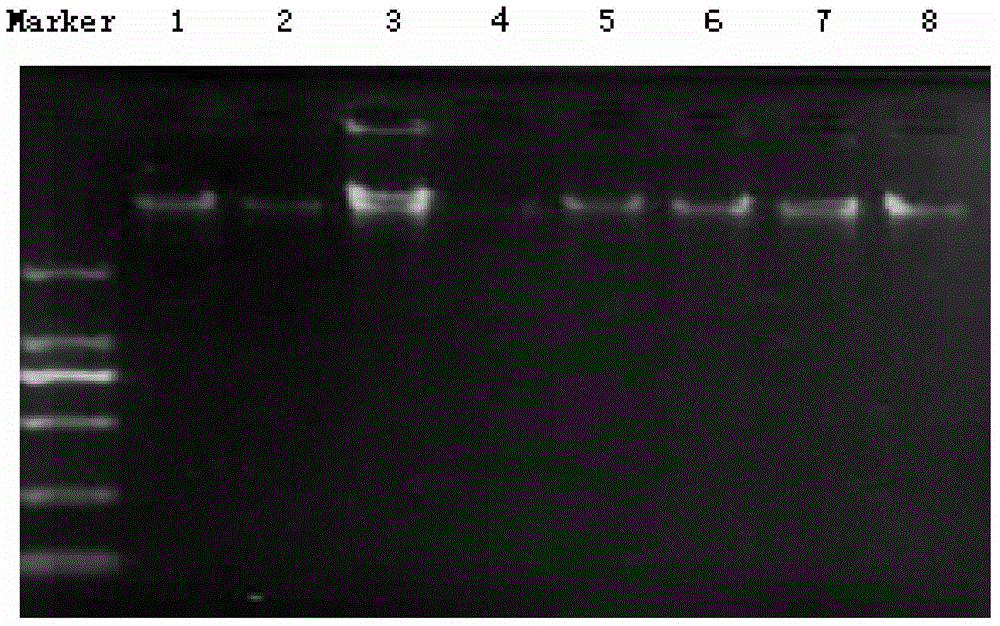
Method for extracting DNA from dry apricot leaf
A leaf and drying technology, applied in the field of DNA extraction, can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining high-quality apricot leaves, affecting PCR amplification, genetic polymorphism analysis research, and great differences in species and content, etc., to improve the extraction purity and yield The effect of high yield, good quality of extracted DNA, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A method for extracting DNA from dry apricot leaves, comprising the following steps:
[0020] (1) Remove the petiole of the apricot leaf, weigh 20 mg of the leaf, add 0.001 g of PVP-40T, add liquid nitrogen, grind the leaf into a fine powder, and add the fine powder to a 2.0 mL centrifuge tube;
[0021] (2) Add 1mL of pre-cooled buffer extract solution, mix well and then ice bath for 15 minutes, invert and mix 2-3 times during the ice bath;
[0022] (3) Centrifuge at 7000g for 10min, discard the supernatant;
[0023] (4) Repeat steps (2) and (3) until the supernatant is not viscous;
[0024] (5) Quickly add 0.8mL of CTAB Buffer preheated to boiling to each tube, mix well, bathe in 65℃ water for 0.5-1h, and shake once every 15min;
[0025] (6) Add 0.01mL 100mg / L RNase, bathe in 37℃ water for 30-60min;
[0026] (7) Take it out and cool to room temperature, add 0.8mL of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol with a volume ratio of 25:24:1 to each tube, store at 4°C, gently i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com