A device io queue method based on atomic operation
An atomic operation and queue technology, applied in the field of computer system software programming, can solve problems such as excessive overhead, complex and impractical implementation of atomic queues, saving computing resources and speeding up data input and output.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
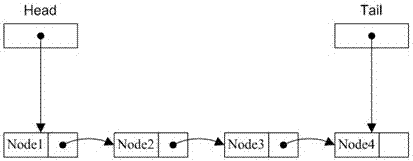
[0021] as attached figure 1 Shown: When performing enqueue operation, first use atomic swap to replace the tail pointer with a pointer to the new node, and take out the pointer of the original tail node at the same time. Then point the link pointer of the original end node to the new end node. If the original tail pointer is empty, directly point the first pointer to the new node, indicating that the new node is the first node in the queue, and it also means that the producer who submitted the new node has obtained control of the queue, that is, the producer It can be transformed into a consumer to take out nodes from the queue. Because the atomic operation guarantees the order of submission, when there are multiple producers enqueuing at the same time, only one producer can gain control.
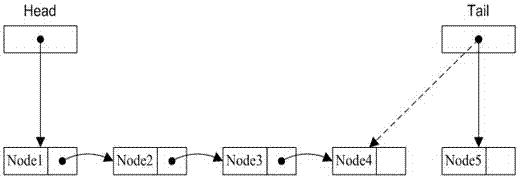
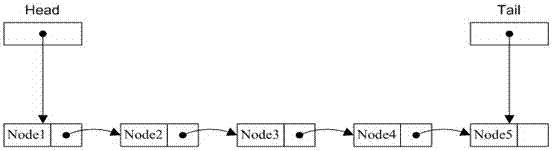
[0022] as attached figure 2 Shown: Use the atomic swap operation to replace the tail pointer pointing to the 4th node with the pointer pointing to the 5th node, and take out the pointer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com