Method and system for correcting incident light fluctuations in absorption spectroscopy
A technology of absorption spectroscopy and incident light, applied in the field of absorption spectroscopy, which can solve problems such as low frequency modulation sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
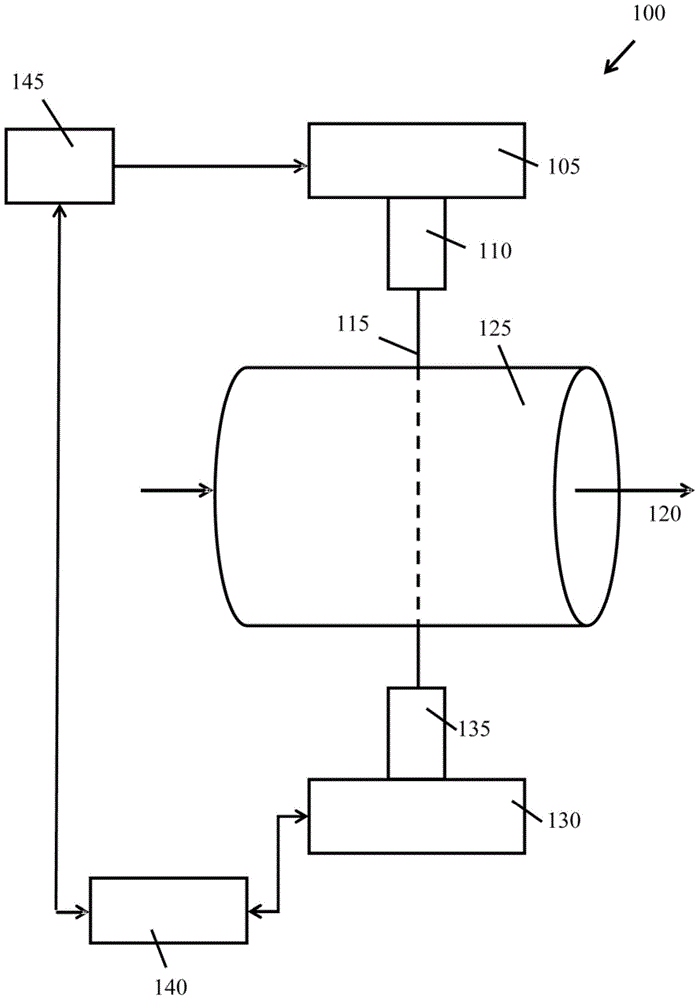
[0127] Embodiment 1: A method for correcting the intensity fluctuation effect of incident light in an absorption spectrum system, comprising steps:
[0128] Controlling the light source to emit wavelength-modulated beams;
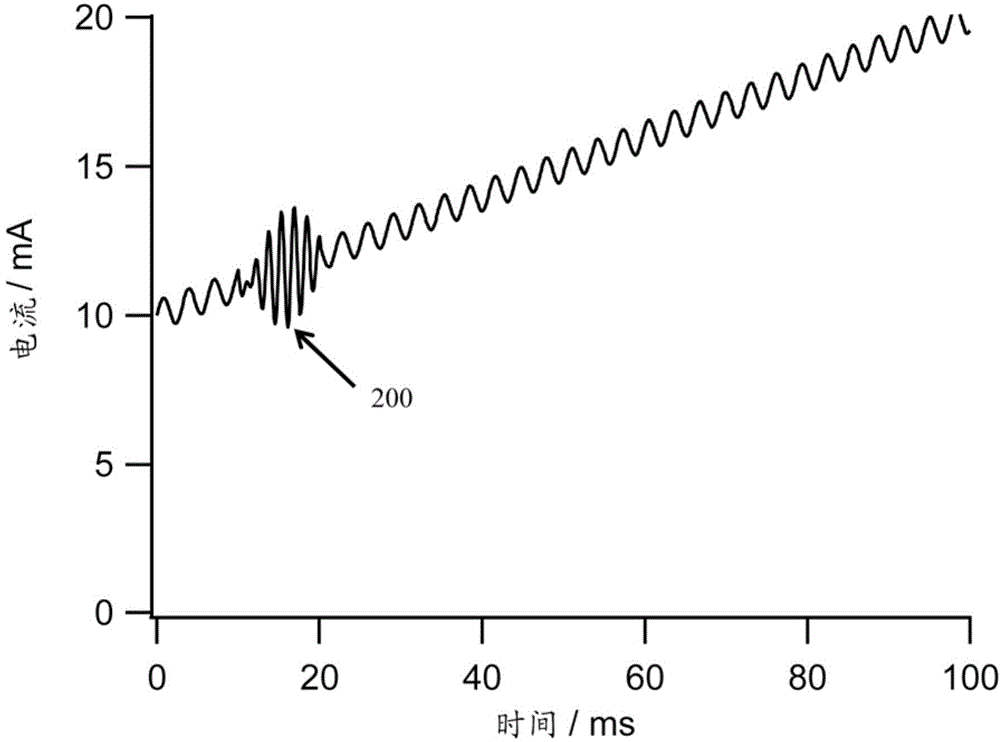
[0129] applying at least one modulation burst signal to modulate the wavelength modulated beam and / or to modulate a separate beam synchronized with the wavelength modulated beam, the at least one modulated burst signal being a cone signal modulation;
[0130] detecting the one or more modulated light beams after transmission through the sample medium;
