Low-voltage differential signal driver
A low-voltage differential signal and driver technology, applied in the direction of logic circuit connection/interface layout, etc., can solve the problems of device characteristics and mismatch sensitivity, common-mode level shift and fluctuation, limit circuit application, etc., to improve the charging and discharging speed , improve stability and work speed, and reduce the effect of impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
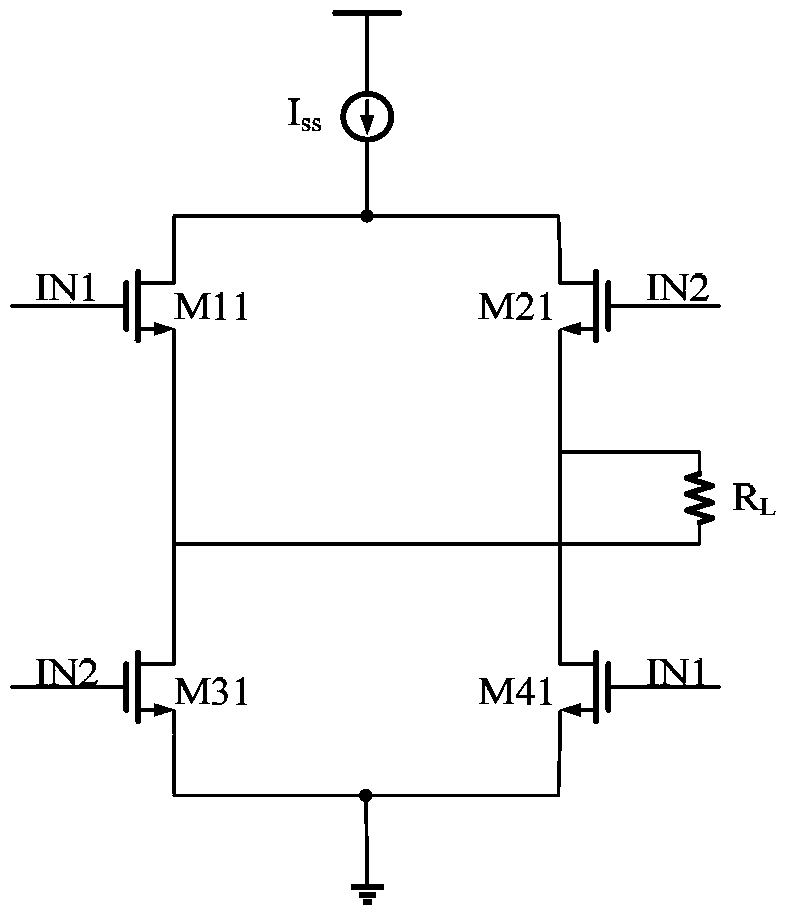
[0038] In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and advantages to be solved by the present invention clearer, the following will describe in detail with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
[0039] Such as image 3 As shown, an embodiment of the present invention provides a low-voltage differential signal driver, including:
[0040] The main drive circuit is used to generate high-speed differential transmission data with low voltage swing;
[0041] a common-mode feedback network, connected to the main body driving circuit, for comparing the common-mode voltage at the output terminal of the main body driving circuit with a target common-mode voltage, so as to adjust the common-mode voltage to the target common-mode voltage Level.
[0042] Wherein, the main body drive circuit includes:
[0043] The first NMOS transistor M1, the second NMOS transistor M2, the third NMOS transistor M3, the fourth NMOS transistor M4, the fifth NMOS transistor ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com