Audiometric self-testing
A technology of hearing and test results, applied in audiometer, diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, etc., can solve problems such as stress, inaccurate and inaccurate test results, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
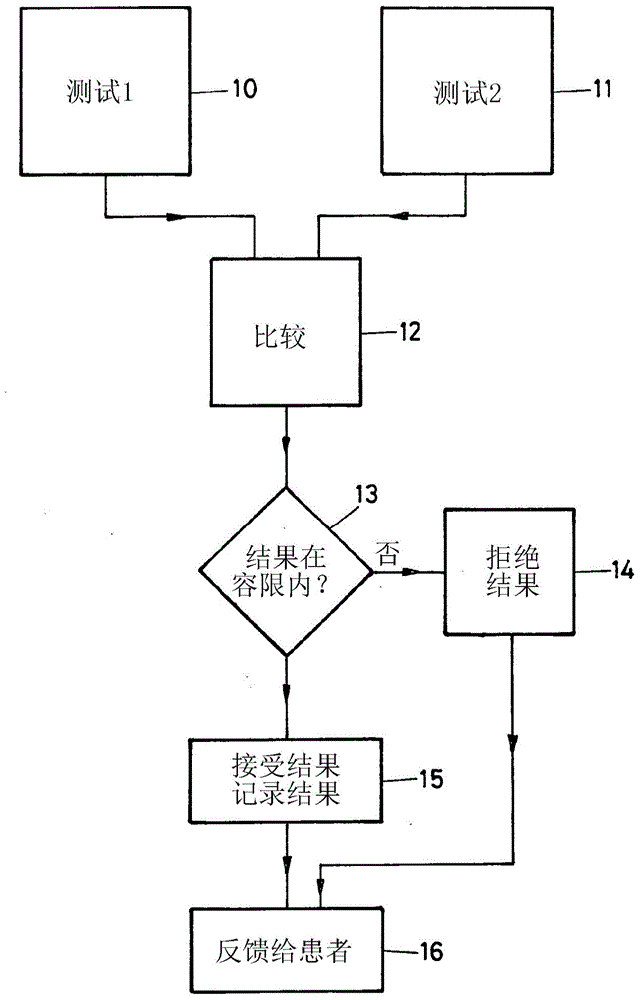
[0028] figure 1 The principle of the invention is schematically illustrated by means of a flowchart.
[0029] In step 10 a first test is performed by the patient. For example, the first test in its simplest form involves the patient adjusting the sound pressure level of an audio stimulus, such as a pure tone or a pure tone presented with masking noise, until the hearing threshold (HL), comfort loudness level (MCL), or uncomfortable Loudness Level (UCL). The patient then selects this sound pressure level.
[0030] Subsequently, in step 11, a second test is performed by the patient in which the same audio stimulus is presented and the same sound pressure level is adjusted and selected in the same way.
[0031] It is advantageous that the patient does not receive any indication of the selected absolute value when performing the first test and the second test, as this may bias the test results.
[0032] Subsequently, in step 12 the value of the sound pressure level selected by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com