Salt-free low-alkali dyeing process for cellulosic fibers
A cellulose fiber and process technology, applied in the field of textile dyeing, can solve problems such as inability to apply to large-scale production, high chromaticity of dyeing residue, difficult treatment of waste water, etc., and achieves high success rate, good cationization effect, and reduced dye consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
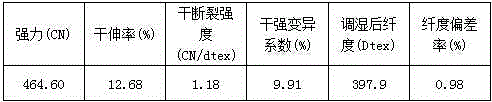
[0080] Cellulose fiber dyeing process:
[0081] A salt-free and low-alkali dyeing process for cellulose fibers, comprising the following process steps:
[0082] A. Cellulose fiber modification treatment
[0083] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then modify the cellulose fiber with two kinds of quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifiers, Modifier A and Modifier B, and obtain Modified cellulose fiber; the modifier A is a small-molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, and the modifier B is a high-molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier;
[0084] B. Washing treatment
[0085] Washing the modified cellulose fibers obtained through the modification treatment in step A;
[0086] C. Dyeing
[0087] Putting the modified cellulose fibers washed with water in step B into a dyeing container, adding a dye solution for dyeing, then raising the temperature, continuing to dye for a period of time, and finishing dyeing t...
Embodiment 2
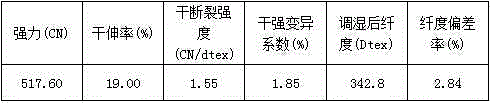
[0092] Cellulose fiber dyeing process:
[0093] A salt-free and low-alkali dyeing process for cellulose fibers, comprising the following process steps:
[0094] A. Cellulose fiber modification treatment
[0095] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then use two kinds of quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifiers, modifier A and modifier B, to modify the cellulose fiber, and obtain Modified cellulose fiber; the modifier A is a small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, and the modifier B is a high molecular weight quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier;
[0096] B. Washing treatment
[0097] Washing the modified cellulose fibers obtained through the modification treatment in step A;
[0098] C. Dyeing
[0099] Putting the modified cellulose fibers washed with water in step B into a dyeing container, adding a dye solution for dyeing, then raising the temperature, continuing to dye for a period of time, and finishing...
Embodiment 3
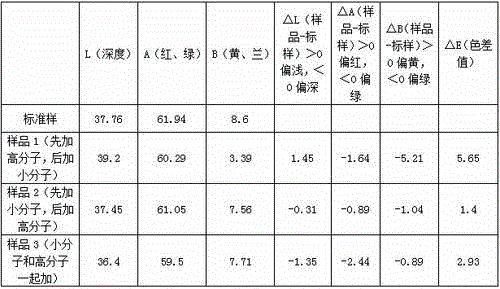
[0105] Cellulose fiber dyeing process:
[0106] A salt-free and low-alkali dyeing process for cellulose fibers, comprising the following process steps:
[0107] A. Cellulose fiber modification treatment
[0108] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then use two kinds of quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifiers, modifier A and modifier B, to modify the cellulose fiber, and obtain Modified cellulose fiber; the modifier A is a small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, and the modifier B is a high molecular weight quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier;
[0109] B. Washing treatment
[0110] Washing the modified cellulose fibers obtained through the modification treatment in step A;
[0111] C. Dyeing
[0112] Putting the modified cellulose fibers washed with water in step B into a dyeing container, adding a dye solution for dyeing, then raising the temperature, continuing to dye for a period of time, and finishing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com