A method for allocating node frequency in ad Hoc network
A frequency allocation and allocation method technology, applied in network topology, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as interference, frequency dissimilarity, and inability to be similar, so as to reduce interference, meet restrictive conditions, and ensure communication quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
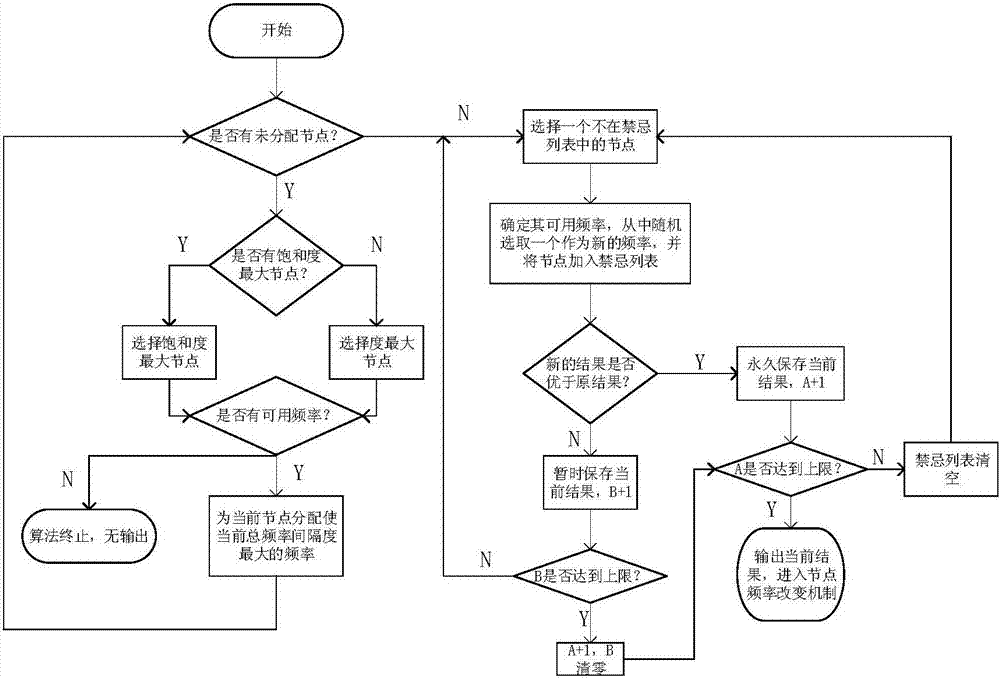
[0023] This embodiment includes the following steps:
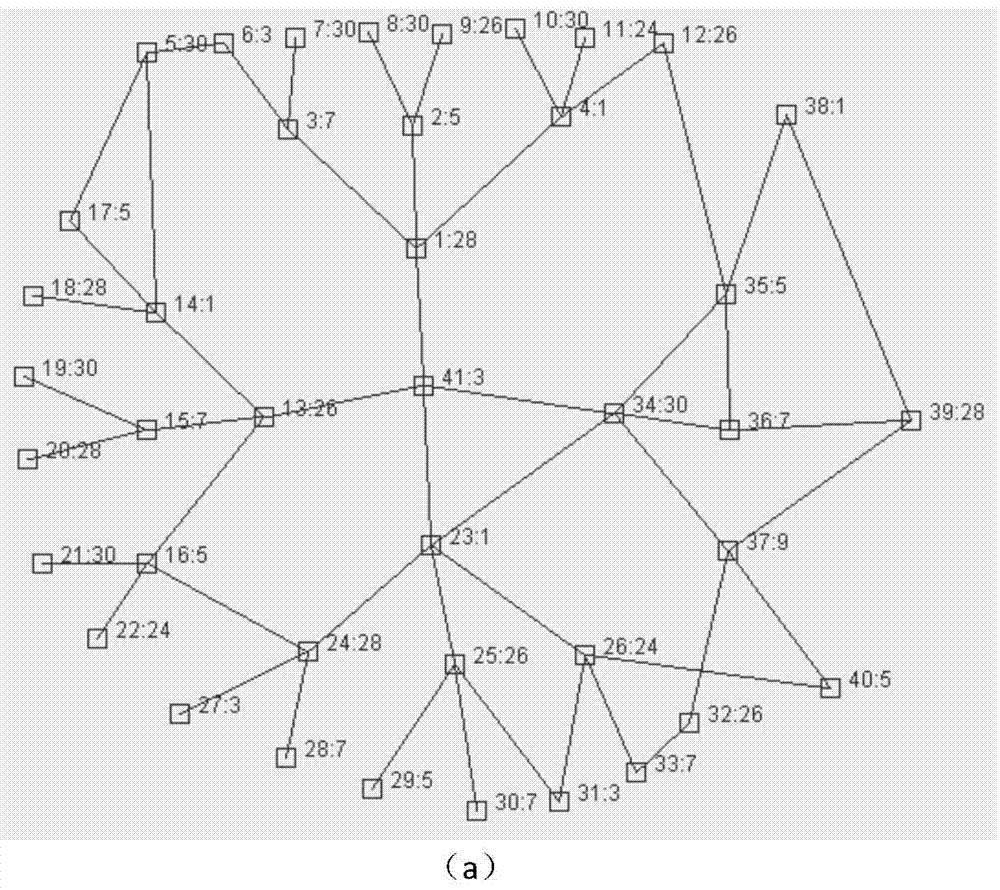
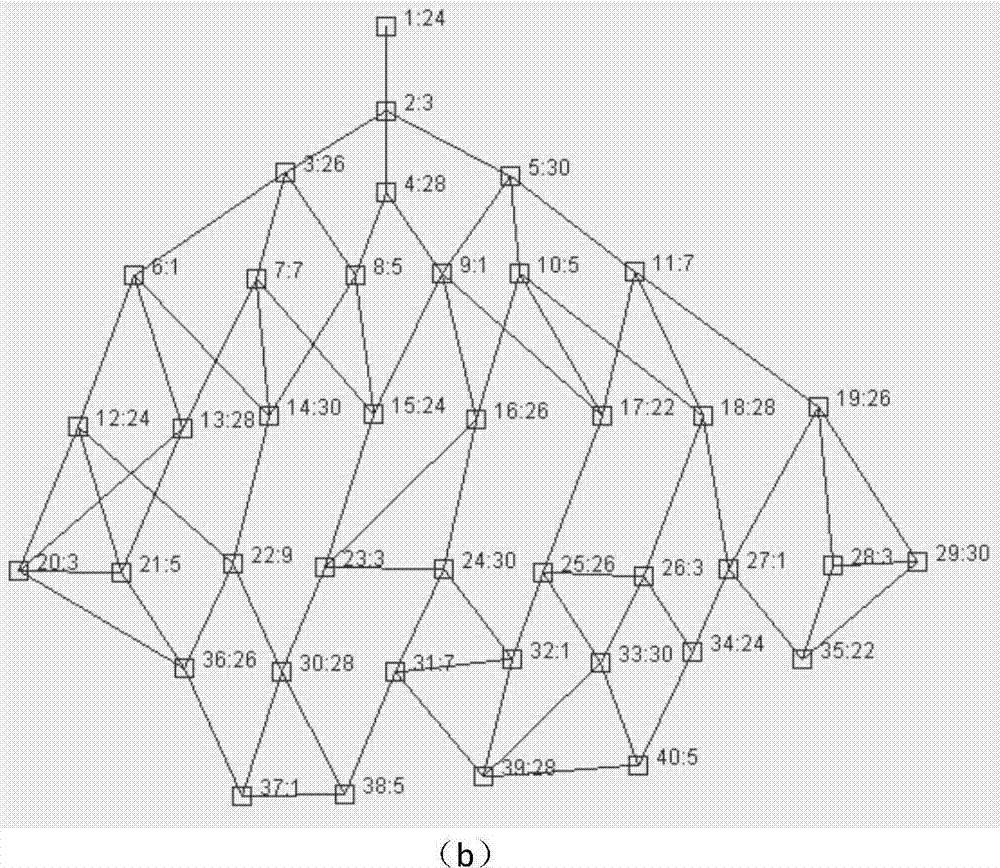
[0024] In the first step, the "interference graph" of the Ad Hoc network is obtained, represented by G(V, E). In this embodiment, the total number of nodes is 40, and each node has a maximum of 4 neighbors. Start to execute the algorithm, the whole flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown. Select the next node to be assigned a frequency, as follows: if there is no node with an unassigned frequency, go to the third step; otherwise, select the node with the largest saturation in the current situation (the node with the largest saturation refers to the current unallocated frequency node with the most assigned frequency neighbors). If there are several nodes with the same degree of saturation, select the node with the largest degree (the node with the largest degree refers to the node with the most neighbors among the nodes without frequency allocation), and enter the second step. Note that the node selected according to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com