Method for removing heavy metal chromium in bottom mud by using modified nano zero-valent iron
A nano-zero-valent iron and heavy metal technology, applied in metal processing equipment, chemical instruments and methods, sludge treatment, etc., can solve the problems of nano-zero-valent iron instability, reduced reactivity, and mobility, and achieve good surface effects. , The effect of low repair cost and short processing cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
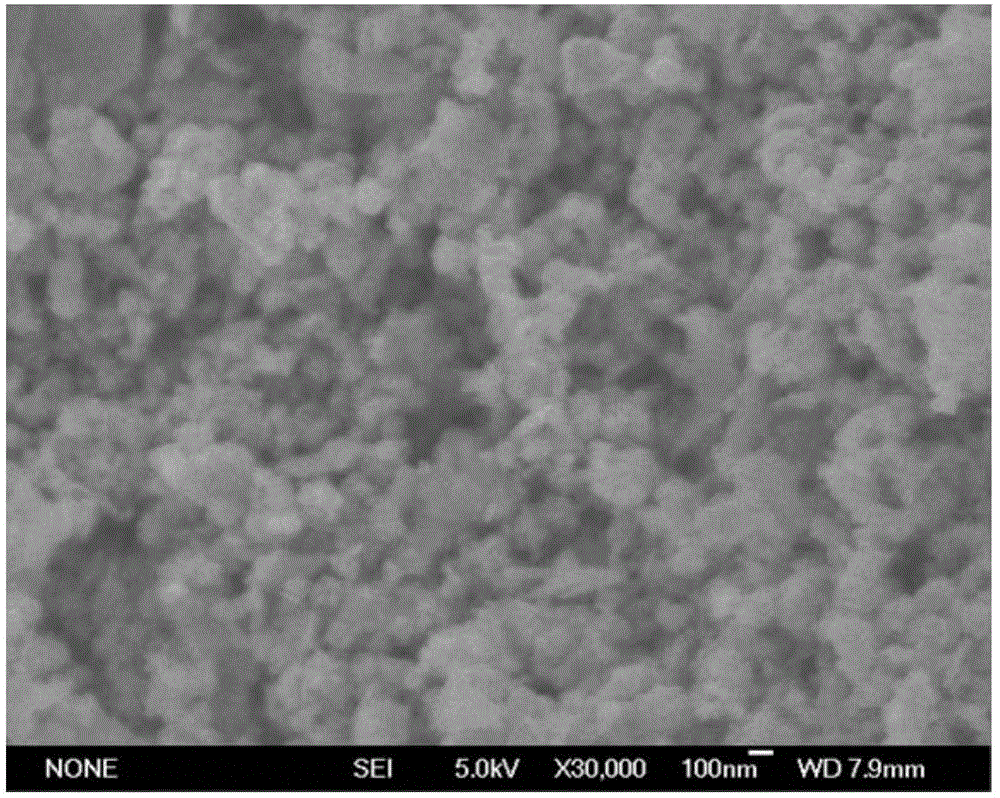
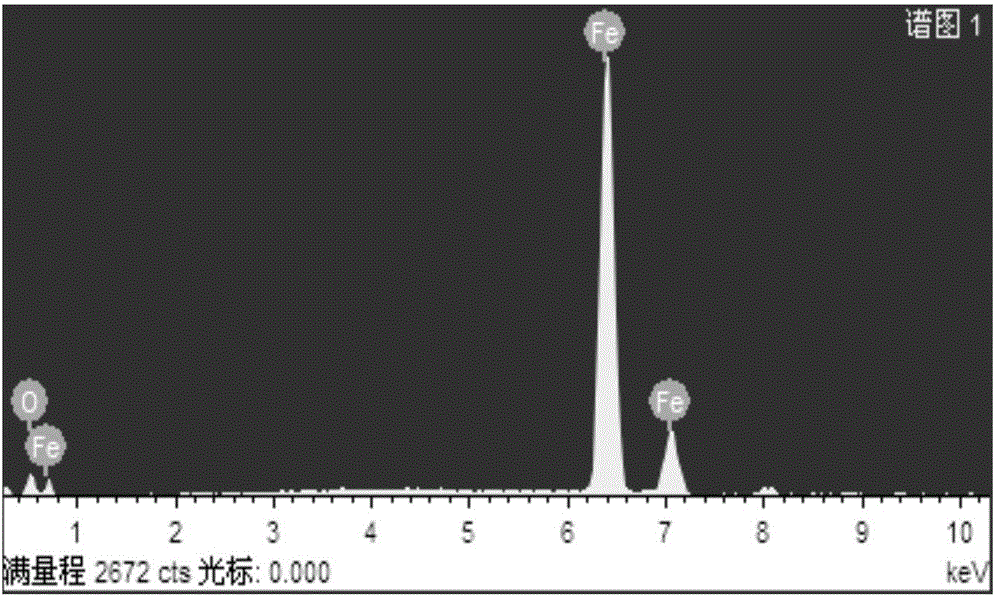
[0036] Example 1: Preparation of modified nano zero-valent iron.