[0131] processing the one or more detected beams to obtain at least one detected burst signal and measuring the absorption effect of the one or more measured objects, wherein the processing comprises combining the at least one detected burst signal with an applied at least one A modulated burst signal is compared to determine incident light intensity fluctuations separated from the absorption effect of one ...
Embodiment 2
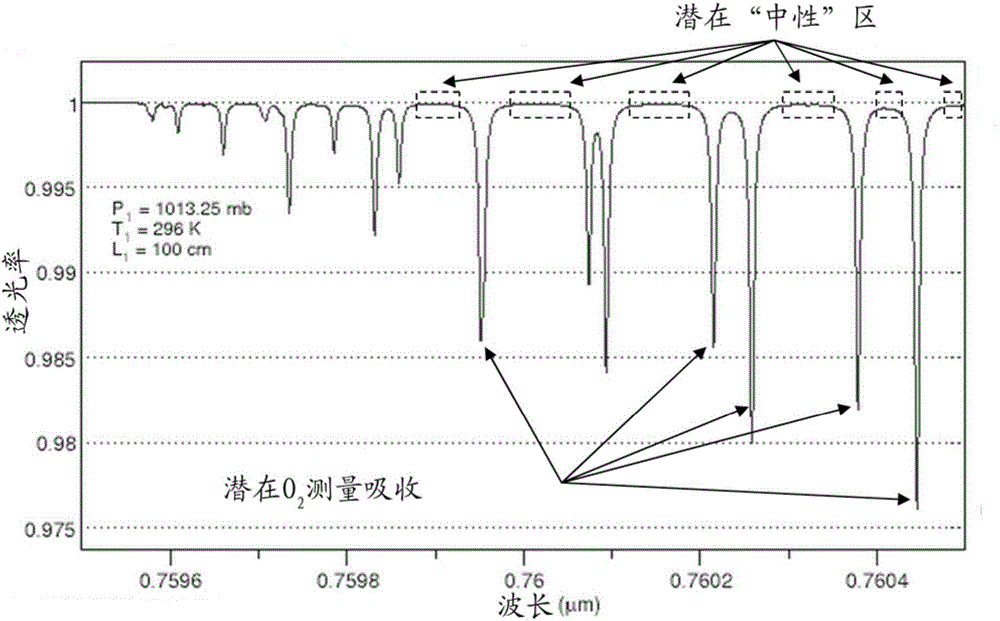
[0132] Embodiment 2: The method of embodiment 1, comprising selecting at least one wavelength region location and / or duration for at least one burst signal to isolate the burst signal from the measured absorption lines of the one or more measured objects.
Embodiment 3
[0133] Embodiment 3: The method of Embodiment 1 or 2, wherein the light source is a tunable diode laser, and the laser's beam is repeatedly scanned at a scan rate with a period T across a range of values for wavelength modulation of the laser's beam bias current, and wherein the duration of the burst signal is less than period T.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com