Method for producing hydrogen by reforming of methane steam
A technology for producing hydrogen from methane steam and reforming, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrogen, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as low purity, low hydrogen production efficiency and yield, poor conversion capacity and cycle stability of adsorbents, etc. Achieve the effects of expanding the temperature range, promoting the hydrogen production reaction, and excellent cycle stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
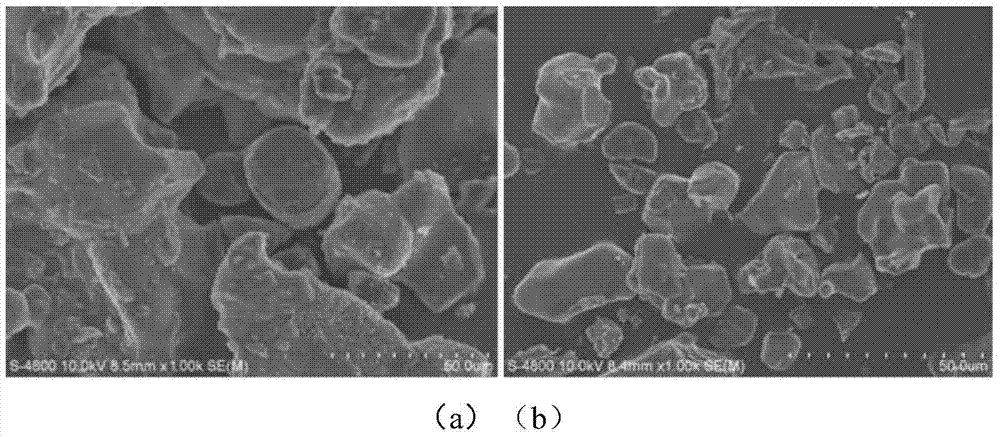
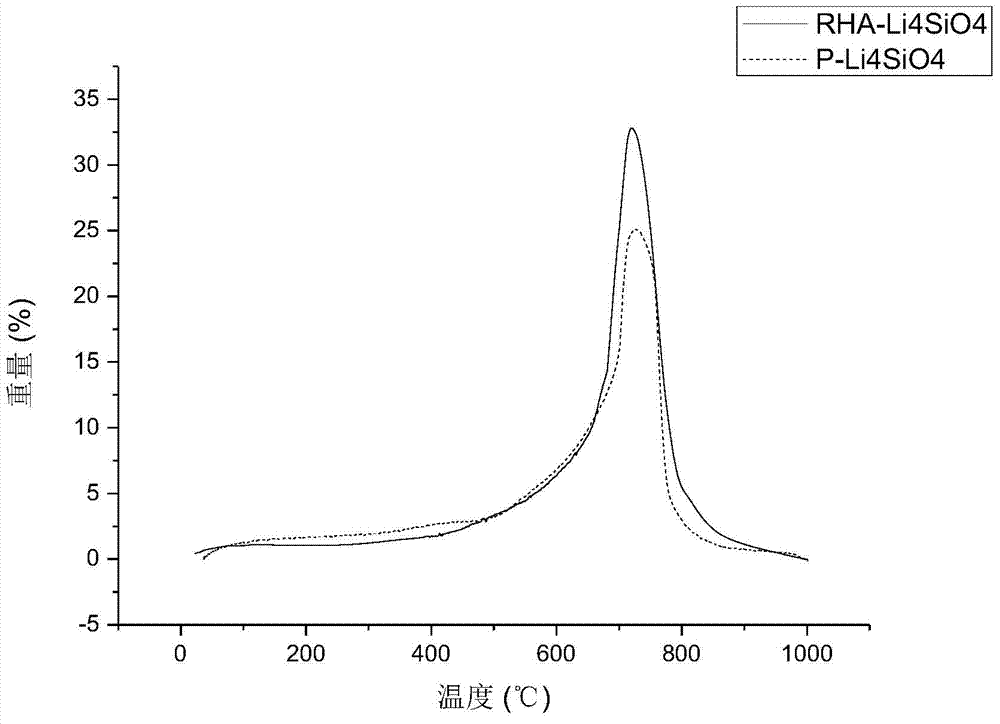
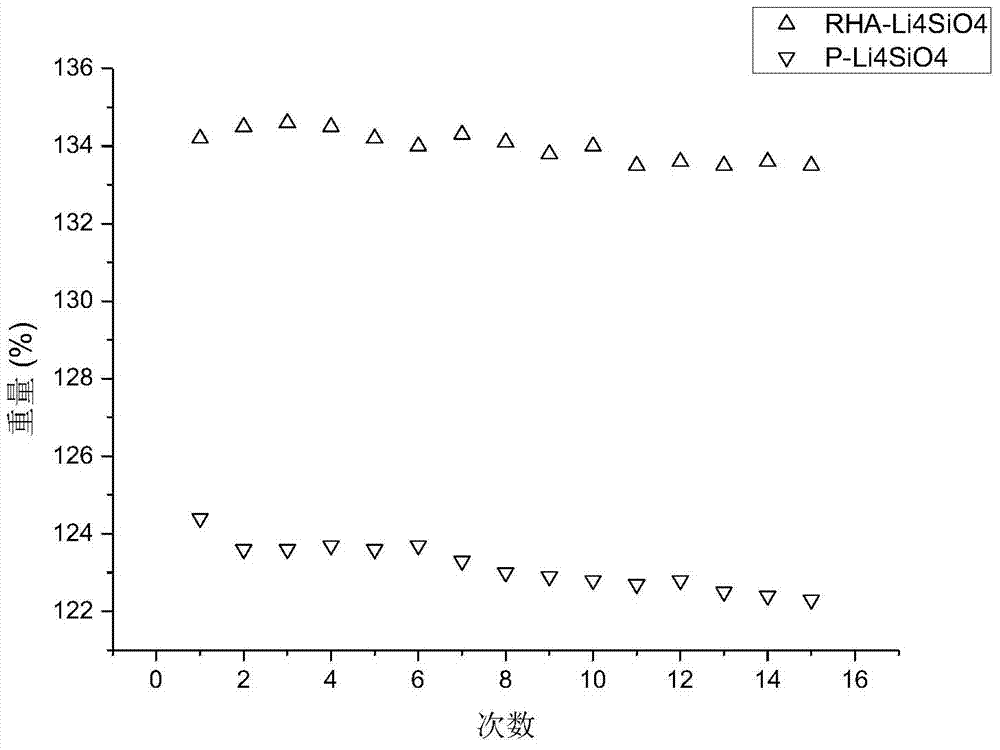
[0036] Rice husk ash lithium silicate with a particle size of 150 μm and Ni / γ-Al 2 o 3Mix to form a mixture, and in the mixture, the mass ratio of the catalyst to the rice husk ash lithium silicate is 1:1. The molar ratio of lithium to silicon in the rice husk ash lithium silicate contained in the mixture is equal to 4.2:1. The rice husk ash lithium silicate is a calcined mixture obtained by calcination at 1000°C for 1 hour using clean rice husk and lithium carbonate. . Ni / γ-Al 2 o 3 The mass of Ni in the catalyst accounts for 20% of the mass of the entire catalyst, and the particle size of the catalyst is 180 μm. The mixture of the catalyst and the adsorbent is placed in a fixed bed reactor, and the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor is 20mm. First pass nitrogen gas for sweeping, then pass methane water vapor mixed with methane and water vapor, the molar ratio of methane and water vapor in the methane water vapor is 4:1. The reaction temperature was set to 650° C.,...