[0037] Preparation of nano zero-valent iron:
[0038] (1) FeSO 4 Solution preparation: weigh 0.7000g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 Put O in a beaker, add an appropriate amount of ultrapure water to dissolve and transfer to a 50mL volumetric flask, set the volume to the mark, and shake well to obtain 0.05M FeSO 4 solution.
[0039] (2)NaBH 4 Solution preparation: weigh 0.3783g NaBH 4 Put it in a beaker, add an appropriate amount of ultrapure water to dissolve and transfer it to a 50mL volumetric flask, set the volume to the mark, and shake well to obtain 0.2M NaBH 4 solution.
[0040] (3) Preparation of nanometer zero-valent iron (nZVI) particles: 50mL, 0.05M FeSO 4 The solution was added into a 250mL three-necked flask, and under the protection of nitrogen and mechanical stirring, an equal volume of 0.2M NaBH 4The solution was dropped into the three-necked flask drop by drop at a constant speed. After the constant-spee...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: To investigate the effect of the amount of stabilizer added on the treatment efficiency of heavy metal chromium.
[0047] The chromium-containing sludge is pretreated, and the specific pretreatment steps are:
[0048] (1) The chromium-containing bottom sludge is freeze-dried at minus 40 degrees Celsius in a freeze dryer;
[0049] (2) Mechanically grind the chromium-containing bottom sludge that has been freeze-dried, first pass through a 1mm sieve, and then pass through a <0.63mm sieve to complete the pretreatment of the bottom sludge.
[0050] The modified nano-zero-valent iron A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5 were respectively used to treat the heavy metals in the pretreated sediment and the heavy metals in the tail water of the sediment dredging.
[0051] The method for processing the heavy metal content in the bottom mud dredging tail water is specifically: according to the dosage of 1.0g / L, add it to 100mL of chromium-containing bottom mud dredging tail water wit...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: Investigating the treatment efficiency of modified nanometer zero-valent iron on heavy metal chromium in sediment under different pH conditions.
[0058] Experiment 1 group (SDS-nZVI): get 250g of chromium-containing bottom mud (the chromium-containing bottom mud is pretreated according to the method in Example 2), and detect the heavy metal Cr in the chromium-containing bottom mud. 6+ The concentration is 100mg / kg, and the chromium-containing bottom mud is divided into 5 parts on average, each 50g. The stabilizer (SDS) concentration that is made in embodiment 1 is respectively the modified nanometer zero valent iron of 0.3g / L according to 1.0g / kg wet weight is added in the chromium-containing bottom mud of 50g, with 1M HCl and NaOH The solution adjusts the pH value of the bottom mud to be 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 respectively, then shakes at a constant temperature at 25°C and 300rmp, and after 24h, the bottom mud after the treatment is leached (leaching treatment metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com