MicroRNA trace detection method based on exponential order non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemical luminescence principle
A non-enzymatic amplification and detection method technology, applied in the field of microRNA trace detection, can solve the problem of low sensitivity and achieve the effect of specificity guarantee
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
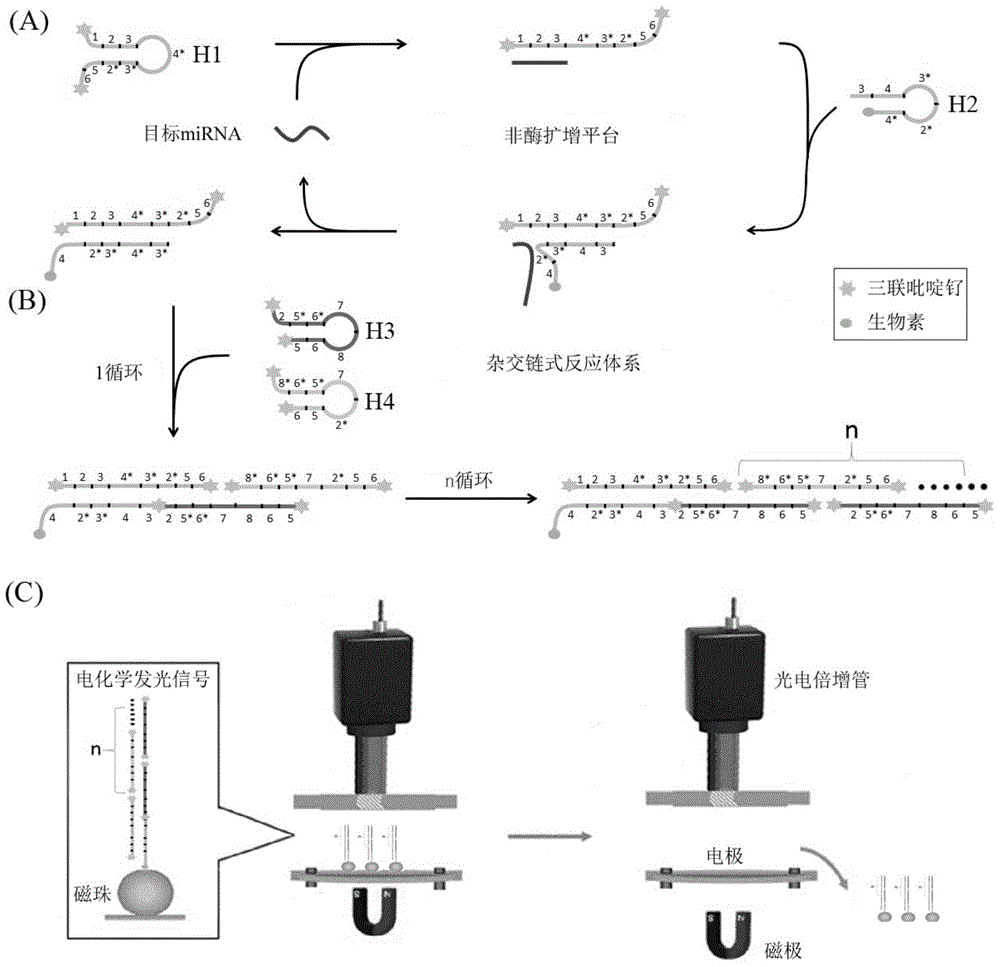
[0069] Example 1 Construction of exponential signal enhanced non-enzyme amplification platform and its feasibility verification
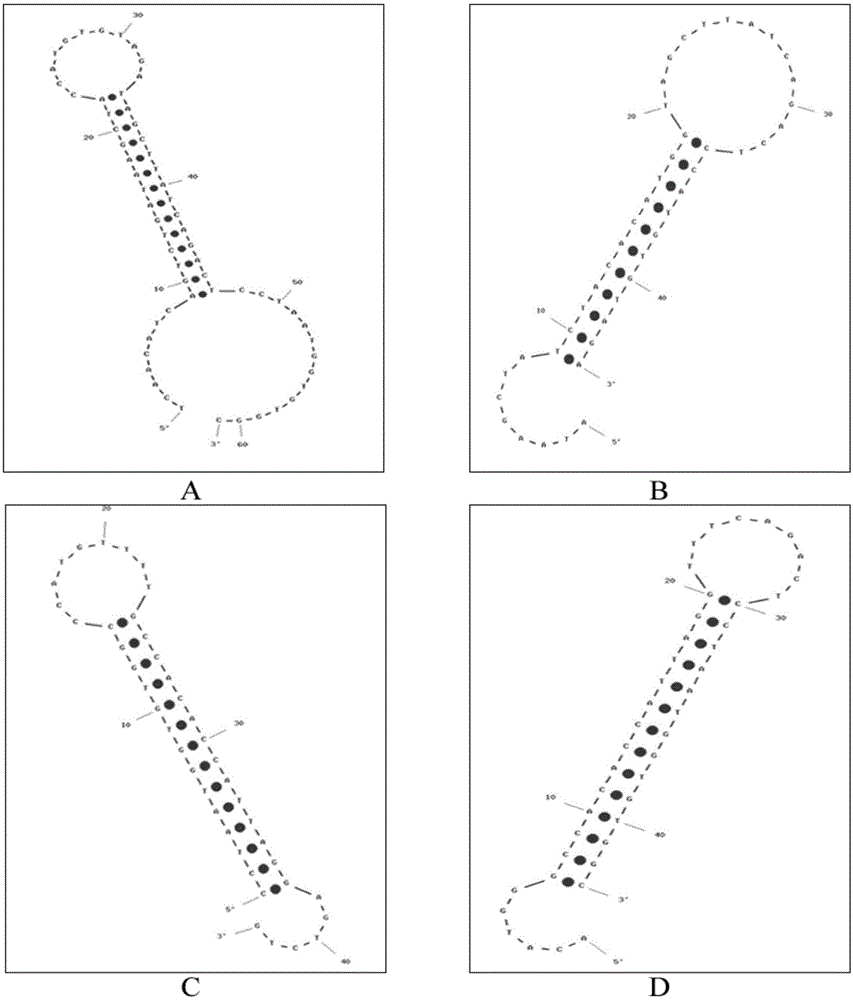
[0070] According to the principle of the above-mentioned exponential signal enhanced non-enzymatic amplification platform, the hairpin probes H1, H2, H3, and H4 required for the microRNA21 sequence were designed for the non-enzymatic amplification system. Their sequences are shown in Table 1, and their two-dimensional structures are shown in Table 1. figure 2 shown. The 5' and 3' ends of hairpin probes H1, H3, and H4 are labeled with six carbon amino groups, and the corresponding 3' ends of H2 are labeled with biotin. The hairpin probes were all synthesized by Yingwei Jieji (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd. H1, H3, and H4 need to be labeled with electrochemiluminescent groups, while H2 can be dissolved in TE buffer (final concentration 10 μM, stored in -20 refrigerator) . The labeling process of H1, H3, and H4 is as follows: take 2.5OD hairpin probe, ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 The establishment of exponential signal enhanced non-enzyme amplification platform and its sensitivity experiment
[0077]The establishment of the exponential signal enhanced non-enzymatic amplification platform includes the establishment of the amplification system and the detection of electrochemical signals. The establishment of the amplification system is shown in Example 1. The main steps of electrochemiluminescence signal detection are as follows: add streptavidin-coated magnetic beads (final concentration 0.2 mg / mL) to the non-enzymatic amplification system, incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes, separate with a magnetic separator, and remove the solution Afterwards, 100 μL of PBS buffer solution (final concentration: 1×) was added to dissolve, and then separated, thereby repeatedly washing three times. Finally, the product was put into a Roche Elecsys 2010 electrochemiluminescence automatic immunoassay analyzer to detect the electrochemiluminescence signal. ...
