A nucleic acid aptamer, kit and method for detecting pancreatic ductal carcinoma
A technology of nucleic acid aptamer and pancreatic ductal carcinoma, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, measurement/testing of microorganisms, DNA preparation, etc., which can solve the problems of lack of sensitivity of pancreatic cancer, long antibody preparation cycle, and difficult immunogenicity, etc. problem, to achieve non-immunogenicity, short cycle, high affinity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
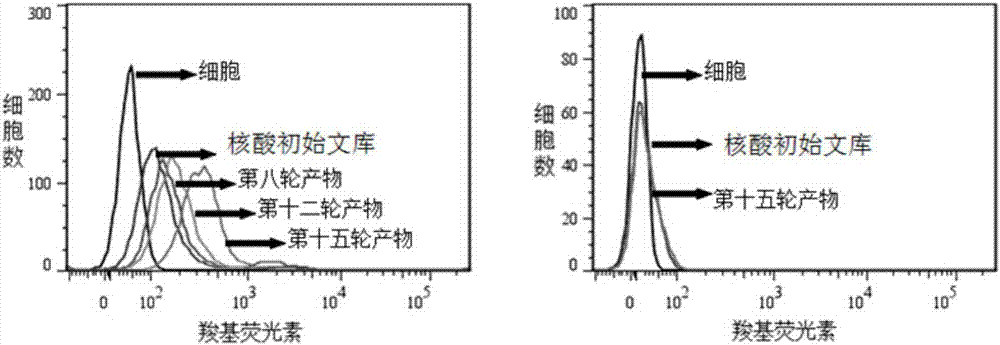
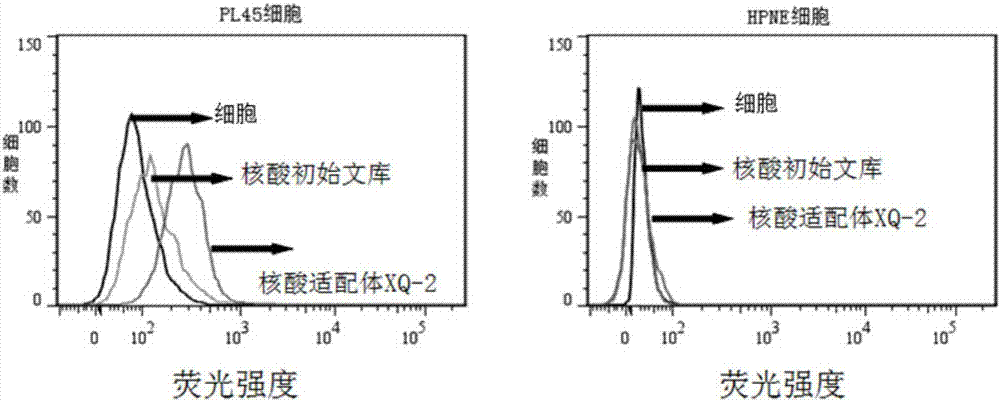
[0038] Example 1: Screening of pancreatic ductal carcinoma cell-specific nucleic acid aptamers
[0039] (1) Design of the nucleic acid library and primers used:
[0040] Random ssDNA library:
[0041] 5'-ACCGACCGTGCTGGACTCANNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNACTATGAGCGAGCCTGGCG-3' (N represents A, T, C and G four bases) (SEQ ID NO.3), that is, the theoretical library capacity of the random single-stranded DNA library is 4 42 DNA;
[0042] Upstream primer: 5'-fluorescein isothiocyanate-ACCGACCGTGCTGGACTCA-3' (SEQ ID NO.4);
[0043] Downstream primer: 5'-biotin-CGCCAGGCTCGCTCATAGT-3' (SEQ ID NO.5);
[0044] (2) Positive screening:
[0045] 2.1 Incubation: Dissolve the above random nucleic acid library with binding buffer (D-PBS, 5mM magnesium chloride), denature at a constant temperature of 95°C for 5 minutes, and quickly put it on ice; then mix it with the cultured and pretreated pancreatic ductal carcinoma cell line PL45 Incubate for 1 hour at 4°C.
[0046] 2.2 Dis...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Screening of pancreatic ductal carcinoma cell-specific nucleic acid aptamers
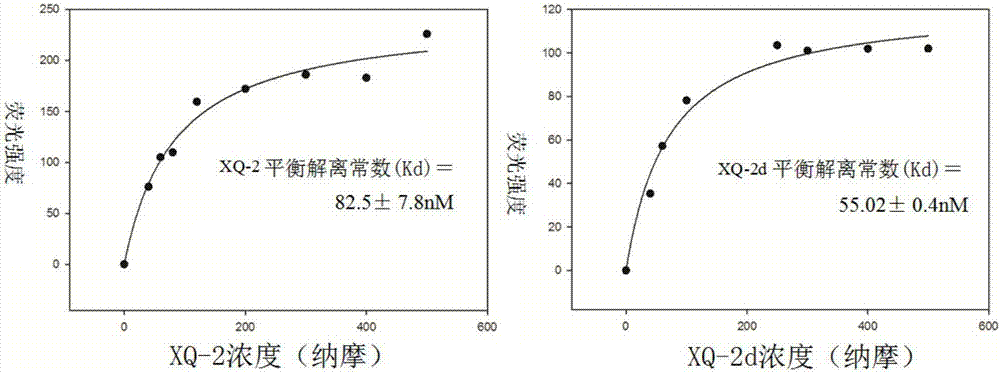
[0058] The obtained nucleic acid aptamers were labeled with fluorescent molecules at the 5' end to make molecular probes, and the molecular probes of 0nM, 20nM, 40nM, 60nM, 80nM, 100nM, 120nM, 140nM, 160nM, 200nM, 300nM, 400nM, 500nM were taken respectively. needle solution, with 3 x 10 5 PL45 cells were incubated on ice for 1 hour, then washed twice with washing buffer, and the fluorescence intensity on the cell surface was measured by flow cytometry. If the cells can bind fluorescently labeled nucleic acid aptamers, plot the fluorescence intensity against the probe concentration, and use the formula Y=BmaxX / (Kd+X) to calculate the equilibrium dissociation constant Kd of the nucleic acid aptamers. The results showed that the equilibrium dissociation constants of the nucleic acid aptamers were all in the nanomolar range.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: Analysis of the stability of nucleic acid aptamer (SEQ ID NO.2) in complete medium
[0060] 3 micromolar fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled nucleic acid aptamer (SEQ ID NO.2) was respectively placed in 200 microliters of DMEM cell culture medium containing 10% fetal calf serum. At different investigation time points, the samples were quickly cooled in dry ice-ethanol and then stored in a -80°C refrigerator. When the samples at all time points were collected, the samples were placed at 4° C., and after they were dissolved, 20 microliters of samples were taken for separation in 4% agarose gel, and then imaging analysis was performed. Such as Figure 4 It can be seen that the nucleic acid aptamer (SEQ ID NO.2) can exist stably in the above medium for 6 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com