Synchronous test system based on tame rubidium clock and method thereof for increasing synchronization precision
A technology of synchronous testing and rubidium clocks, which is applied to clocks driven by synchronous motors, synchronization, and instruments using atomic clocks. It can solve the problems of immediate failure of the synchronization function and synchronization accuracy that cannot meet the positioning requirements, and achieve high synchronization accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the drawings:
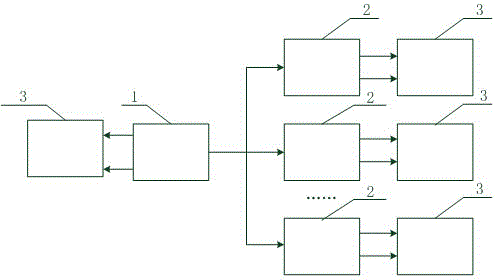
[0026] Such as figure 1 Shown: The synchronization test system based on the tamed rubidium clock includes the master base station synchronizer 1 and the slave base station synchronizer 2. The master base station synchronizer 1 and the slave base station synchronizer 2 respectively give the 10MHz clock signal and the tamed rubidium clock After the stable PPS second pulse signal, connect these two signals with the AIS shore station (3).
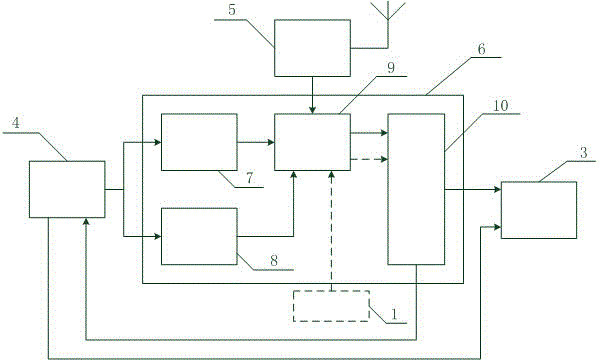
[0027] Such as figure 2 and image 3 Shown: The main base station synchronizer 1 and the slave base station synchronizer 2 are basically the same in structure, mainly composed of rubidium clock 4, GNSS receiver 5 and FPGA chip 6. The slave base station synchronizer 2 needs to be connected to the master base station synchronizer 1 to give The FPGA chip 6 is mainly composed of a frequency dividing module 7, an up-conversion module 8, a counting compariso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com