Controlling melt fracture in bimodal resin pipe
A melt fracturing, polyethylene resin technology, used in pipes, rigid pipes, molecular entity identification, etc., can solve problems such as surface irregularity, reduced production speed, melt fracture, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
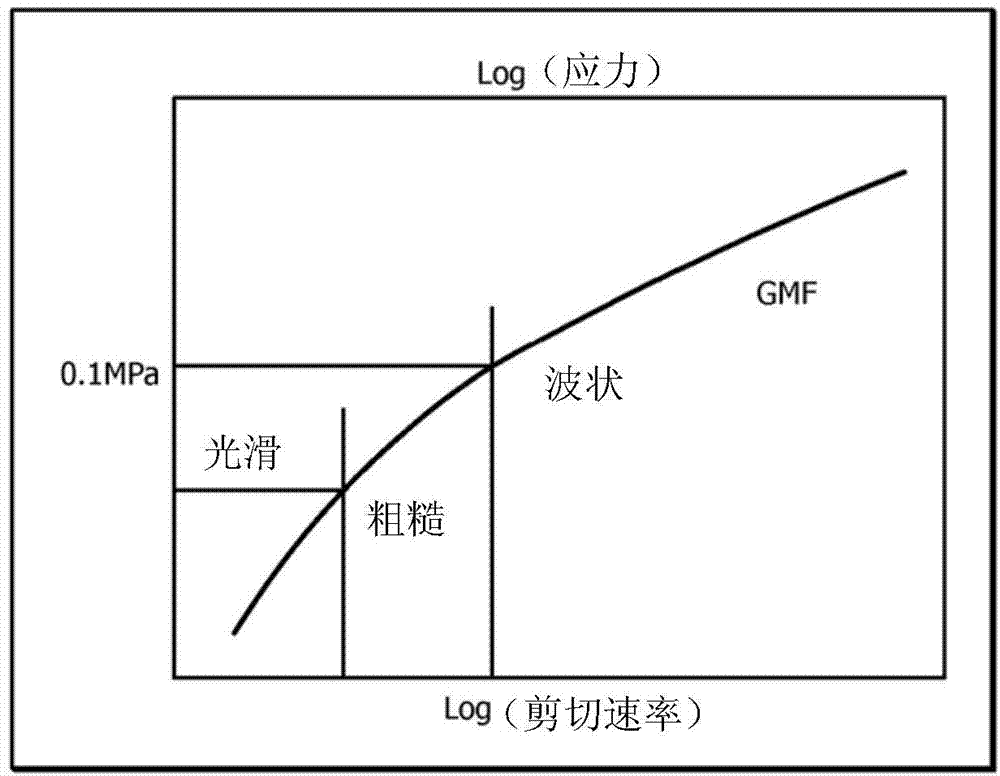
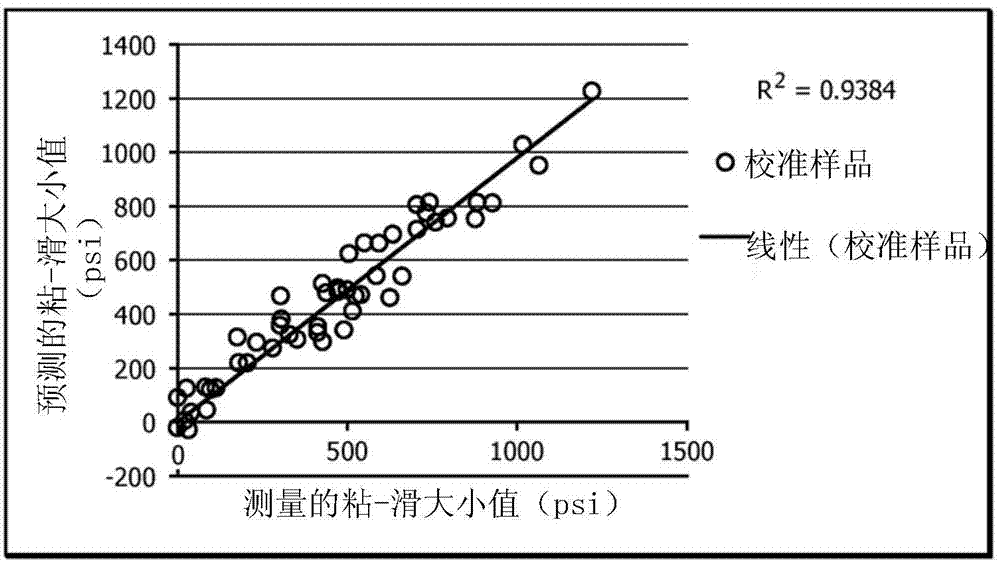
[0127] A first embodiment, which is a method for improving the processing of polyethylene resins, comprises obtaining a plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples; measuring the shear rate of the plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples using capillary rheometry Shear stress as a function of shear rate, where measurements yield values for slip-viscosity magnitude, stress for smooth-to-rough transition, and shear rate for smooth-to-rough transition; Individual multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene resins having a reduced tendency to melt fracture from a slip-stick magnitude greater than about 300 psi, a smooth-to-rough transition stress greater than about 90 kPa, and greater than about 10 s -1 Shear rate characterization of the smooth-to-rough transition.
no. 2 approach
[0128] A second embodiment, which is the method of the first embodiment, wherein each of the plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples comprises a polymer blend.
no. 3 approach
[0129] A third embodiment, which is the method of any one of the first to second embodiments, wherein each of the plurality of multimodal metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene samples includes a high molecular weight component and a low molecular weight component.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The melt flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com