Embodiment 3
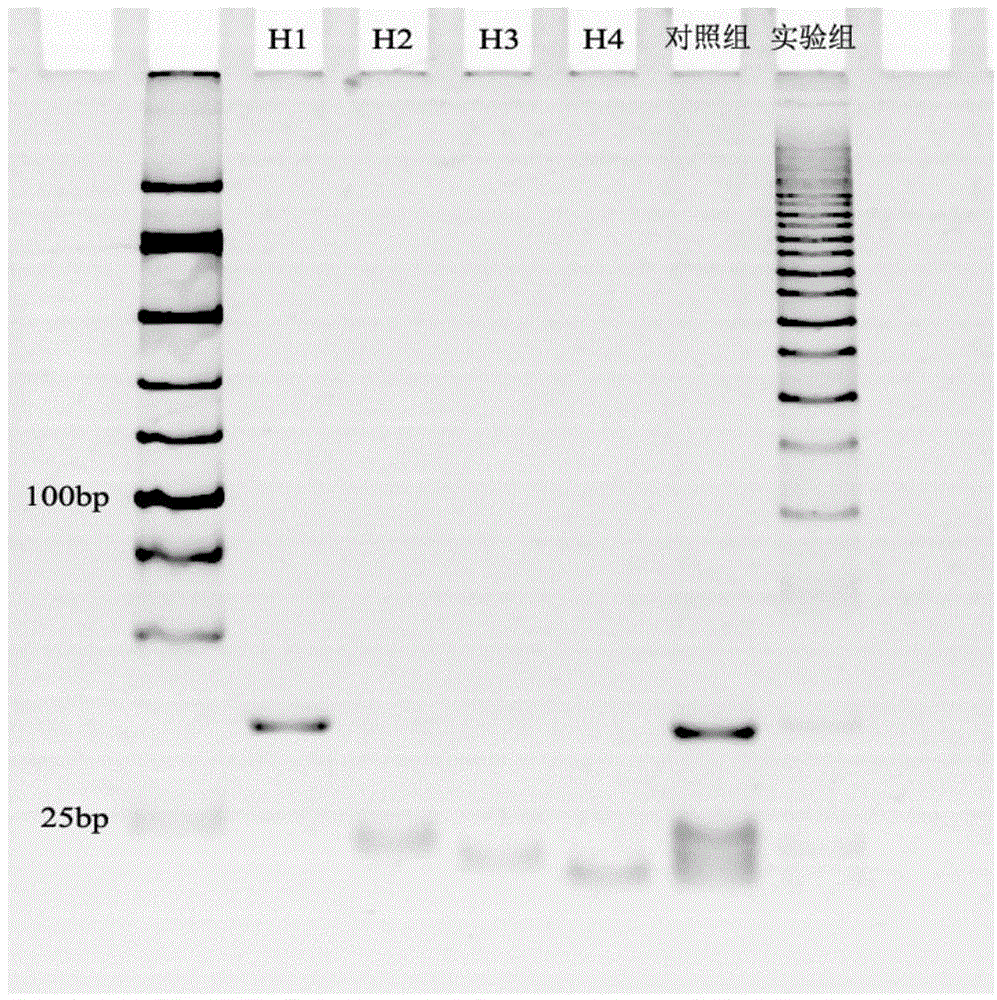
[0079] Example 3 Exponential signal enhanced non-enzyme amplification platform specificity verification
[0080] In order to verify the specificity of the exponential signal enhancement non-enzymatic amplification platform, microRNA210 and microRNA214 were added to the platform (the amount added was 10 pmol respectively), and the electrochemiluminescent signal was detected. The experimental results are as follows Figure 5 shown. Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the control group is a blank control, the electrochemiluminescence signals of the microRNA210 and microRNA214 experimental groups are the same as those of the control group, and the experimental group obtains stronger electrochemiluminescent signals. Therefore, the platform specificity is better.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com