Electromagnetic flowmeter with variable excitation frequency
A technology of electromagnetic flowmeter and excitation frequency, which is applied in the application of electromagnetic flowmeter to detect fluid flow, volume/mass flow generated by electromagnetic effect, measurement device, etc. The effect of good zero-point stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
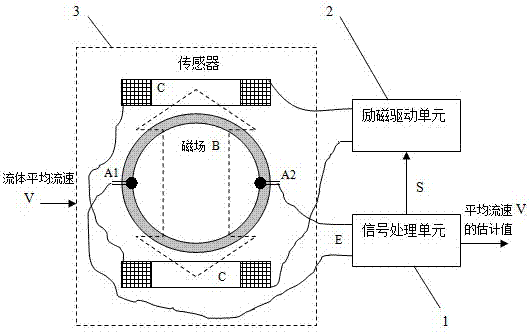
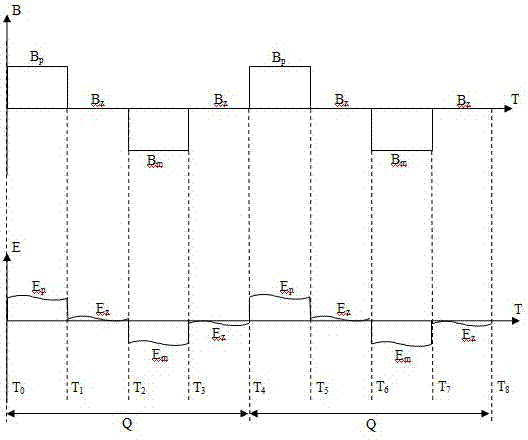
[0027] An electromagnetic flowmeter with variable excitation frequency, including a signal processing unit 1, an excitation drive unit 2, and a sensor 3 with a coefficient K0; it is characterized in that: the signal processing unit 1 is electrically connected to the excitation drive unit 2 and has The sensor 3 with coefficient K0, the excitation drive unit 2 is electrically connected with the sensor 3 with coefficient K0; the signal processing unit 1 outputs the sequence S to the excitation drive unit 2, so that the excitation drive unit 2 makes the sensor 3 Generate a magnetic field B with an excitation frequency F that changes in direction positive and negative; when the fluid with an average velocity V passes through the sensor 3, the sensor 3 outputs an induced potential signal E=K0×V×B; the induced potential signal E is input to the signal processing unit 1. The signal processing unit 1 allows the excitation drive unit 2 to make the excitation frequency F of the magnetic f...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0031] In the above-mentioned electromagnetic flowmeter with variable excitation frequency, for the slurry fluid, the signal processing unit 1 estimates the slurry concentration value X of the fluid according to the current excitation frequency F and the fluid flow velocity V value:
[0032] ,
[0033] Among them, F 0 It is the frequency value that is one step lower than the current excitation frequency F value among the M fixed frequency points, and K is the coefficient that needs to be corrected for different types of slurry fluids. Obviously, as the number of M fixed frequency points of the excitation frequency F increases, the signal processing unit 1 can estimate the slurry concentration value X of the fluid more carefully.
[0034] In the above-mentioned electromagnetic flowmeter with variable excitation frequency, the signal processing unit 1 outputs the time seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com