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Rice husk ash lithium silicate with a particle size of 180 μm and Ni / γ-Al 2 o 3 Mix to form a mixture, and in the mixture, the mass ratio of the catalyst to the rice husk ash lithium silicate is 2:3. The molar ratio of lithium to silicon in the rice husk ash lithium silicate contained in the mixture is equal to 6:1. The rice husk ash lithium silicate is a calcined mixture obtained by calcination at 1000°C for 3 hours with clean rice husk and lithium carbonate. . Ni / γ-Al 2 o 3 The mass of Ni in the catalyst accounts for 25% of the mass of the entire catalyst, and the particle size of the catalyst is 200 μm. The mixture of the catalyst and the adsorbent is placed in a fixed bed reactor, and the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor is 20mm. First pass nitrogen gas for sweeping, then pass methane water vapor mixed with methane and water vapor, the molar ratio of methane and water vapor in the methane water vapor is 2:1. The reaction temperature was set to 600° C., ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Rice husk ash lithium silicate with a particle size of 250 μm and Ni / γ-Al 2 o 3 Mix to form a mixture, and in the mixture, the mass ratio of the catalyst to the rice husk ash lithium silicate is 1:6. The molar ratio of lithium to silicon in the rice husk ash lithium silicate contained in the mixture is equal to 5:1. The rice husk ash lithium silicate is a calcined mixture obtained by calcination at 1000°C for 10 hours in advance with clean rice husk and lithium carbonate. . Ni / γ-Al 2 o 3 The mass of Ni in the catalyst accounts for 24% of the mass of the entire catalyst, and the particle size of the catalyst is 240 μm. The mixture of the catalyst and the adsorbent is placed in a fixed bed reactor, and the inner diameter of the fixed bed reactor is 20 mm. First pass nitrogen gas for sweeping, then pass methane water vapor mixed with methane and water vapor, the molar ratio of methane and water vapor in the methane water vapor is 3:1. The reaction temperature was set...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com