Efficient nitrogen-fixing alfalfa rhizobium strain and method for screening molecular marker
A method of alfalfa and molecular markers, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve high yield, low nitrogen fixation efficiency, mixed types of rhizobia strains, etc., and achieve good affinity , Increased planting yield and good adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Sampling and separation and purification: For the alfalfa planted in the surrounding areas of Huanghua, Cangzhou, Hebei, the plants with good growth and robustness were selected, and the root nodules were sampled at the early flowering stage of the alfalfa. At each sampling location, 5-point sampling method was used. Sampling, the sampling area of each point is 1m 2 , each plant selects plump and pink root nodules, selects 3 large root nodules, selects two locations, selects 45 root nodules in each location, and obtains 90 root nodules in two locations;
[0026] To isolate and purify bacterial strains from selected root nodules, the specific steps are:
[0027] (a) Select a complete and undamaged root nodule and fully soak it in sterile water;
[0028] (b) Nodule surface disinfection: 95% ethanol for 3 minutes—0.5% hypochlorous acid for 3 minutes—sterile water rinse 6-8 times;
[0029] (c) Separation by streaking on the plate: crush the sterilized root nodule wi...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Identification of embodiment 2 strains
[0062] The preservation name of the strain provided by the present invention is Sinorhizobium meliloti 729-2-4, the preservation unit is CGMCC, the preservation number is CGMCC No.9755, and the preservation date is October 10, 2014. The address of the depository unit is No. 3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[0063] The high-yielding Rhizobium alfalfa strain provided by the present invention has an optimum growth temperature of 28°C and is an aerobic culture. The colony on the YMA medium is translucent, milky white, round, thin at the edge, thick in the middle, and thin. The time is 48-72 hours, the colony size is 3-5mm; the bacterial cell is rod-shaped, with strong refractive hydroxy fatty acid particles, accounting for 1 / 3 of the cell volume, slightly rounded at both ends, and the size is 2-3μm×3- 5 μm, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram stain is red.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The application of embodiment 3 new bacterial strains
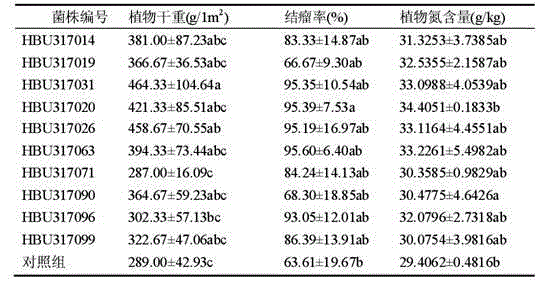
[0065]Experimental method: inoculate the bacterial strain obtained in Example 1 of the present invention onto alfalfa planted in the field (around Huanghua), its inoculation method, inoculation area and sampling detection method are shown in step 8 of Example 1; meanwhile, adopt the same The experimental conditions were inoculated with American strain (AM185H2) and Australian strain (AU128) as a comparative experiment.
[0066] Experimental results:
[0067] Table 4 Application results of strains
[0068]
[0069] Note: The Tukey test is used, a b c are different subsets, the above data are the average value of the five-point sampling of the experiment, and three parallel experiments.
[0070] As can be seen from the table, the bacterial strains from Australia and the United States do not have a good effect on improving the yield of alfalfa than the bacterial strains screened by the present invention. It can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com