Method and apparatus for controlling printing sleeving alignment
A technology for controlling printing and printing conditions, applied in printing and other directions, can solve problems such as non-uniform encoding pulse signal, image overprint error, image error of four color surfaces, etc., and achieve the effect of improving printing quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
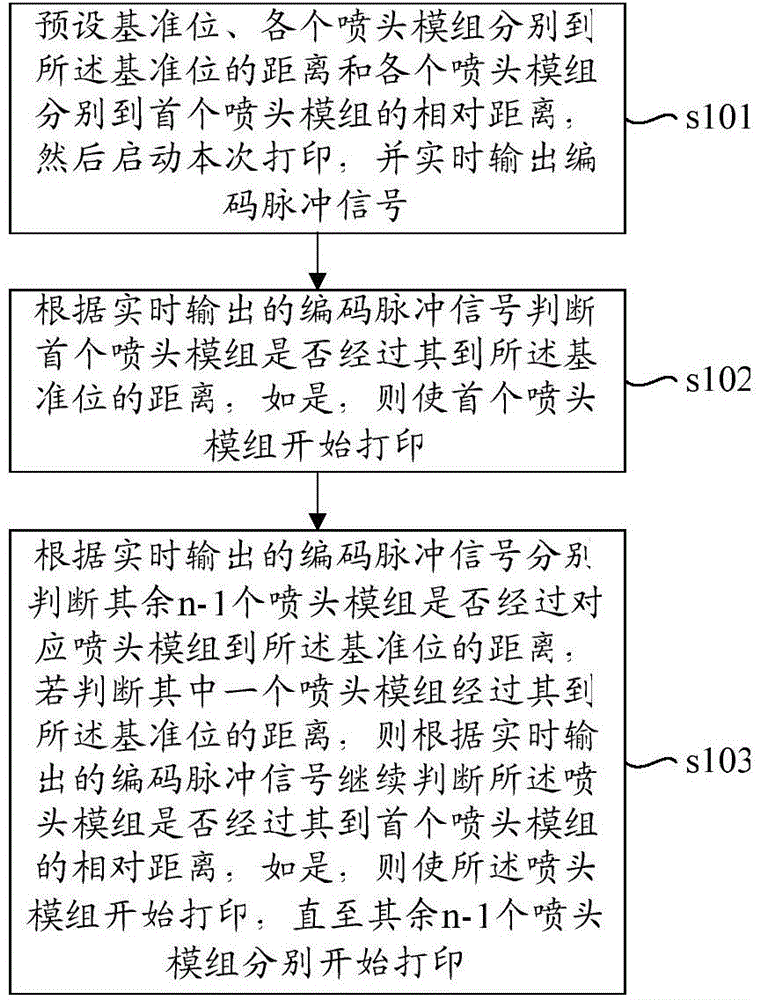
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for controlling printing registration, which is used to control the image synchronization of n color planes formed by n nozzle modules respectively, n is greater than 1, and the value of n depends on the color plane to be formed For example, YCMK four-color printing requires 4 nozzle modules, that is, n=4. The so-called image synchronization of n color planes refers to ensuring that n color planes of the same page are printed on the same position of the substrate to form a complete image on one page. The n nozzle modules are evenly arranged along the paper-feeding direction. Since the printing width in the direction perpendicular to the paper feeding direction (that is, the width of the page to be printed) is generally relatively wide, each nozzle module is generally composed of multiple small nozzles.
[0044] The method comprises the steps of:
[0045] s101. Preset the reference position, the distance fro...
Embodiment 2
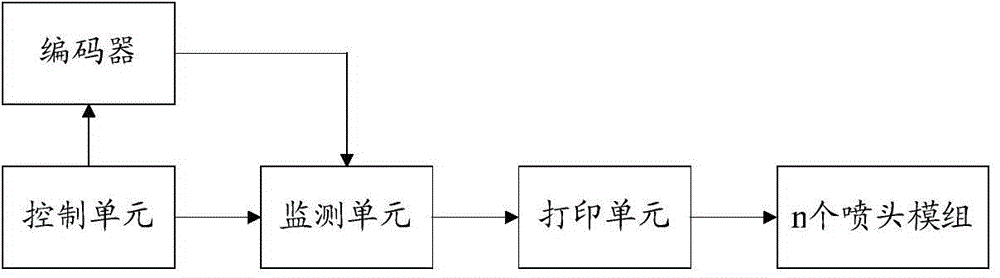
[0059] Such as image 3 As shown, the present embodiment provides a method for controlling printing registration, including the following steps:
[0060] s201. Preset the reference position, the distance from each nozzle module to the reference position and the relative distance from each nozzle module to the first nozzle module, and then start this printing after the printing conditions are met, and Real-time output of coded pulse signals; the first nozzle module refers to the nozzle module that first passes through the paper when the paper is fed.
[0061] Wherein, the method for judging whether the current printing meets the printing conditions is: judging whether the job has received imaging data, if yes, judging that the current printing meets the printing conditions, if not, judging that the current printing does not meet the printing conditions.
[0062] s202. According to the coded pulse signal output in real time, it is judged whether the first nozzle module has pass...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for controlling printing registration, which is used to control the image synchronization of the four color planes formed by the four spray head modules respectively. The four nozzle modules are evenly arranged along the paper-feeding direction. The first nozzle module refers to the nozzle module that first passes through the paper when the paper is fed. In this embodiment, the first nozzle module is represented by nozzle module 1, and the remaining 3 nozzle modules that pass through the paper in turn when the paper is fed are respectively It is represented by nozzle module 2, nozzle module 3 and nozzle module 4.
[0083] The method comprises the steps of:
[0084] s301. Start a job and prepare to start printing, so that each component returns to its working position.
[0085] s302. Preset the reference position, the distance from each nozzle module to the reference position, and the relative distance from...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com