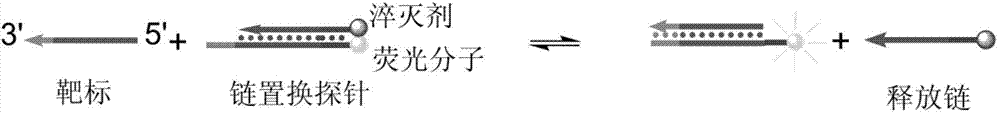Thermodynamic optimization-based high specificity nucleic acid hybridization method
A thermodynamically optimized and highly specific technology, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to fully satisfy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] (1) Design and preparation of probes
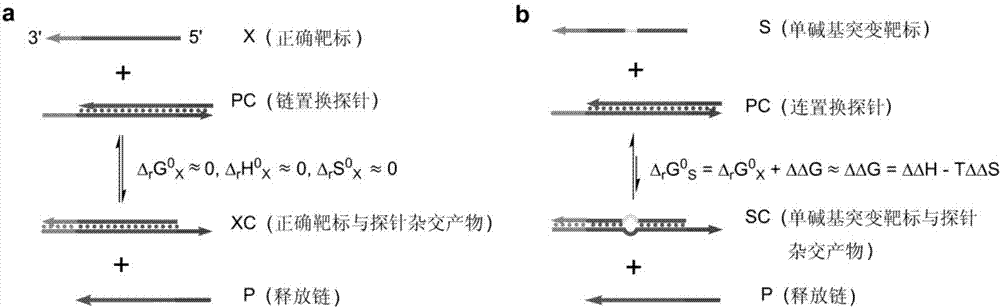
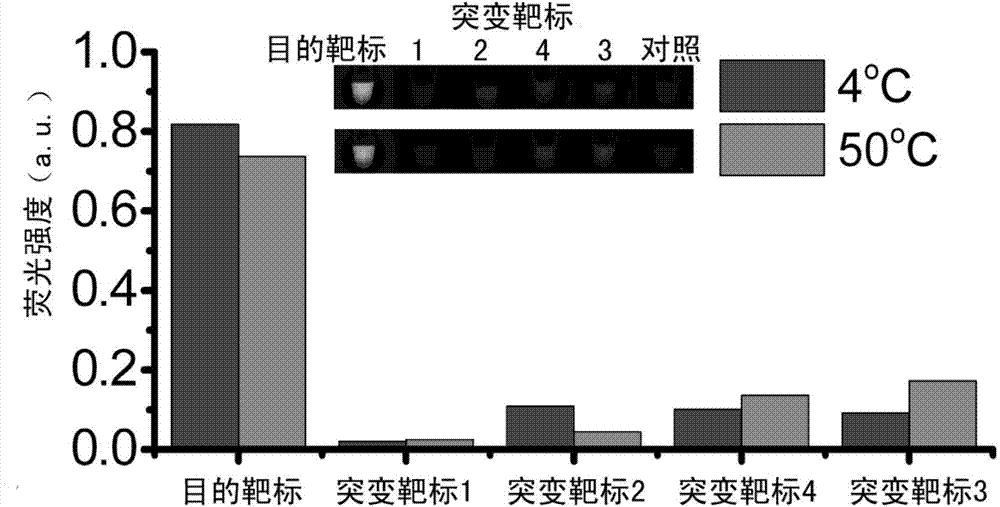
[0073] First, strand displacement probes were designed according to the target microRNA-125 to be detected. The specific design method is to design a nucleic acid single strand that is completely complementary to the target of interest, and then add several bases to one end of the nucleic acid single strand, called the complementary strand. When designing the other strand of the probe, it should be identical to the partial sequence of the target sequence to be detected, which is called the release strand. Adjust the base sequence of certain positions in the probe so that the standard enthalpy of reaction Δ r h 0 and reaction standard entropy Δ r S 0 The value is approximately equal to 0. The designed probes will be synthesized by the company. After the probe sequence is synthesized, the complementary strand and the release strand are mixed and hybridized according to a certain ratio and diluted to an appropriate concentration...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com