Rapid analysis method of high-content harmful element in blast furnace iron material
A technology for rapid analysis of harmful elements, applied in the field of spectral analysis, can solve the problems of limited blast furnace operation rate, difficulty in collecting high standard samples, and large demand for dissolution reagents, so as to improve blast furnace operation level and production technical and economic indicators, and solve complex problems Matrix effect, the effect of eliminating mineral effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
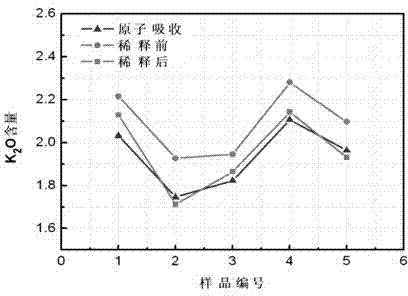
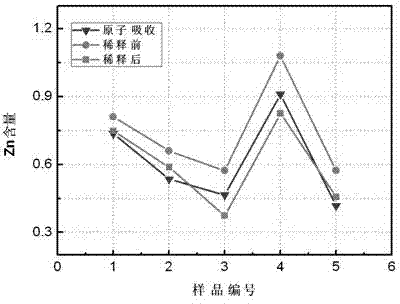
[0031] 1. The present invention determines the optimal instrumental analysis conditions by selecting the optical and electrical conditions for each element, deducting background interference and spectral line interference, as shown in Table 2.
[0032] The equipment used in the present invention is the S8 Tiger type wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer of Bruker Company, with a power of 3KW, a maximum voltage of 60KV, and a maximum current of 150mA.
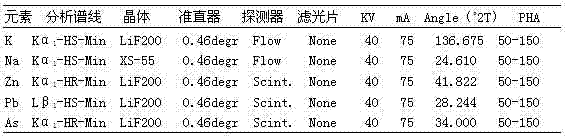
[0033] In order to accurately analyze harmful elements in blast furnace iron materials, it is necessary to analyze spectral lines, crystals, collimators, detectors, filters, voltages, currents, peak angles, etc. of K, Na, Zn, Pb, and As elements. Instrument conditions are selected.
[0034] (1) Selection of electrical conditions: Since K, Na, Zn, Pb, and As elements are trace elements in iron ore, the X-ray...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com