Dynamic bandwidth allocation method based on non-fixation multithreading polling
A bandwidth allocation method and multi-threading technology, applied in the field of dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm, can solve the problems of resource allocation impact and large data difference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
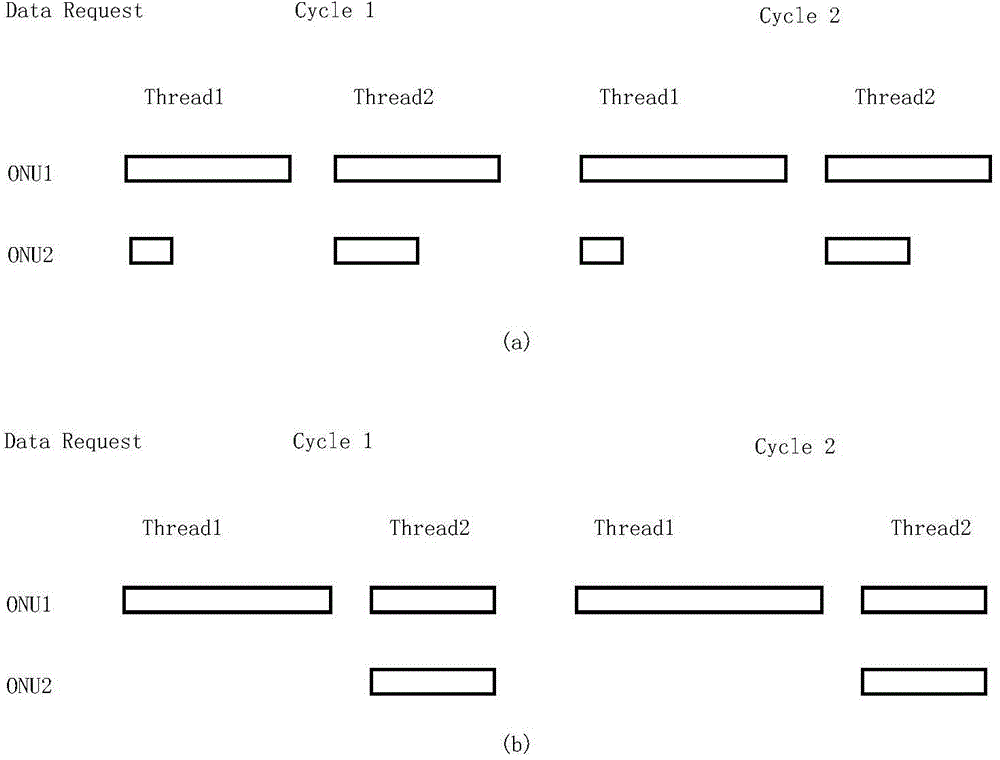
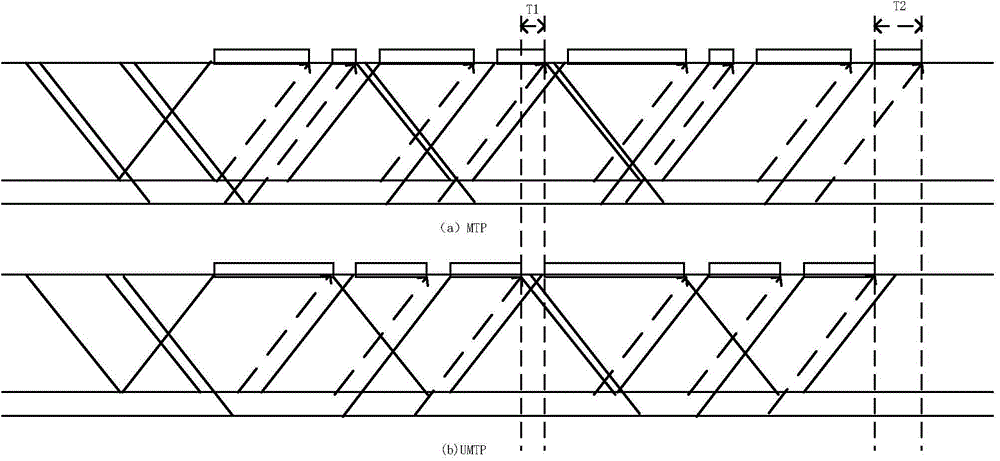
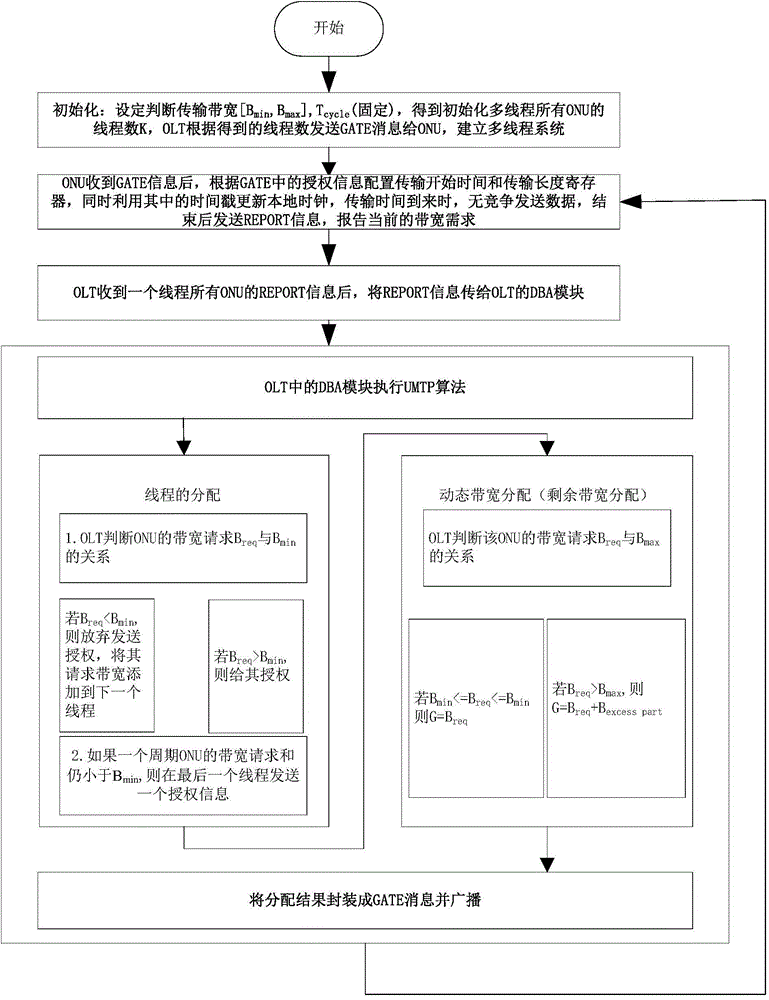
[0019] In order to make the object, technical scheme and advantages of the present invention clearer, the following in conjunction with the attached image 3 The implementation of this algorithm is further described in detail. The GATE and REPORT messages are all MAC control frames used in the EPON message interaction protocol. The GATE message is sent from the OLT to the ONU, and is used to allocate the time slot for the ONU to transmit, including the transmission start time and the length of the transmission window; The REPORT message is the feedback mechanism used by the ONU to pass the local status (such as the cache occupancy, this algorithm is understood as the amount of data cached by the ONU between thread requests, which can be understood as the requested bandwidth) to the OLT, and is used to help the OLT intelligently Allocate time slots. The specific implementation is as follows:
[0020] (1) System initialization: OLT first calculates the number K of available th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com