An atmospheric pressure jet plasma wet anti-felting method for wool knitted fabrics
A jet plasma, anti-felting technology, applied in physical treatment, textile and papermaking, fiber treatment and other directions, can solve problems such as unresearched, achieve the effect of improving treatment effect, improving dyeing performance, and improving dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Plasma treatment of dry wool textiles.
[0021] After the wool textiles were conditioned for 48 hours at a temperature of 20±1 °C and a humidity of 10±1%, the samples were evenly spread on the operating table, and plasma was applied to both the front and back sides under normal pressure. Treatment, 1 treatment per side. Adjust the parameters of the plasma generator: the discharge power is 150 W, the processing speed is 12.0 mm / s, the height from the sample to the outlet is 5.0 mm, He / O 2 Controlled at 30.0 / 0.4 L / min.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Plasma treatment of wet wool textiles.
[0024] After the woolen textiles were sealed and placed for 48 h at a temperature of 20±1 °C and a humidity of 98±1 % for balanced humidity adjustment, the samples were evenly spread on the operating table, and both the front and back sides were tested under normal pressure. Plasma treatment, 1 treatment per side. Adjust the parameters of the plasma generator: the discharge power is 150 W, the processing speed is 12.0 mm / s, the height from the sample to the outlet is 5.0 mm, He / O 2 Controlled at 30.0 / 0.4 L / min.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Plasma treatment of water-soaked wool textiles.
[0027] Soak the wool textile in distilled water, place it in a sealed place at a temperature of 20±1°C for 48 hours to balance the humidity, spread the sample evenly on the operating table, and conduct plasma on both the front and back sides under normal pressure Treatment, 1 treatment per side. Adjust the parameters of the plasma generator: the discharge power is 150 W, the processing speed is 12.0 mm / s, the height from the sample to the outlet is 5.0 mm, He / O 2 Controlled at 30.0 / 0.4 L / min.
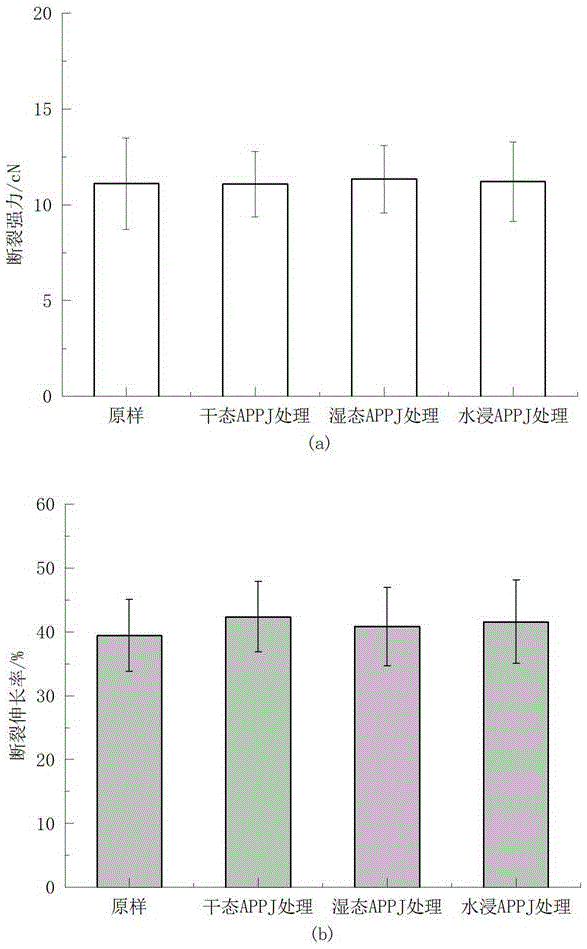
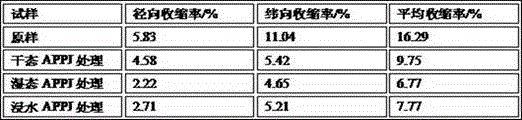
[0028] Implementation effect of the present invention.
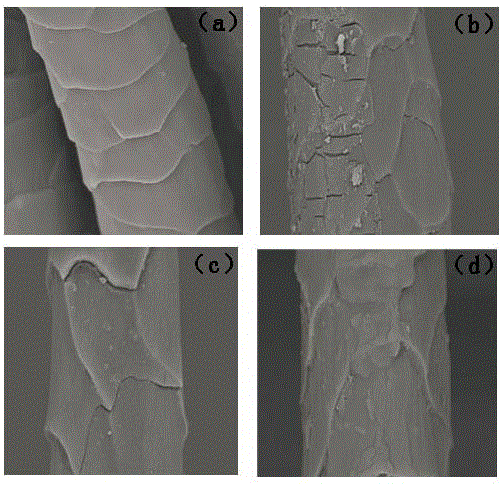
[0029] (1) Treat the microscopic morphology of the wool surface
[0030] For samples with different moisture contents processed according to Example 1, Example 2 and Example 3, use a scanning electron microscope (JSM-5600LVModel, Japan Electron Optical Company) to carry out microscopic morphology analysis on the surface of wool fibers before and after APPJ treatment. Aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com