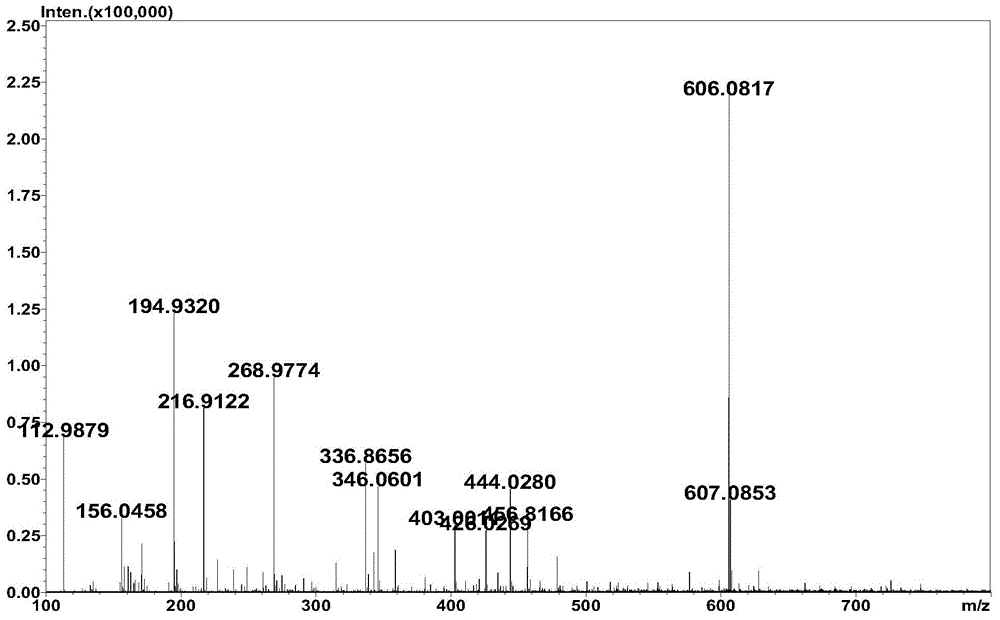
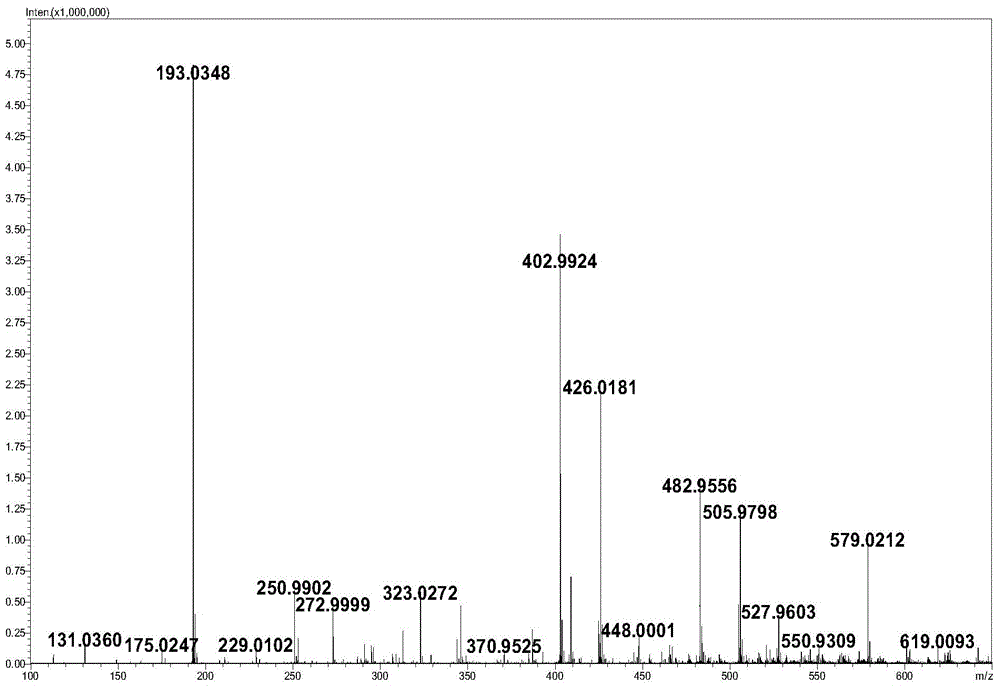
Method for synthesizing hyaluronic acid from monosaccharides as initial substrates by multienzyme coupling
A hyaluronic acid and monosaccharide technology, applied in the field of enzymatic synthesis of hyaluronic acid and multi-enzyme coupling synthesis of hyaluronic acid, can solve the problems of in-depth enzymatic synthesis of hyaluronic acid, cumbersome product purification steps, Acid pollution and other problems, to achieve the effect of mild conditions, easy operation, and reduce production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 A method for synthesizing hyaluronic acid by multi-enzyme coupling initiated by monosaccharide
[0040] Proceed as follows:
[0041] (1) Preparation of catalytic reaction enzyme solution
[0042] N-acetylglucosamine kinase, derived from Bifidobacterium longum (Bifidobacterium longum), recombinant vector construction and protein expression methods refer to (Nishimoto, M., and Kitaoka, M. (2007) Identification of N-acetylhexosamine 1-kinase in the complete lacto-N-biose I / galacto-N-biose metabolic pathway in Bifidobacterium longum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73, 6444-6449);
[0043] Glucuronokinase, derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, recombinant expression vector construction and protein expression method see (Pieslinger, A.M., Hoepflinger, M.C., and Tenhaken, R. (2010) Cloning of glucuronokinase from Arabidopsis thaliana, the last missing enzyme of the myo-inositol oxygenase pathway to nucleotide sugars. J Biol Chem 285,2902-2910);
[0044] N-acetylglucosamine t...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 A method for synthesizing hyaluronic acid by multi-enzyme coupling initiated by monosaccharide
[0072] The method for the multi-enzyme coupling synthesis of hyaluronic acid initiated by monosaccharide as described in Example 1, the difference is:
[0073] The volume ratio of uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) reaction solution and uridine diphosphate-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcA) reaction solution described in step (6) is 1:0.8 mixing, 28 Incubate in a water bath at ±1°C for 10±2 minutes, and add a hyaluronidase solution of 40% of the volume of the mixture during incubation.
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3 A method for synthesizing hyaluronic acid by multi-enzyme coupling initiated by monosaccharide
[0075] The method for the multi-enzyme coupling synthesis of hyaluronic acid initiated by monosaccharide as described in Example 1, the difference is:
[0076] The volume ratio of the uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) reaction solution and the uridine diphosphate-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcA) reaction solution described in step (6) is 1:1.2 mixing, Incubate in a water bath at 28±1°C for 10±2 minutes, add a hyaluronidase solution with a volume of 60% of the mixture during incubation, and the reaction time is 48 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com