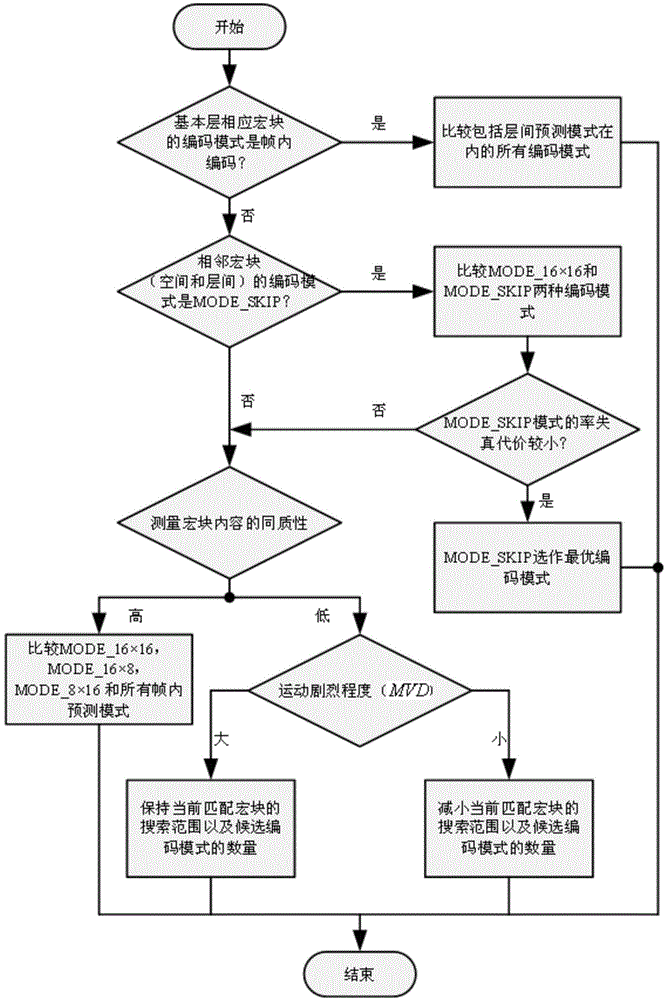
[0027] Specific implementation mode 1: A hierarchical mode decision-making method for scalable video coding in this implementation mode is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
[0028] Step 1. Define the correlation between the coding modes of the base layer and the enhancement layer; that is, when the coding mode of the base layer macroblock is MODE_SKIP, in the enhancement layer, the coding mode of the macroblock corresponding to the base layer macroblock is also MODE_SKIP Probability; in the present invention, it is applicable to the situation that the scaling coefficient of the enhancement layer is 2 for the base layer, that is, the length and width of the enhancement layer macroblock are 2 times of the base layer macroblock; wherein, the base layer macroblock is in the enhancement layer The positional relationship of the corresponding macroblock is as follows figure 1 shown;
[0029] Step 2. For video sequences with different motion intensity and im...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0054] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step 1, the formula for defining the correlation Mode correlation between the coding modes of the base layer and the enhancement layer is:
[0055]
[0056] Among them, MB B&E_SKIP is the number of macroblocks whose encoding mode is MODE_SKIP in both the base layer and the enhancement layer; MBB_SKIP is the number of macroblocks whose encoding mode is MODE_SKIP in the base layer. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0057] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in step three, the coding mode correlation Mode correlation between the current macroblock and the spatially adjacent macroblocks of the current macroblock is defined as formula (2):
[0058]
[0059] Among them, MB C&N_SKIP is the number of macroblocks whose encoding modes are both MODE_SKIP for the current macroblock and the spatially adjacent macroblocks of the current macroblock; MB N_SKIP is the number of adjacent macroblocks whose encoding mode is MODE_SKIP. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com